Last spring and summer, The Fulcrum published a 30-part series on Project 2025. Now that Donald Trump’s second term has started, Part 2 of the series has commenced.
The Trump administration is already implementing and planning historic changes to the U.S. Department of State, many of which were influenced by Project 2025. Its chapter on the State Department, authored by Kiron K. Skinner, outlines a vision for restructuring the agency to better align with the president’s foreign policy agenda—assuming a Republican victory in the 2024 election. These proposed reforms are already shaping discussions on the future of U.S. diplomacy.
The U.S. Department of State is responsible for managing foreign affairs and diplomacy, representing the nation in international relations, negotiating treaties, issuing passports and visas, and promoting global stability. Thus, any changes greatly impact the role of the United States in all international relationships.
Despite our flaws, I believe in American exceptionalism and worry that a less active State Department will weaken it. American exceptionalism is not just about military strength—it is rooted in ideals like democracy, human rights, and innovation. The State Department plays a vital role in promoting these values worldwide. If the U.S. disengages, it risks losing its standing as a moral and democratic leader.
The chapter on the State Department in Project 2025 called for many fundamental changes, including:
- Reforming the Bureaucracy: The chapter argues that the State Department has historically resisted conservative administrations due to a workforce predisposed to disagree with their policies. It calls for reshaping the department into a more streamlined diplomatic entity that fully serves the president’s agenda.
- Increasing Political Appointees: The proposal suggests appointing more political officials to key positions to ensure alignment with the administration’s priorities.
- Restructuring Diplomatic Efforts: The chapter emphasizes the need for a diplomatic machine focused on national interests as defined by the elected president.
- Policy Implementation: The chapter stresses that the State Department should be instrumental in communicating and executing the president’s foreign policy vision.
In the first 100 days, the Trump administration has already implemented several recommendations from Project 2025 regarding the State Department. Significant changes include budget cuts, mission closures, and policy realignments.
The most controversial move has been an executive order targeting the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), shutting it down and freezing all federal foreign aid. This decision aligns with Project 2025’s recommendation to scale back and “deradicalize” USAID by eliminating programs deemed overly politicized or inconsistent with conservative values. The report specifically criticizes USAID for funding progressive initiatives, such as policies addressing systemic racism and central economic planning, arguing that U.S. foreign aid has become a “massive and open-ended global entitlement program,” benefiting left-leaning organizations.
Expect even more sweeping changes to the State Department in the near future, specifically aligned with Project 2025. On April 20, CNBC reported that it had obtained a draft executive order outlining additional reforms that go far beyond those already implemented.
Key provisions in the draft order include:
- Eliminating all “non-essential” embassies and consulates in Sub-Saharan Africa while consolidating regional bureaus worldwide.
- Terminating offices and positions focused on environmentalism, women’s issues, democracy, human rights, migration, and criminal justice.
- Drastically reducing America’s diplomatic presence in Canada. Under the order, State Department operations in Canada would be reassigned to a significantly reduced team within Secretary of State Marco Rubio’s office, designated as the North American Affairs Office.
Most of the proposed State Department restructuring would be carried out through executive orders issued by the president and directives from the secretary of state. However, budget cuts, personnel reductions, and major reorganizations that require funding reallocations would likely need congressional approval.
It remains unclear whether the administration can implement many of these structural changes unilaterally or if legislative action would be required to modify the department's mandate.
These proposals are sparking intense debate among policymakers, diplomats, and foreign policy experts.
The proposed changes to the State Department are critical because they directly impact how the U.S. exercises power, diplomacy, and global leadership. As the leader of the free world, the U.S. depends on a strong diplomatic corps to advance its interests, defend democracy, and shape international policies.
Reducing bureaucracy could enhance efficiency, allowing diplomats to focus on key priorities such as national security and great power competition. However, eliminating offices dedicated to human rights, war crimes, and global conflict resolution could weaken America’s moral authority and soft power—two essential pillars of its global influence.
Ultimately, these reforms signal a shift in how the U.S. defines leadership: Will it emphasize strategic, security-driven diplomacy, or maintain its broad influence through values-based foreign policy? The outcome will shape America’s global role for years to come and is likely to be fiercely debated in the months ahead.
