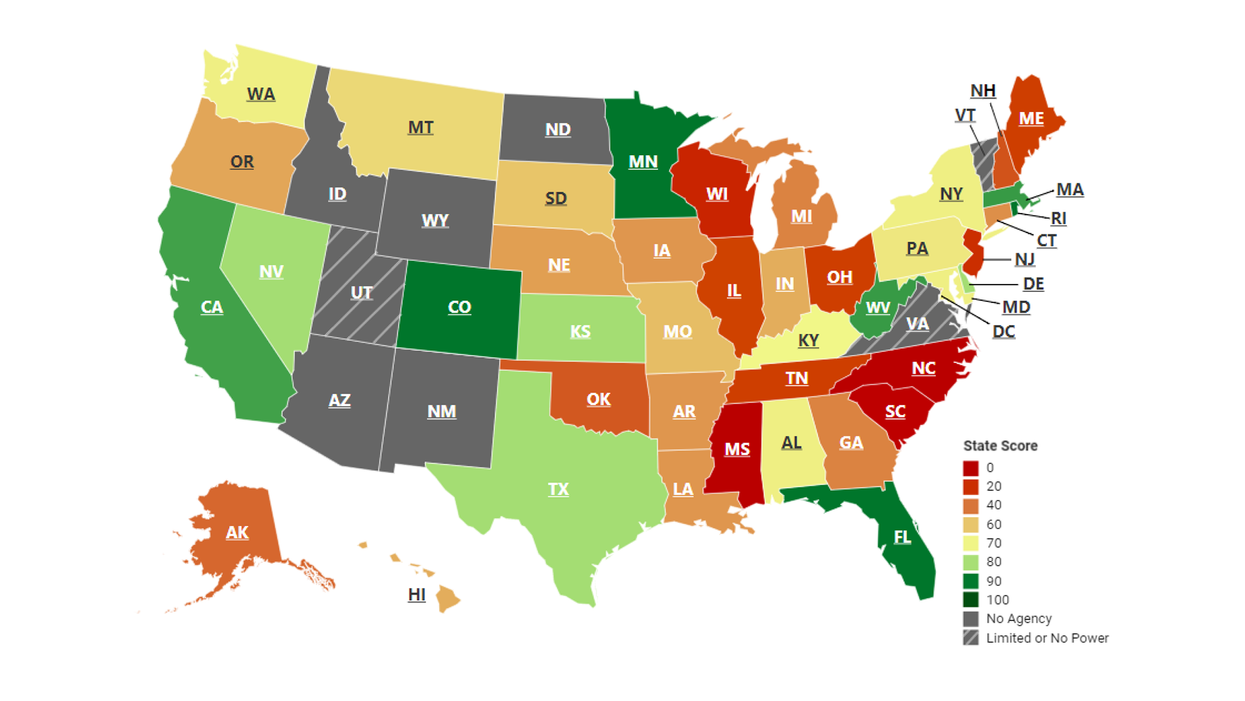
Only a handful of states earned high marks in a new report analyzing the enforcement power and transparency of state ethics agencies.
The researchers behind "Enforcement of Ethics Rules by State Agencies" surveyed 2018 enforcement statistics for every state ethics agency and scored states by how well those agencies made their actions publicly available. The study was released last week by the nonprofit Coalition for Integrity, which works to combat corruption in both governments and business.
Four states — Colorado, Florida, Minnesota and Rhode Island — received perfect scores for transparency in part because their agencies publish annual reports detailing the number of ethics complaints received and how those complaints were investigated and resolved in a format that's both publicly available and easy to understand, the group said.
But almost half the states in the country — 23 of them — earned failing grades (50 percent or below on a 100-point scale) in terms of transparency. And eight more were excluded from the study altogether because they didn't have state ethics agencies in 2018 (Arizona, Idaho, New Mexico, North Dakota and Wyoming) or had agencies with "limited or no investigative or sanctioning power" (Utah, Vermont and Virginia).
The states that scored poorly on ethics transparency did so for a variety of reasons. Failing to hold public proceedings of probable ethics violations, opting not to publish information about violations, and withholding details about sanctions taken against ethics offenders were the most cited reasons in the report.
"The report on Enforcement of Ethics Rules reflects the huge variation in enforcement efforts by state ethics agencies — and the lack of transparency of those efforts in many states," said Shruti Shah, president and CEO of Coalition for Integrity. "In addition to meaningful enforcement actions, state ethics agencies should strive to be transparent and publish information on complaints received, cases resolved, and sanctions issued."




















 U.S. Secretary of War Pete Hegseth speaks during a news conference at the Pentagon on March 2, 2026 in Arlington, Virginia. Secretary Hegseth and Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff General Dan Caine held the news conference to give an update on Operation Epic Fury. (Photo by Alex Wong/Getty Images) (Photo by Alex Wong/Getty Images)
U.S. Secretary of War Pete Hegseth speaks during a news conference at the Pentagon on March 2, 2026 in Arlington, Virginia. Secretary Hegseth and Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff General Dan Caine held the news conference to give an update on Operation Epic Fury. (Photo by Alex Wong/Getty Images) (Photo by Alex Wong/Getty Images)