Kull is program director of the Program for Public Consultation. Lewitus is a research analyst at Voice of the People.
As major proposals to change U.S. trade policy have come into the discourse, a new public consultation survey finds bipartisan majorities of Americans in six swing states, as well as nationally, support the United States maintaining low tariffs with other countries so long as they abide by agreed-upon rules. At the same time, bipartisan majorities approve of the increased tariffs that have been imposed on China in response to its alleged violations of international trade rules.
This survey is the eighth Swing Six Issue Survey, a series being conducted in the run-up to the November election in Arizona, Georgia, Michigan, Nevada, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin, and nationally, on major policy issues by the Program for Public Consultation at the University of Maryland.
Unlike standard polls, respondents in a public consultation survey go through an online “policymaking simulation” in which they are provided briefings and arguments for and against each policy. Content is reviewed by experts on different sides to ensure accuracy and balance. All Americans are invited to go through the same policymaking simulation as the survey sample.
While Americans do support the tariff increases targeted at China, bipartisan majorities oppose a tariff increase on imports from all countries. Large bipartisan majorities support the U.S. continuing to be part of the international agreements for low tariffs within a rules-based system.
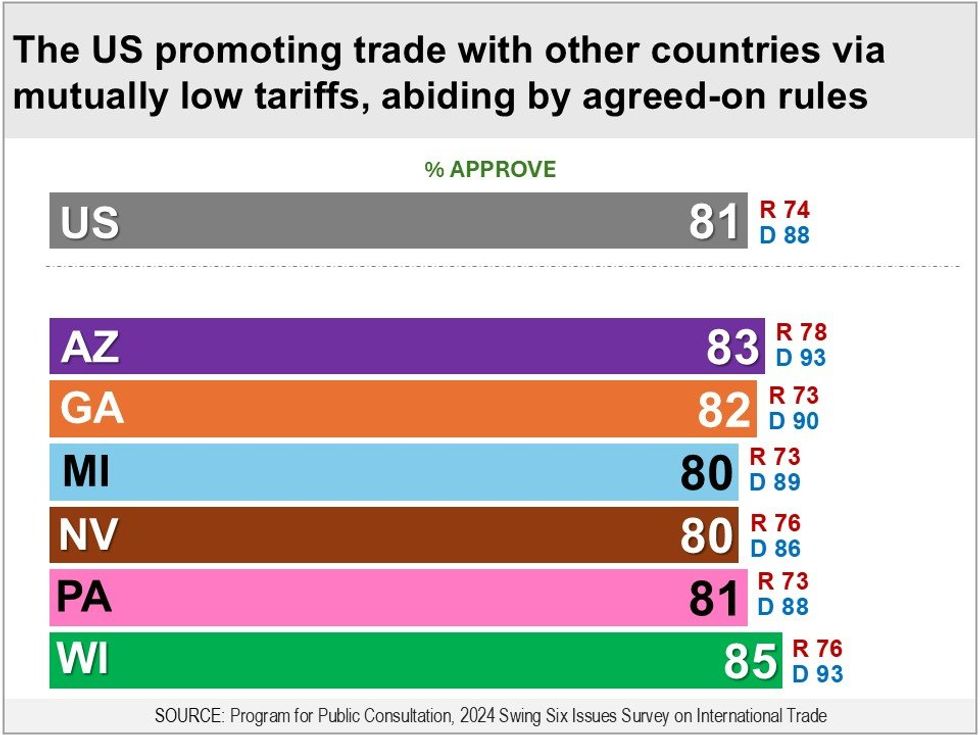
Support for Continuing International Trade System of Low Tariffs
Respondents were informed that, since World War II, the United States has been actively working to promote international trade through a system in which countries negotiate to lower their tariffs on a mutual basis, provided each country abides by agreed-upon rules. The U.S. has such trade arrangements with almost all countries — through free trade agreements and the General Agreement on Trade and Tariffs. As a result, average tariffs globally have decreased from about 22 percent in the 1940’s to about 2 percent today.
