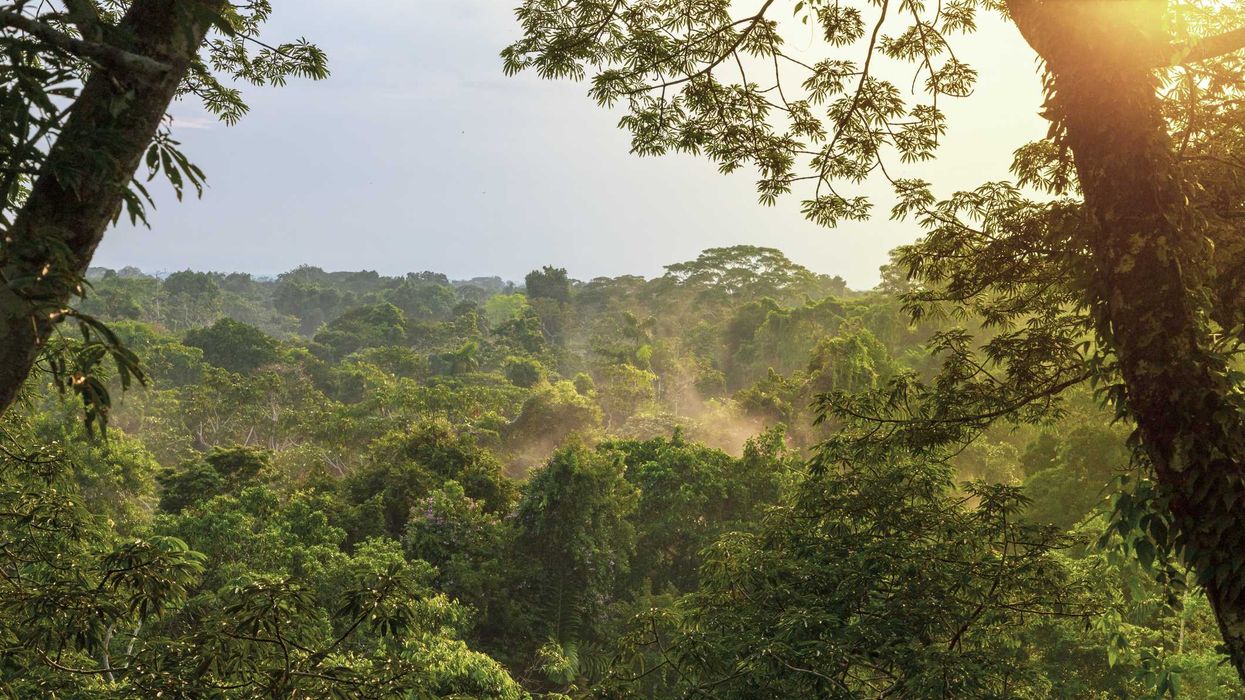
In August, I traveled by bus, small plane, and canoe to the sacred headwaters of the Amazon, in Ecuador. It’s a place with very few roads, yet like many areas in the rainforest, foreign business interests have made contact with its peoples and in just the last decade have rapidly changed the landscape, scarring it with mines or clearcutting for cattle ranching.
The Amazon Rainforest is rightly called the “lungs of the planet.” It stores approximately 56.8 billion metric tons of carbon, equivalent to nearly twice the world’s yearly carbon emissions. With more than 2,500 tree species that account for roughly one-third of all tropical trees on earth, the Amazon stores the equivalent to 10–15 years of all global fossil fuel emissions. The "flying rivers" generated by the forest affect precipitation patterns in the United States, as well our food supply chains, and scientists are warning that in the face of accelerating climate change, deforestation, drought, and fire, the Amazon stands at a perilous tipping point.
As world leaders prepare to meet this November at the United Nations’ Climate Change Conference, known as COP 30, in Belém, Brazil, the future of the Amazon—and the climate system that depends on it—hangs in the balance.
On the plus side, there is growing interest among U.S. investors and foundations in projects that will lead to regrowth of the rainforest. But too often, when companies enter the carbon sequestration market, profits flow back to them almost exclusively. I have been working with foundations for more than a decade and have observed firsthand how more and more investors want to see their dollars benefit the community as well as the planet. For example, I coordinated Divest Invest Philanthropy, a coalition of some 170 foundations representing more than $50 billion in assets that are being shifted away from fossil fuels and into impact solutions.
In the Ecuadorian Amazon, for another example, a new, indigenous led project will reforest 10,000 acres as it seeds vanilla and other crops in the understory. This regenerative model—in which funding supports community priorities, livelihoods, and leadership—offers a more just and sustainable pathway forward.
At pre-COP meetings such as last month's Climate Week in New York, coalitions such as the Amazon Sacred Headwaters Alliance, which is leading the restoration project in Ecuador, will be engaging government and business leaders to support the concept of buen vivir, or living well in harmony with nature. The alliance represents 30 Indigenous organizations across Peru and Ecuador that are working to make a 35-million acre region off-limits to industrial-scale resource extraction, advance legal recognition of Indigenous territories, restore degraded forests, and build a regenerative bioeconomy.
But COP meetings are famously siloed: government leaders, business leaders, and grassroots groups each often have separate meetings and produce their own declarations. To achieve durable climate solutions, we must build stronger bridges between these spheres—ensuring that the lived wisdom and priorities of frontline communities inform and shape global policy frameworks. A great example of this is the inspiring work of the Pachamama Alliance, which has been engaged in deep trust building work between philanthropists, investors and community leaders for 30 years. (I have Pachamama Alliance to thank for leading the journey I participated in in Ecuador).
Global carbon markets are expanding rapidly, but their legitimacy and effectiveness will depend on designing mechanisms that are rooted in Indigenous governance and that deliver real, measurable benefits back to communities.
That dual purpose is essential. At the Ecuadorian headwaters, the Achuar, Shuar and Sapara communities engaged in deals that have led to much deforestation of their land. Many local leaders would like to restore the rainforest and generate sustainable economic opportunities. Carbon credits, crops such as vanilla, and ecotourism offer alternatives.
Research consistently shows that forests managed by Indigenous peoples experience far lower rates of deforestation and degradation. The ecological knowledge and cultural values Indigenous communities bring are essential tools for combating climate change and biodiversity loss. Yet these communities face mounting threats: illegal logging, mining, land grabs, violence, and the growing impacts of a warming planet.
COP 30 will be held in the very heart of the Amazon, and global leaders face both a pivotal opportunity and a profound responsibility. It is time to place Indigenous rights and leadership at the forefront of climate action. This means recognizing Indigenous peoples as equal partners in designing and implementing both policy and investment strategies–not just including indigenous people at the table but also investing in their vision. It means providing them with the legal protections, financial resources, and political support necessary to safeguard their lands and livelihoods while ensuring that new economic opportunities are structured to strengthen, rather than erode, community resilience.
The climate crisis demands urgent and systemic change. Protecting the Amazon through Indigenous stewardship is one of the clearest, most effective solutions available.
Jenna Nicholas is an investor, entrepreneur, advisor, a PD Soros Fellow, and a Public Voices Fellow with The OpEd Project.