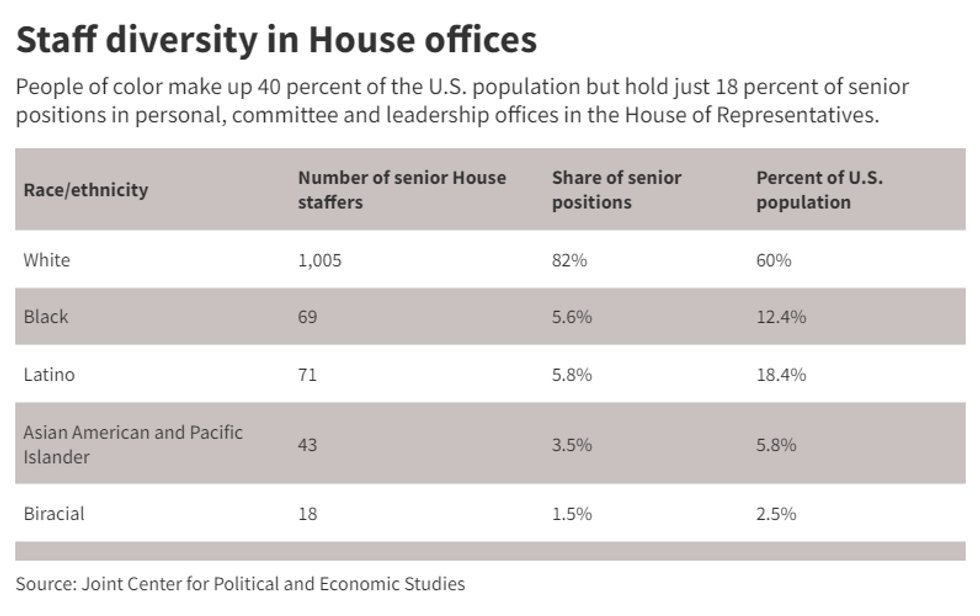
While people of color make up a larger share of senior staff positions in the House of Representatives than they did four years ago, the top ranks remain far away from the national demographics.
The latest census data shows people of color make up 40 percent of the U.S. population but, according to the Joint Center for Political and Economic Studies, they comprise just 18 percent of senior House positions. Only 23 of 308 personal offices of white lawmakers have a chief of staff who is also a person of color.
The ranks of senior staffers have become more diverse – up from 13.7 percent when the first edition of the report was published four years ago.
“While Congress has made significant progress since 2018, members of Congress and their leadership must do more to ensure that the diversity of the U.S. House workforce reflects the diversity of the American people,” writes LaShonda Brenson, senior researcher at the Joint Center and author of the report.
The study tallied the number top staffers in three levels of House offices:
- Chiefs of staff, legislative directors and communications directors in lawmakers’ personal offices as
- Chiefs of staff, policy directors and communications directors in leadership offices.
- Staff directors for full committees.
"While we currently have one of the most diverse Congresses in history, their staff still falls short of reflecting the multiplicity of communities that make up the United States. By increasing the diversity of top Hill staff, especially in senior-level positions, Congress is able to make smarter policies, communicate more effectively, and ensure that everyone's needs are met,” said Kayla Primes, president of the Congressional Black Associates, a bipartisan organization of Black staffers on Capitol Hill. “We acknowledge that 18 percent is an improvement from 13.7 percent, but there is still a long way to go to account for the 40 percent of BIPOC Americans in the U.S. today."
Democrats hired a significantly higher share of people of color for senior positions, accounting for 82 percent, according to the research, and at a higher rate among all the racial groups studied. Republicans’ biggest share is among Native American staffers, but that’s only one of a total of three aides. They also have 26.8 percent of the Lantino staffers in senior positions. Just 5.1 percent of staffers in the offices of white Republicans are people of color.
But even within the Democratic side of the aisle there are differences, with 40 percent of top positions unders members of the Congressional Progressive Caucus filled by people of color. That’s compared to 23.6 percent under members of the moderate Blue Dog Coalition.
Lawmakers of color account for the largest share of senior staffers who are racial minorities. For example, members of the Congressional Black Caucus are responsible for hiring 75 percent of the senior Black staffers across all three office types.
While Asian American/Pacific Islander, biracial, Middle Eastern/North African and Native American staffers do hold senior positions in lawmakers personal offices, none of them serve in a top post in a leadership office or as a committee staff director.
The report also examined which personal offices represent districts that are at least one-third minorities but do not have people of color in senior roles. It found 239 districts that meet the population requirement, and of those nearly half (48.1 percent) do not have a person of color in any of the top positions.
“The lack of top staff diversity is a structural challenge for the entire institution rather than a problem attributable to a single member or political party,” according to Brensen. “The lack of racial diversity impairs House members’ ability to understand their constituencies’ diverse perspectives.”
The study identified 20 senior positions in House leadership (the offices of the speaker, the majority and minority leaders, the majority and minority whips, and the caucus chairs). Of those 20 people, two are Black and one is Latino. The remaining 17 are white. The only leaders with a person of color in a top spot are:
- Majority Whip Jim Clyburn
- Democratic Caucus Chairman Hakeem Jeffries
- Minority Leader Kevin McCarthy
Primes noted that her organization is trying to help Congress become more diverse.
“CBA recently re-launched our resume bank as a resource for Members and staff to find that diverse talent because they are here and ready to be of service,” she said.
The Select Committee on Modernization of the Congress, a bipartisan panel that has spent the past four years developing proposals to make the House more effective and transparent, has made suggestions for improving staff diversity.
One such proposal that was implemented turned the Office of Diversity and Inclusion into a permanent element of the House structure. Another directs the ODI and the Office of the Chief Administrative Officer to conduct a compensation and diversity study every two years.




