Bipartisan majorities in all swing states (80 percent to 85 percent) approve of the U.S. working with other countries to continue this system, including majorities of Republicans (73 percent to 78 percent) and Democrats (86 percent to 93 percent). Nationally, 81 percent approve (Republicans 74 percent, Democrats 88 percent).
Opposition to Across-the-Board Tariffs of 10 percent to 20 Percent
Respondents evaluated a proposal to impose tariffs of 10 percent to 20 percent on imports from all countries, including arguments that these higher tariffs would generate substantial government revenue and thus allow for reductions in taxes, as well as stimulate U.S. manufacturing and lead to better-paying jobs. They also evaluated arguments against, that raising all tariffs would violate U.S. trade agreements and likely cause the country’s biggest trading partners to retaliate with tariff increases, as well as raise consumer prices for everyone. Arguments on both sides were found convincing by bipartisan majorities.
Finally, asked which policy they prefer, less than half in all six swing states (28 percent to 35 percent) support the U.S. raising tariffs on imports from all countries to 10 percent to 20 percent, including just 34 percent to 42 percent of Republicans and 20 percent to 34 percent of Democrats. Instead, large majorities prefer the U.S. continuing to have low tariffs on a mutual basis with other countries, provided they abide by agreed-upon rules (64 percent to 71 percent), including majorities of Republicans (57 percent to 65 percent) and Democrats (66 percent to 77 percent). Nationally, 68 percent prefer continuing the current policy of low tariffs (Republicans 60 percent, Democrats 77 percent).
Support for High Tariffs on China
