Simon is a technology consultant and a contributing author of “Leveraging: A Political, Economic and Societal Framework.”
No matter where you fall on the political spectrum, it’s clear that democracy in America has been weakened by events over the past decade. In fact, one of the few things that people can agree on in an increasingly polarized country is that the very foundations of American democracy have become threatened. In such an environment, we need to look for ways to strengthen our trust in the democratic process.
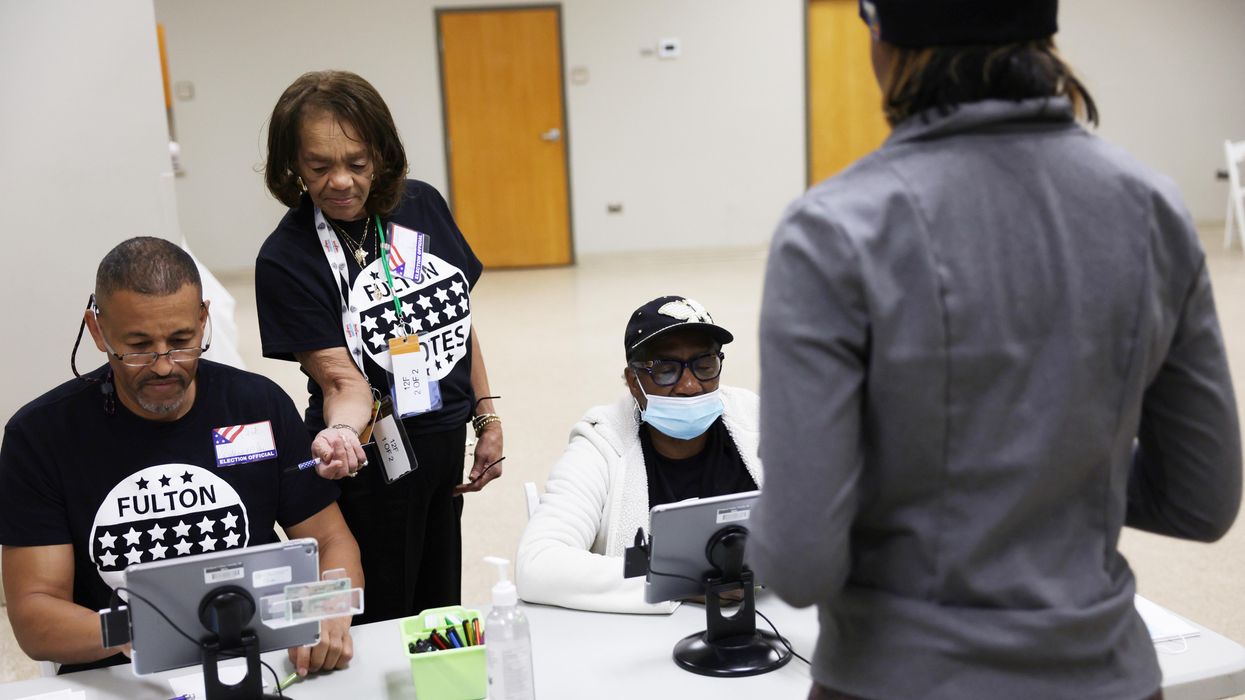
There is no magic bullet to quickly restore Americans’ confidence in elections; that trust will need to be rebuilt over time. For those who have lost faith in the election process, regardless of the reason, it will take many small building blocks to repair the foundation. To that end, I propose that establishing “election poll duty,” akin to jury duty, could be one of those building blocks.
Some factions in America have been attacking the election process by raising doubts about voting methods, tabulation of votes, voting equipment and systems used, as well as the audits and controls built into the process. At the same time, experts in the field widely view recent elections as some of the most secure in American history.
My contention is that the more people understand the process, the less likely they would be to try to bring it down. If more people were to participate in the election polling process over time, this would increase the understanding and appreciation for what goes on — thereby making it harder to cast aspersions on the process with baseless attacks.
Currently, most people are aware that they could be called upon for jury duty. Names are periodically selected from motor vehicle records, voter registration or other governmental records within the state to serve on jury duty. If your name is called, you are legally required to fulfill your obligation as per state rules and regulations. On the other hand, election poll workers are generally volunteers. Fortunately, we have enough civic-minded people in the country who are willing to serve in these roles as election officials, although it has become harder to serve amid increasing personal threats.
There are plenty of volunteer opportunities that don’t require specialized skills or technical knowledge, just a little training. By treating election poll staffing like jury duty and selecting a cross-section of people to serve, we would promote collaboration with other people in a nonpartisan fashion to conduct elections. Polarization has effectively eliminated communication across party lines; random selection of election poll works could help promote communication and understanding that is noticeably absent in society today.
If we are going to stem the tide of polarization in America and restore faith in the election process, we will need to take collective action. The concept of compulsory election poll duty would be a small, but important, step that could be part of a grassroots effort to help preserve the common principles that bind all of us together as Americans.