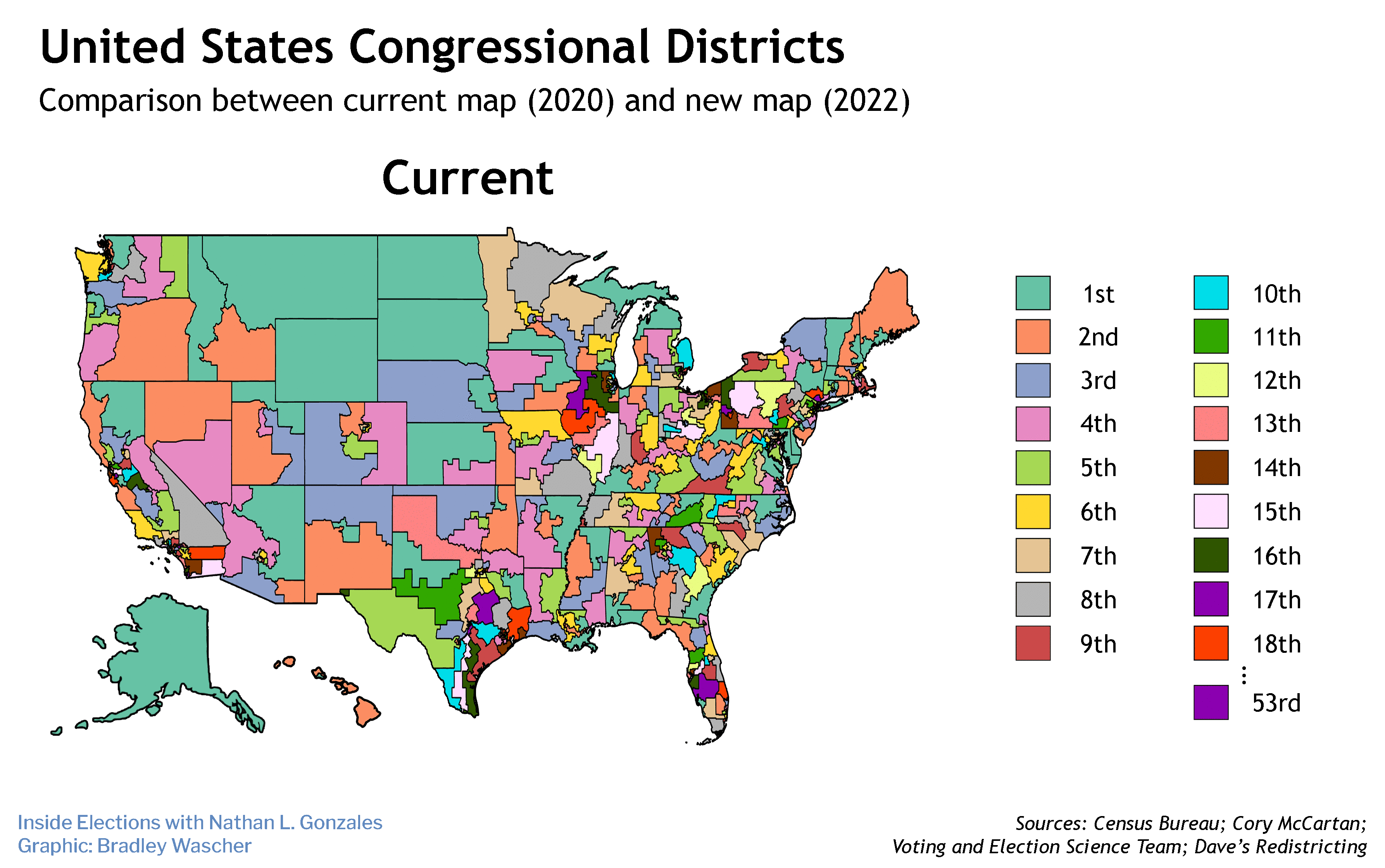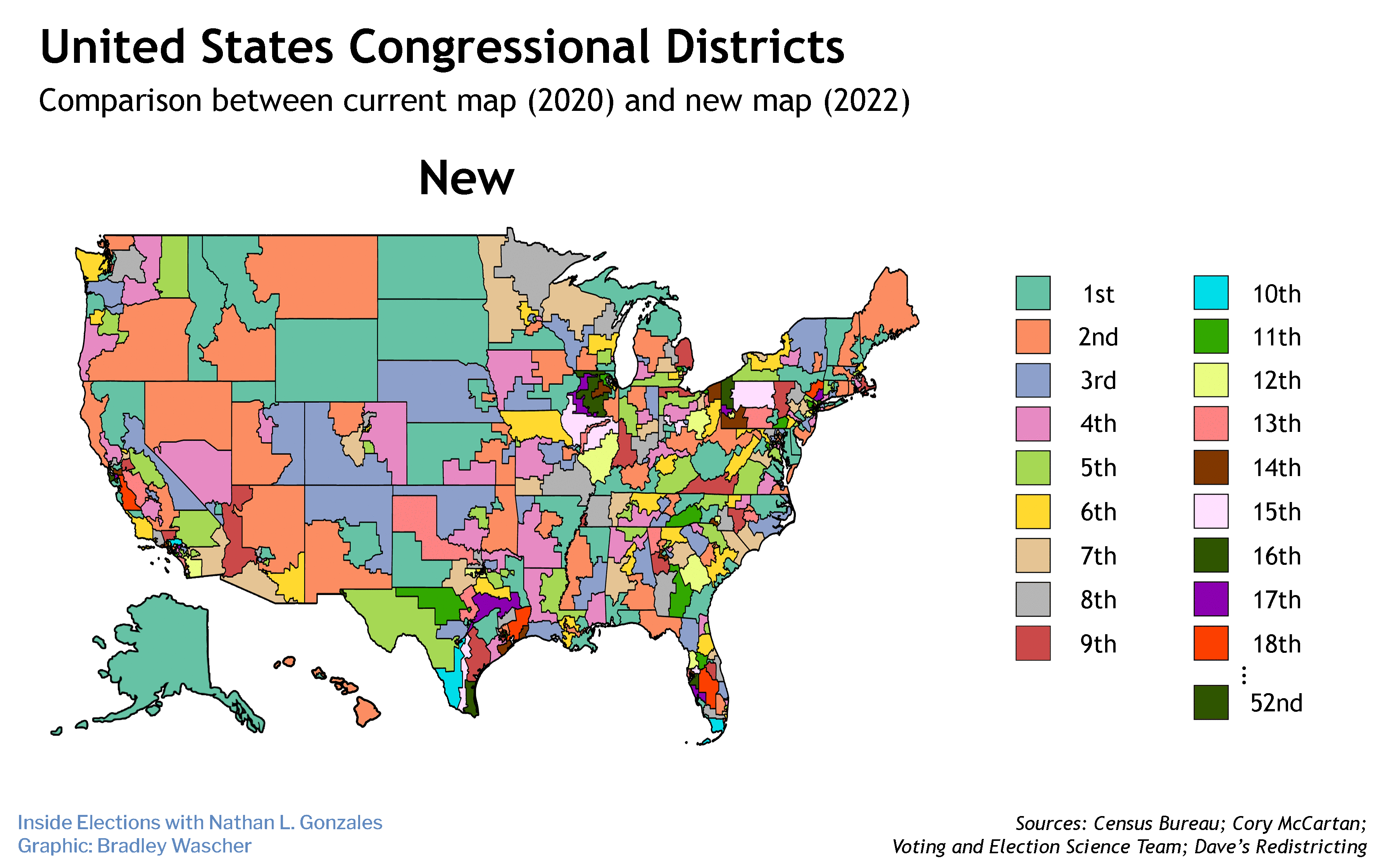
The race is on to see whether a new, more politically competitive congressional map is adopted by the Maryland legislature before the Supreme Court decides if the current map is unconstitutional.
Last week, an independent commission created by GOP Gov. Larry Hogan unanimously embraced a plan to reconfigure two House districts encompassing some Washington suburbs. Even while leaving the rest of the state's sometimes incomprehensibly contorted boundaries intact, a cartographer (redistricting writer Stephen Wolf of the liberal Daily Kos politics website) figured out a visibly clean way to give Republicans a reasonable shot at electing a second House member from the state.
He refigured the 6th district to cover the entire panhandle and stretch as far southeast as Germantown, with most of the rest of Montgomery County south and east of Gaithersburg falling in a new 8th district far more compact and contiguous than as currently drawn.
After a period of public comment, Hogan is on course to send the map to Annapolis on March 22. The solidly Democratic General Assembly would then have until its annual session concludes April 8 to accept or reject it. But two weeks before that deadline, on March 26, the Supreme Court will hear oral arguments on a potential landmark case asking whether the existing map is an unconstitutional partisan gerrymander because its contours virtually guarantee that only one of the eight House members from the state is a Republican – even though the GOP reliably wins 40 percent of the vote statewide.
Sign up for The Fulcrum newsletter
That case is paired with a challenge to the map for North Carolina, where the GOP has held a 12-3 advantage in the congressional delegation all decade even though the total statewide vote for congressional candidates is split almost 50-50 each time. The court is being asked to decide if such maps can ever be drawn with such clear partisan intent as to become unconstitutional.