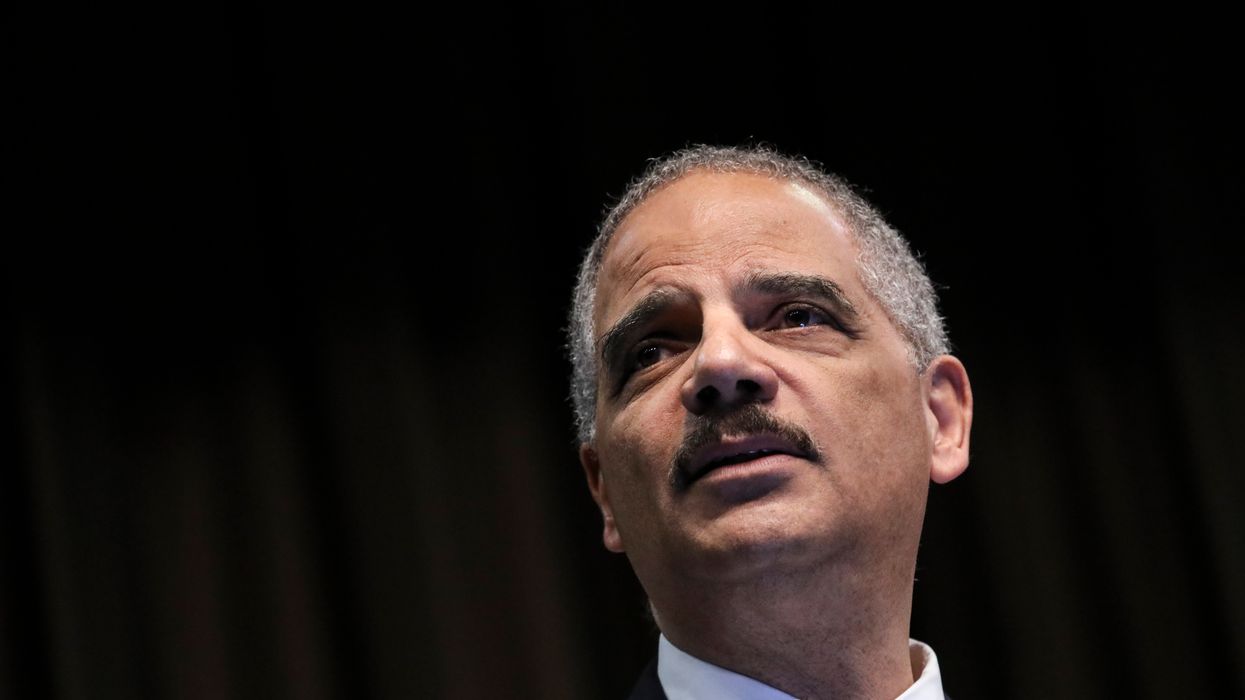
"The biggest rigged system in America is gerrymandering," according to Eric Holder, who was attorney general during President Barack Obama's first term.
And "Maryland is the shamefaced owner of the single worst gerrymander in the nation," in the view of Ashley Oleson, who runs the state's League of Women Voters chapter.
"The 3rd District mangles the central part of the state as it snakes its way northeast from Annapolis, then west, again eastward, and one more time northwest(ish) until it's close to the top of the state — passing in and out (and sometimes back in again) of four counties and Baltimore City," she told The Fulcrum last fall. "The district has been characterized by a federal judge as a 'broken-winged pterodactyl lying prostrate across the state' and also likened to 'blood spatter at a crime scene.' "
As an expert on redistricting drawn by hand, I do love Holder's famous gerrymandering quote. However, I am still puzzled because he has not taken any action yet to combat the egregious practice by the Democrats in control of the General Assembly of a state I've called home.
To review, Democrats have averaged 61 percent of the statewide vote for Congress in the four elections held under the current map. And each time, Democrats have won seven of the state's eight House districts.
Although his office in Washington is only about 30 miles west of the statehouse in Annapolis, Holder has not testified in person or even in writing before any of the legislative committees with jurisdiction over the whopping roster of 13 bills to reform redistricting that were filed this year. (At the end of a session shortened by the spread of the coronavirus, all those measures had stalled without action.)
Similarly, Holder did not attend any of the four oral arguments that preceded the Supreme Court's landmark decision a year ago to steer clear of partisan gerrymandering disputes — despite having an open invitation to take a seat at the highest court in the land, thanks to his being a former attorney general.
Suddenly, after the 2019 hearing in the Maryland redistricting case, Benisek v. Lamone, Holder appeared with one of the nation's best-known anti-gerrymanderers, former Gov. Arnold Schwarzenegger of California, at a National Press Club event. They discussed why they believed redistricting reform is crucial to the future of our democracy. After the conversation, both signed the End Gerrymandering Pledge circulated by Common Cause.
Eight months later, GOP Gov. Larry Hogan of Maryland and the League of Women Voters' Oleson signed it, too. "I see gerrymandering for what it is — voter suppression," she said. "It is essential that we repair the redistricting processes in Maryland and throughout the nation to ensure the voices of the people are heard, and confidence in our democracy can be restored."
But what about Holder? He happens to serve as chairman of the National Democratic Redistricting Committee, which describes itself as "the centralized hub for executing a comprehensive redistricting strategy that shifts the redistricting power, creating fair districts where Democrats can compete." He claims that his program's purpose is to combat gerrymandering.
According to IRS filings, the organization's purpose is to "build a comprehensive plan to favorably position Democrats for the redistricting process through 2022."
To be clear: That does not match with Holder's famous quote.
Here's how he explained the disconnect during an appearance two years ago at Georgetown University Institute of Politics and Public Service: "There are instances you can probably point to where Democrats have not played fairly, but it pales in comparison to what Republicans have done."
Then he mocked a congressional district in Virginia that's "only contiguous at high tide" along with a Pennsylvania district with lines that "run through a parking lot." But, in an interview afterward, he declined to similarly single out Maryland's notorious 3rd District as being an egregious example of partisan mapmaking, despite its ungainly shape.
"I am in complete agreement with your goal of building a democracy where voters pick their elected representatives, not the other way around," Hogan said in a February 2019 letter urging Holder and Obama, who's lent his name to the NDRC, to get behind efforts to end the era of partisan gerrymandering in his state. "With your support, I believe we can set things right in Maryland."
There is no sign Hogan has ever received a response.
And it took until last July for Holder to use the word "Maryland" in anything he's written for public consumption on the topic of partisan gerrymandering
In an opinion piece for The Washington Post headlined "If the Supreme Court won't protect our democracy, voters will," he included the following in a discussion of the court's ruling: "As Justice Elena Kagan wrote in her powerful and prescient dissent, the partisan gerrymanders in Maryland and North Carolina 'debased and dishonored our democracy, turning upside-down the core American idea that all governmental power derives from the people.'"
People like me, who have been fighting partisan mapmaking for a decade, would be more than thrilled if Holder would now apply that newfound rhetorcial zeal equally — to lines drawn by Democrats as well as Republicans.
He can start in Annapolis next year by taking on Democratic state Sen. Paul Pinsky, who has been the chief engineer stalling Hogan's bills on reforming redistricting in each of the past five years.