In the 1980s, Republican President Ronald Reagan often emphasized the responsibility of the U.S. as a moral and ideological leader, promoting democracy and freedom worldwide. The philosophy is summed up in this famous quote:
"America is a shining city upon a hill whose beacon light guides freedom-loving people everywhere.”
The world is watching the Trump administration to see if his America First approach abandons our role as an ideological leader or whether foreign policy will become merely based on transactional relationships. President Trump has often downplayed human rights concerns in favor of pragmatic deals—such as his willingness to engage with authoritarian leaders, like Vladimir Putin and Kim Jong Un, without emphasizing democratic values. His foreign policy is more about economic and strategic interests than projecting the U.S. as a moral force.
This dramatic shift will fuel debates in the next four years and beyond about whether Trump's approach will set back generations as a global influence in shaping a values-based international order.
David Nevins is co-publisher of The Fulcrum and co-founder and board chairman of the Bridge Alliance Education Fund.
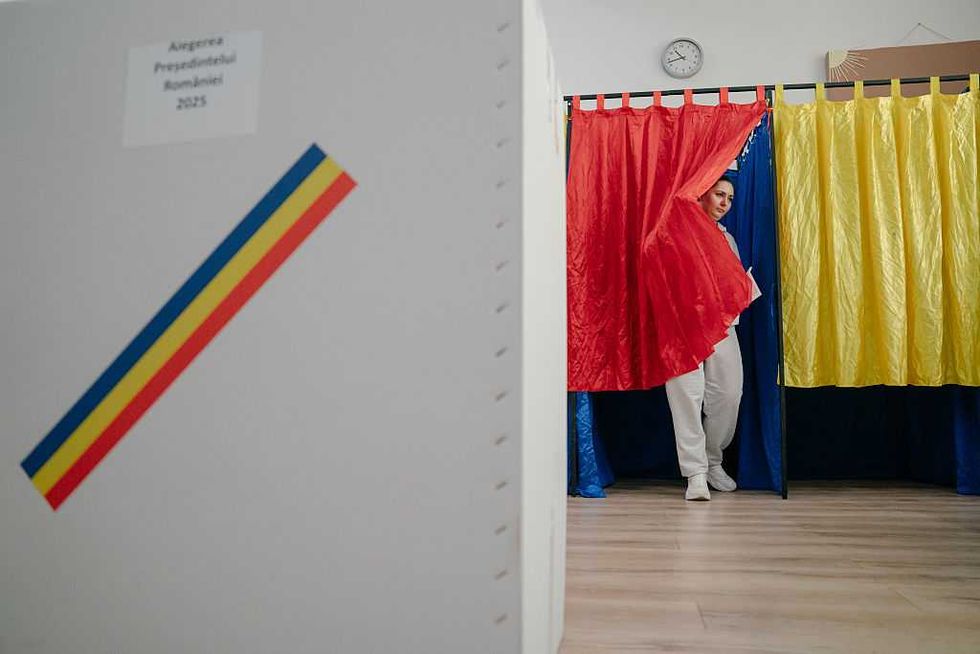



















 A woman prepares to cast her vote on May 4, 2025 in Bucharest, Romania. The first round of voting begins in the re-run of Romania's presidential election after six months since the original ballot was cancelled due to evidence of Russian influence on the outcome. Then far-right candidate Calin Georgescu surged from less than 5% days before the vote to finish first on 23% despite declaring zero campaign spending. He was subsequently banned from standing in the re-rerun, replaced this time round by George Simion who claims to be a natural ally of Donald Trump.Getty Images, Andrei Pungovschi
A woman prepares to cast her vote on May 4, 2025 in Bucharest, Romania. The first round of voting begins in the re-run of Romania's presidential election after six months since the original ballot was cancelled due to evidence of Russian influence on the outcome. Then far-right candidate Calin Georgescu surged from less than 5% days before the vote to finish first on 23% despite declaring zero campaign spending. He was subsequently banned from standing in the re-rerun, replaced this time round by George Simion who claims to be a natural ally of Donald Trump.Getty Images, Andrei Pungovschi