A controversial database used to check whether voters are registered in more than one state has been suspended until security safeguards are put in place.
Use of the Interstate Crosscheck program was put on hold as part of the settlement of a lawsuit filed by the American Civil Liberties Union of Kansas on behalf of nearly 1,000 voters whose partial Social Security numbers were exposed by Florida officials through an open records request.
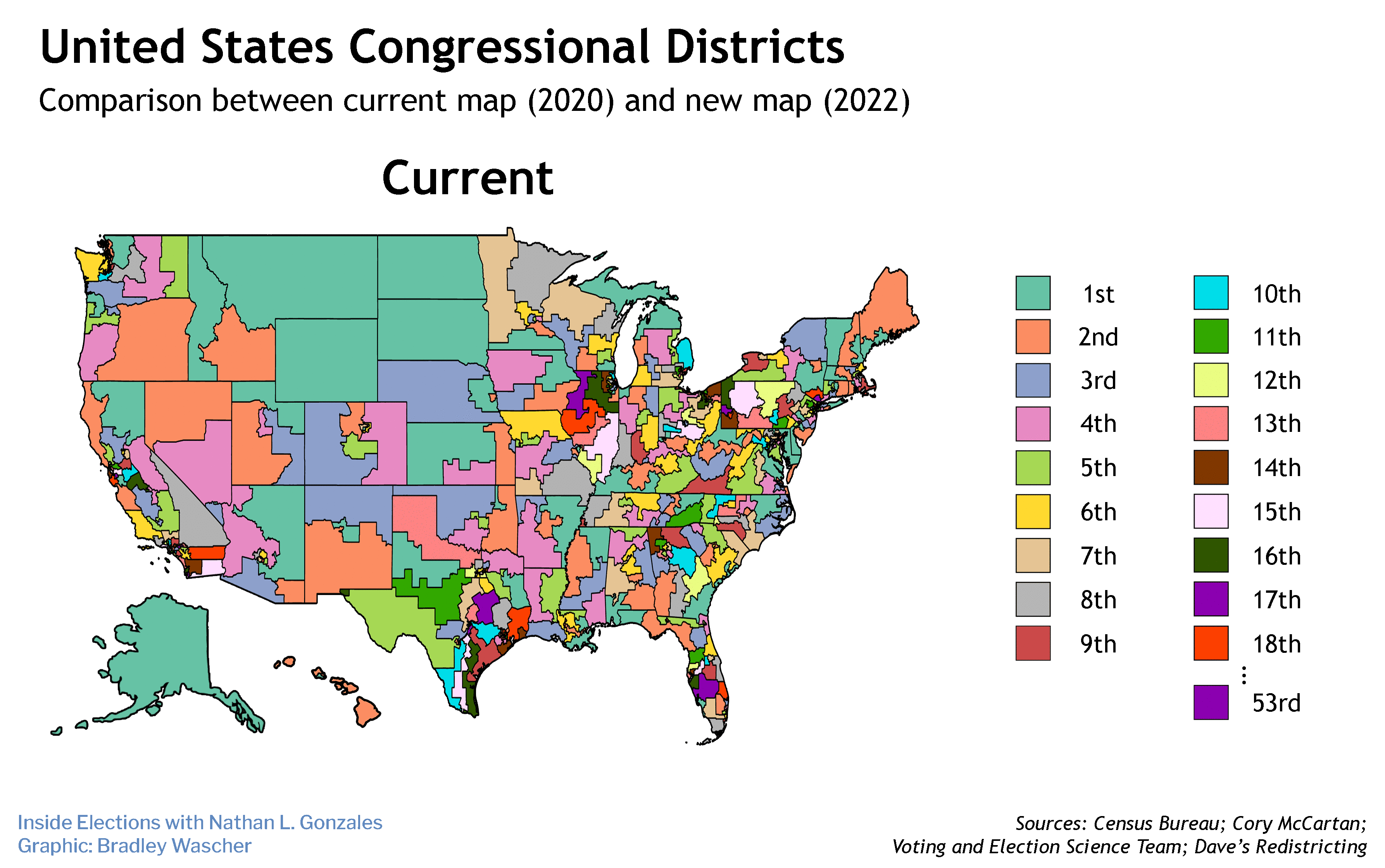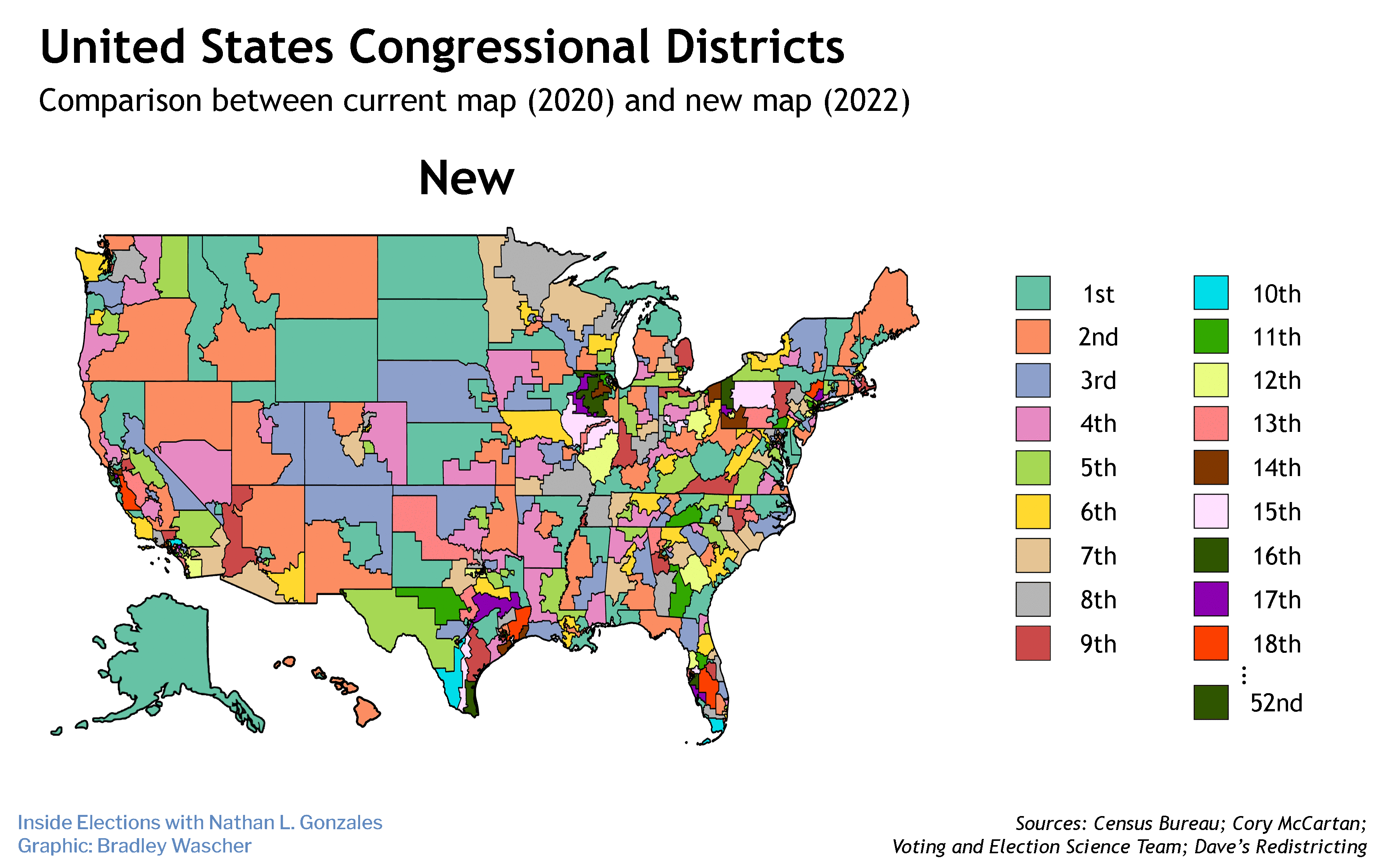
Kansas began operating the multistate program 14 years ago but it has not been used since 2017, when a federal audit discovered its security vulnerabilities.
The settlement includes a list of security improvements the state has promised to make, the ACLU said Tuesday. The civil rights group said the settlement includes a statement from Kansas Secretary of State Scott Schwab's office admitting it made a mistake in allowing the personal information to be disclosed.
Schwab, a Republican, and his office have not shared any comments and were still working on final details of the settlement, which has not yet been posted on the federal courts website.
At least two dozen states shared voter registration records in the Crosscheck program before it was shut down. The program attempted to match names and birthdates to spot people who were registered in more than one state. But it had a high error rate. And that, along with the security problems, caused eight states to drop out of the program.
Sign up for The Fulcrum newsletter
"This is a victory not only for our clients but for every Kansas voter," ACLU Of Kansas Executive Director Nadine Johnson said of the agreement.
The system was created at the behest of Republican Kris Kobach, who was then the secretary of state and has gone on to be one of the most prominent and polarizing election officials in the country. He chaired President Trump's commission to root out voter fraud, which essentially came up empty handed, lost the governor's race last year and is now seeking the GOP nomination for an open Senate seat.
Kobach's successor as secretary of state had ordered a review to determine whether to scrap Crosscheck all together.