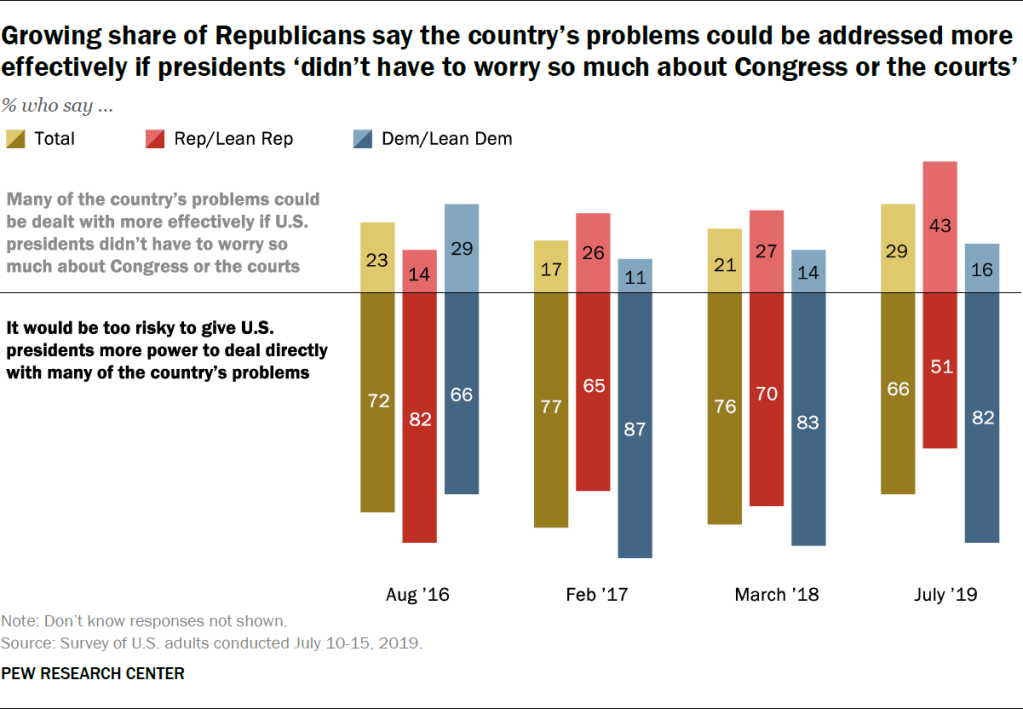
A growing number of Republicans support expanding the power of the presidency, according to a survey by the Pew Research Center.
More than 40 percent of Republicans surveyed in July said presidents would be more effective if "they didn't have to worry so much about Congress or the courts." That was up from 26 percent who supported the idea in February 2017, according to the survey.
The change was primarily driven by those identified as "conservative Republicans," whose support for expanding presidential power rose to 52 percent compared to 26 percent in March 2018. Less than a third of moderate and liberal Republicans supported the idea then and now.
While only 16 percent of Democrats believed in expanding presidential power in the July survey, 29 percent had supported the idea in August 2016, when Barack Obama was president.
Overall, 66 percent of Americans said it would be "too risky" to give presidents more power to deal with the country's problems, down from 76 percent who held the view a year ago.
The survey also found a change in favorability of Congress among Republicans and Democrats.
Forty-three percent of Democrats had a favorable view of Congress, up from 24 percent in March 2018. But the share of Republicans with a favorable view was 27 percent, down from 37 percent a year ago.
Overall, just over a third of Americans viewed Congress favorably versus 59 percent who viewed it unfavorably.



















