The League of Women Voters is launching a half-million-dollar nationwide campaign to make sure the country's electoral boundaries are drawn to assure more competition in the next decade.
The plan, announced Thursday by one of the nation's most venerable civic organizations, is "focused on creating fair political maps nationwide" — a goal that's not otherwise explicitly explained, but seems clearly intended to tackle the rise in aggressively partisan gerrymandering.
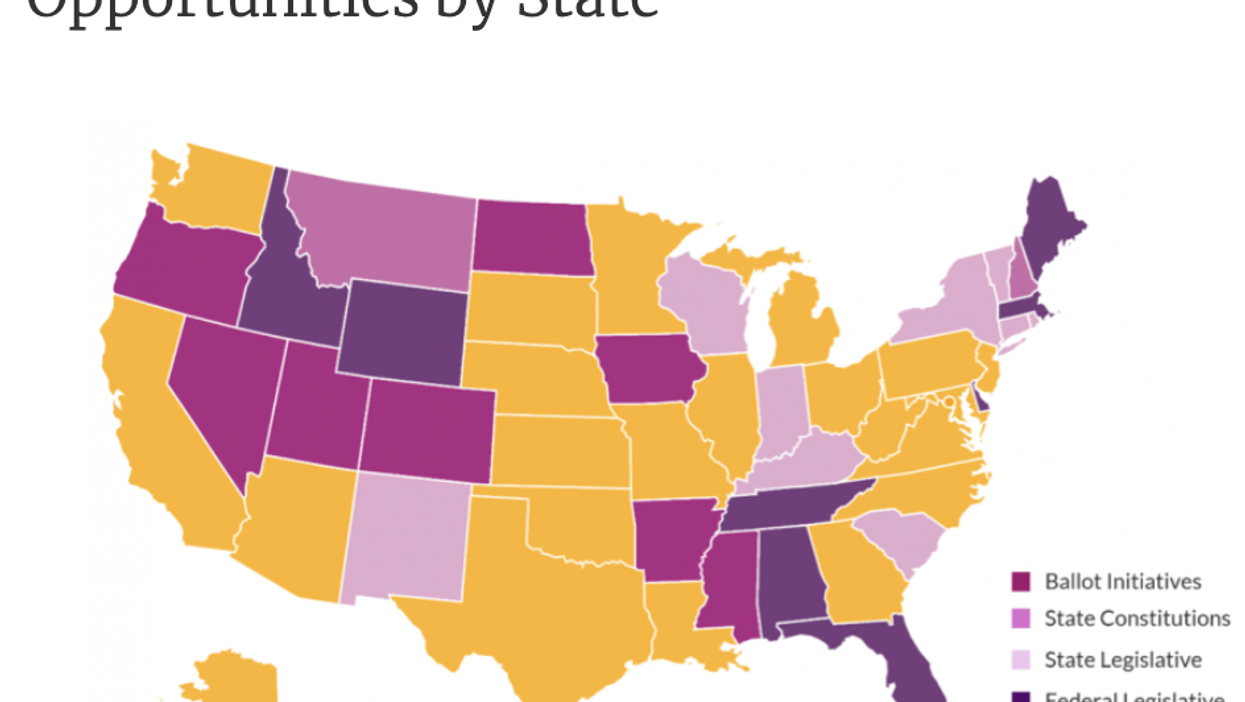
The investment toward the adoption of voting districts drawn without partisan intent following the 2020 census includes varying approaches.
The focus areas include helping pass or protect ballot measures creating independent commissions in 21 states, where such initiatives have already been approved or could be proposed to voters.
The group also plans to ensure fair redistricting provisions are followed in the 18 states where such provisions are mandated in state constitutions. This week, for example, a panel of judges in North Carolina ordered a remapping of all state legislative districts on the grounds the current map's Republican bias violates the rights of Democratic voters under several provisions of the state's constitution. The Supreme Court of Pennsylvania threw out a congressional district map last year.
In 26 states, LWV chapters will focus on state laws related to the redistricting process, such as improving the public input process and increasing transparency over map-making decisions.
Other aspects of the group's People Powered Fair Maps Campaign include working with congressional lawmakers from 18 states to push federal legislation that would strengthen the Voting Rights Act ahead of the next redistricting as well as public outreach to improve community engagement around the redistricting process.
The Supreme Court's ruling in June that banned fair map advocates from challenging partisan gerrymandered districts in federal court spurred LWV's multi-year campaign, League of Women Voters CEP Virginia Kase said in a statement.
"When the Supreme Court ruled that federal courts could not play a role in policing partisan gerrymandering, we realized that, while the decision was a blow to our efforts, it also presented an opportunity for us to lead a national conversation about other fixes to this flaw in our democracy," Kase said.
The $500,000 advocacy, education and mobilization campaign will continue through 2021, when the bulk of redistricting at the congressional, state and local levels will take place.