Respondents were informed that starting in 2018, in response to alleged violations of international trade rules by China, the United States increased tariffs on Chinese products to an average of about 20 percent, and that China retaliated with similarly high tariffs on the U.S. Bipartisan majorities in every swing state favor the U.S. continuing to impose such tariffs on Chinese imports (69 percent to 78 percent), including majorities of Republicans (75 percent to 78 percent) and Democrats (67 percent to 82 percent). Nationally, 71 percent are in favor, with no difference between Republicans (73 percent) and Democrats (72 percent).
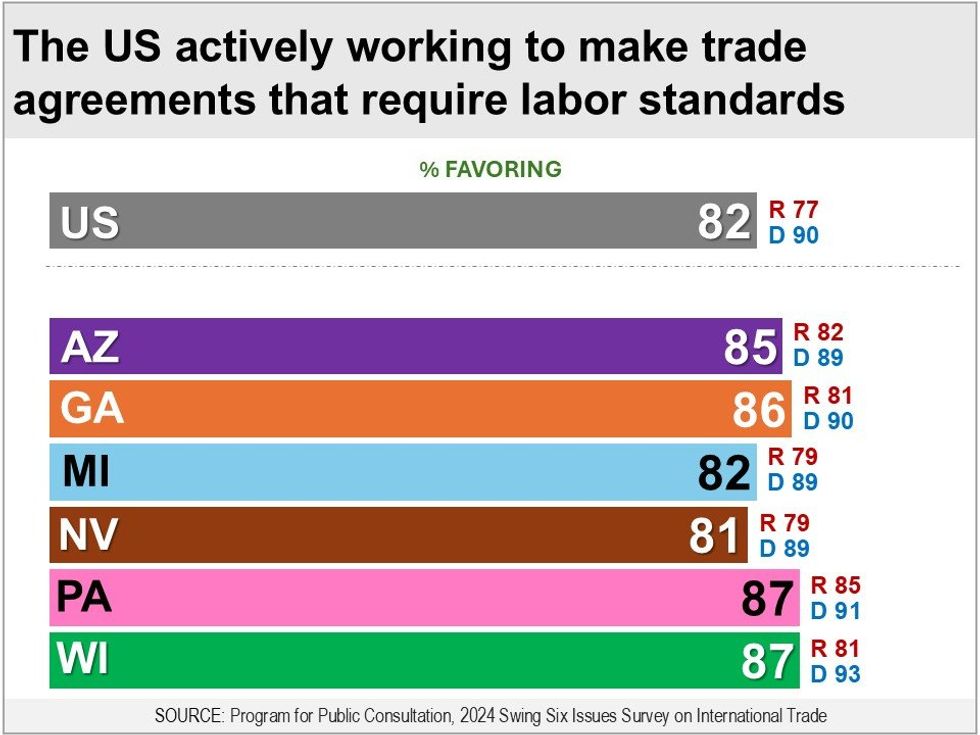
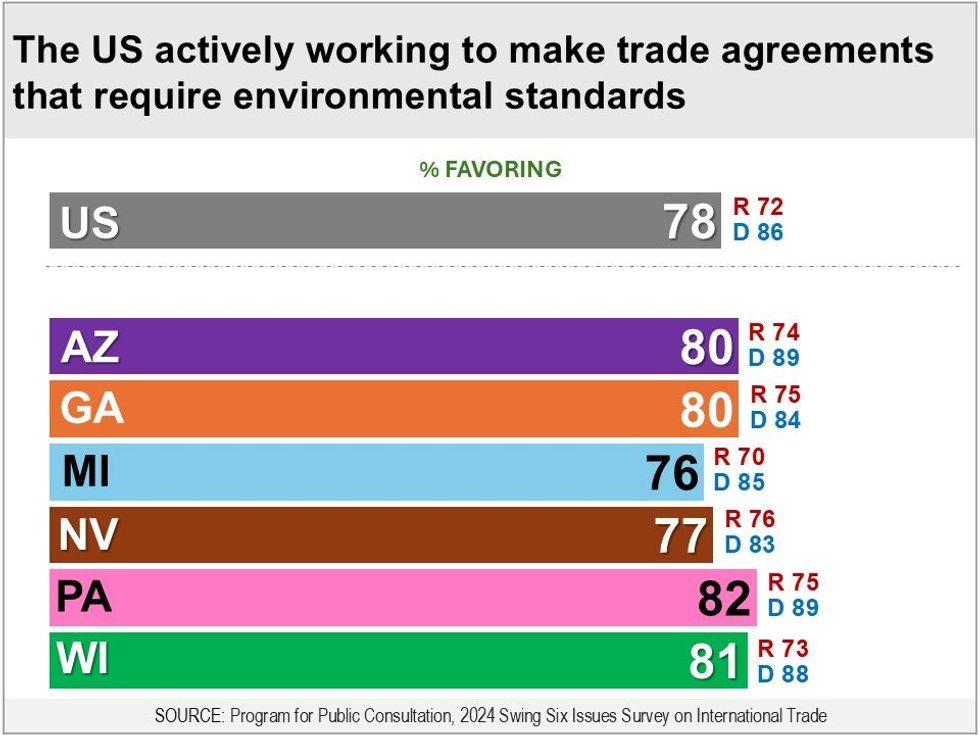
Support for Labor and Environmental Standards in Trade Deals
The United States in its trade deal negotiations has been increasingly pushing for the inclusion of enforceable labor and environmental standards. Respondents evaluated arguments that such standards ensure that trade partners cannot get a competitive advantage by having significantly lower standards than the U.S. They also evaluated arguments against, including that the United States imposing standards on other countries and including too many provisions in trade deals will slow down international trade, which would hurt everyone.
Asked whether the U.S. should actively work to make agreements that include enforceable labor standards — including a prohibition on child labor and the right of workers to collectively bargain — bipartisan majorities are in favor in the swing states (81 percent to 87 percent) including Republicans (79 percent to 85 percent) and Democrats (89 percent to 93 percent). Nationally, 82 percent are in favor (Republicans 77 percent, Democrats 90 percent).
Asked whether the United States should actively work to make agreements that include enforceable environmental standards — which require countries to abide by environmental agreements they have signed, and not lower their standards to get a competitive edge — bipartisan majorities in the swing states are in favor (76 percent to 82 percent), including Republicans (70 percent to 76 percent) and Democrats (83 percent to 89 percent). Nationally, 78 percent are in favor (Republicans 72 percent, Democrats 86 percent).


















Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift