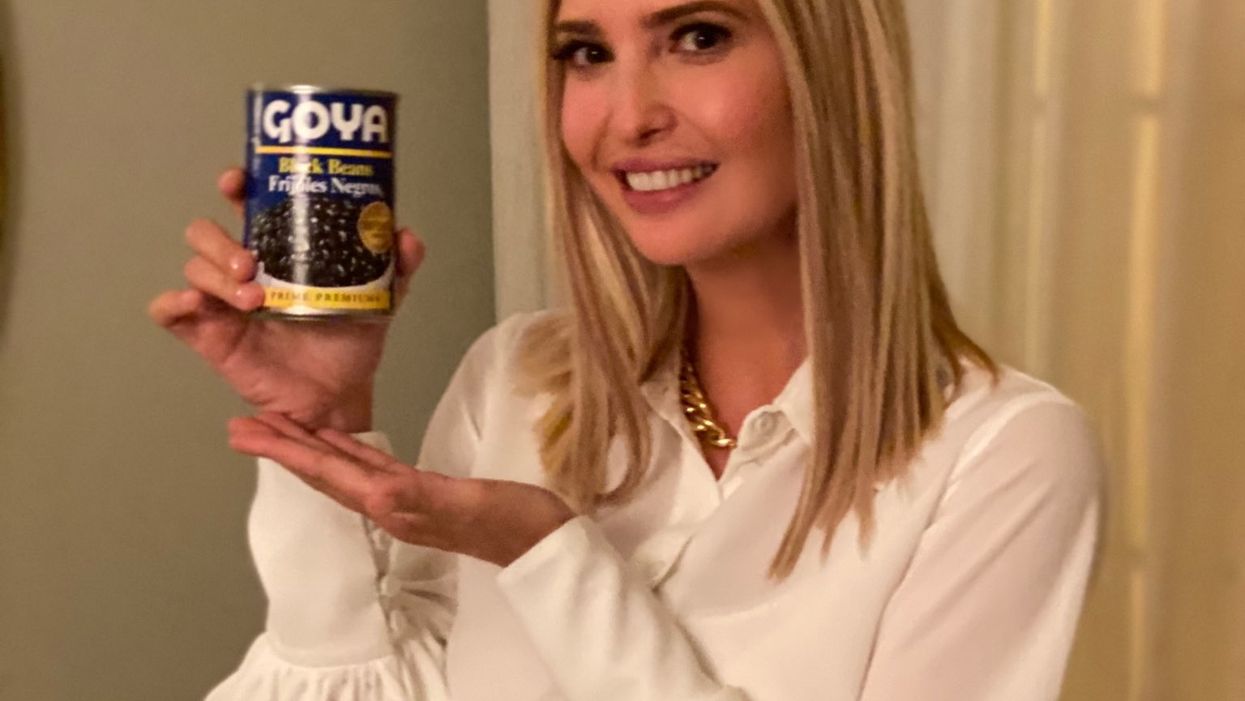
White House adviser and presidential daughter Ivanka Trump posted a photo of herself holding a can of Goya black beans on Twitter last week, including the caption in both English and Spanish: "If it's Goya, it has to be good." The post came after intense criticism of the brand from consumers and Hispanic leaders after CEO Robert Unanue praised President Trump in a Rose Garden event. Unanue said the country is "truly blessed" to have a leader like Trump.
Trump later posted a similar image of him with an array of Goya products sitting on the Resolute Desk. Both of these posts were in direct response to the blowback from Unanue's statements.
Ivanka Trump likely violated a misuse of position ethics guideline that prohibits executive branch employees from using their status to endorse commercial products: "An employee's position or title should not be used to coerce; to endorse any product, service or enterprise; or to give the appearance of governmental sanction." The president is generally exempt from such rules.
Walter Shaub, the former director of the U.S. Office of Government Ethics, asserted that because Ivanka has her official title in her Twitter bio, the endorsement and her executive branch position are strongly linked and make the violation more probable.
The advocacy group Citizens for Responsibility and Ethics (CREW) filed an ethics complaint against Ivanka on Friday. "This is not just about beans; it's another example of a disturbing pattern of this administration acting to benefit the businesses of the president's supporters," CREW Executive Director Noah Bookbinder said in a statement.

















 Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation ranking member Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-WA) (R) questions witnesses during a hearing in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill on February 10, 2026 in Washington, DC. The hearing explored the proposed $3.5 billion acquisition of Tegna Inc. by Nexstar Media Group, which would create the largest regional TV station operator in the United States. (Photo by Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images)
Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation ranking member Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-WA) (R) questions witnesses during a hearing in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill on February 10, 2026 in Washington, DC. The hearing explored the proposed $3.5 billion acquisition of Tegna Inc. by Nexstar Media Group, which would create the largest regional TV station operator in the United States. (Photo by Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images)
