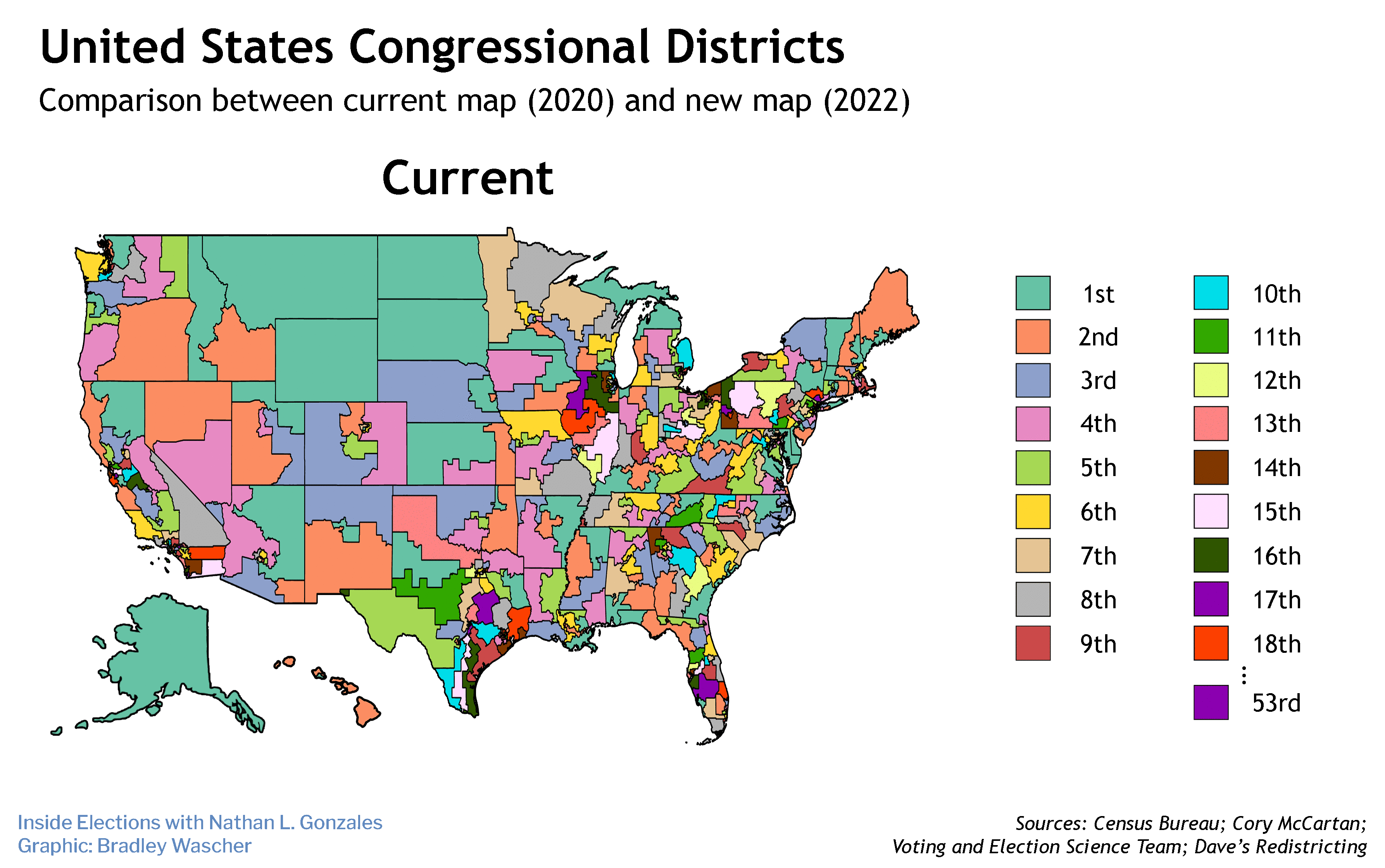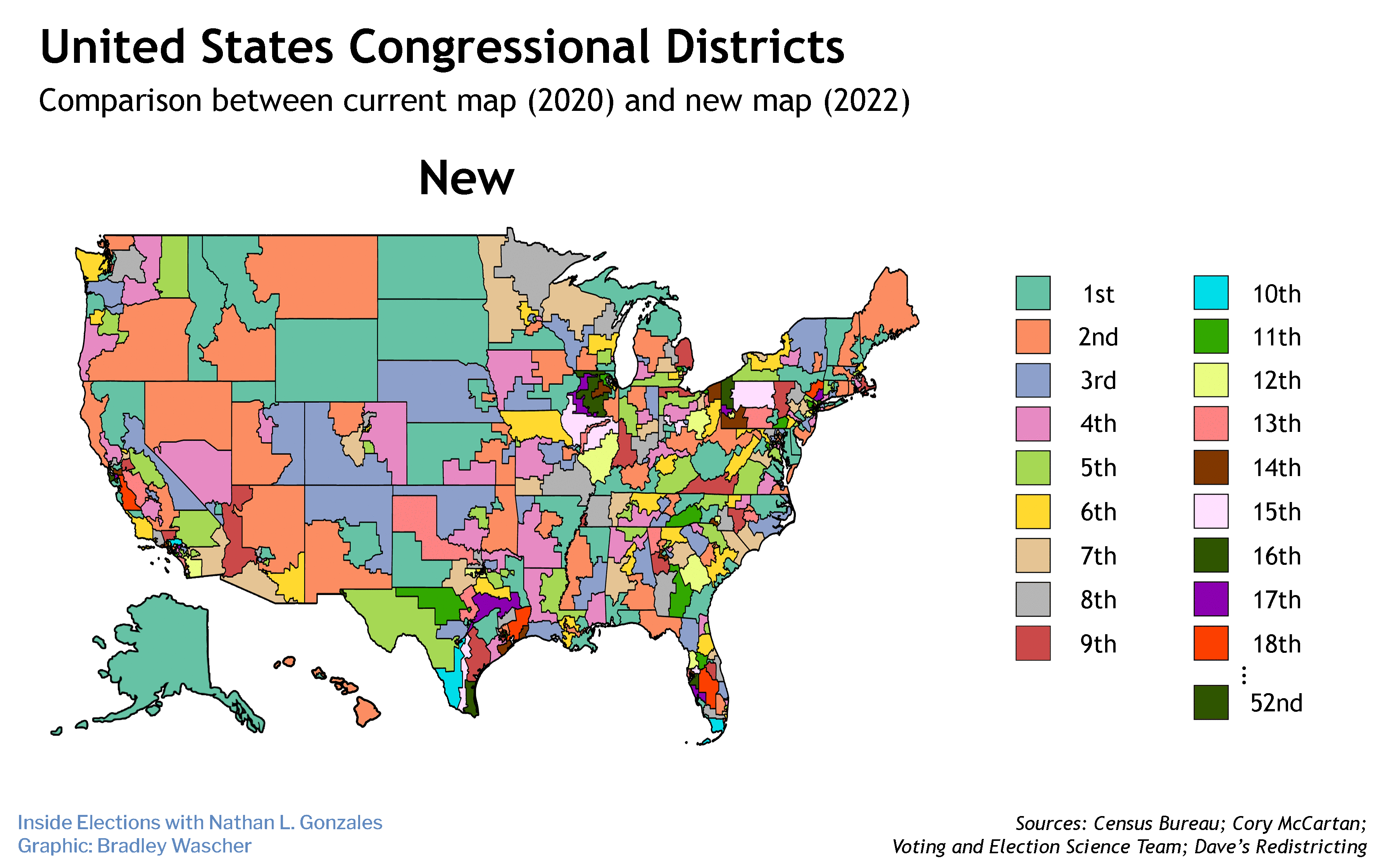
Attempts by Republicans to draw legislative maps for the next decade using only the population of citizens would be discriminatory and result in extreme partisan gerrymanders all across the country, Common Cause says.
Common Cause, a venerable nonprofit advocacy group with a liberal bent, issued a report Monday titled "Whitewashing Representation," citing the failed effort by the Trump administration to include a citizenship question in the 2020 census.
Results of the census are used to calculate federal benefit allocations to states and communities and to draw the boundaries of state legislative and congressional districts. When lawmakers draw the boundaries, they often favor the party in power to an extreme. But the Supreme Court ruled this year that federal courts have no role in deciding if such partisan gerrymandering is unconstitutional, kicking the issue to the states.
On the same day, the court also effectively blocked the administration from adding a citizenship question to next year's census forms. President Trump then ordered federal agencies to provide whatever data they have about citizenship to the Census Bureau, which by the end of next year is supposed to deliver detailed population tabulations to the states so that redistricting can get underway.
Several advocacy groups, include Common Cause, are suspicious that the Republicans poised to lead some states in 2021 — including Arizona, Missouri and Texas — are preparing to draw maps based only on their citizen populations. While the consensus legal view is this would be unconstitutional when it comes to setting congressional boundaries, it's a more open question when it comes to state legislative or local district lines.
Sign up for The Fulcrum newsletter
At the annual meeting of the American Legislative Exchange Council this month, GOP redistricting experts called on Republican legislators to use citizenship data as a way to give their party as much of an advantage as possible in state capitals for the next decade.
"Gerrymandering with citizenship data is a radical effort to undermine our representative democracy," said Suzanne Almeida, counsel for Common Cause and co-author of the report.
Excluding non-citizens when drawing the maps would favor white voters over brown and black voters in how the districts are drawn, the report states.
But proponents of citizens-only maps say that the method is proper because these are the people who have the right to vote.