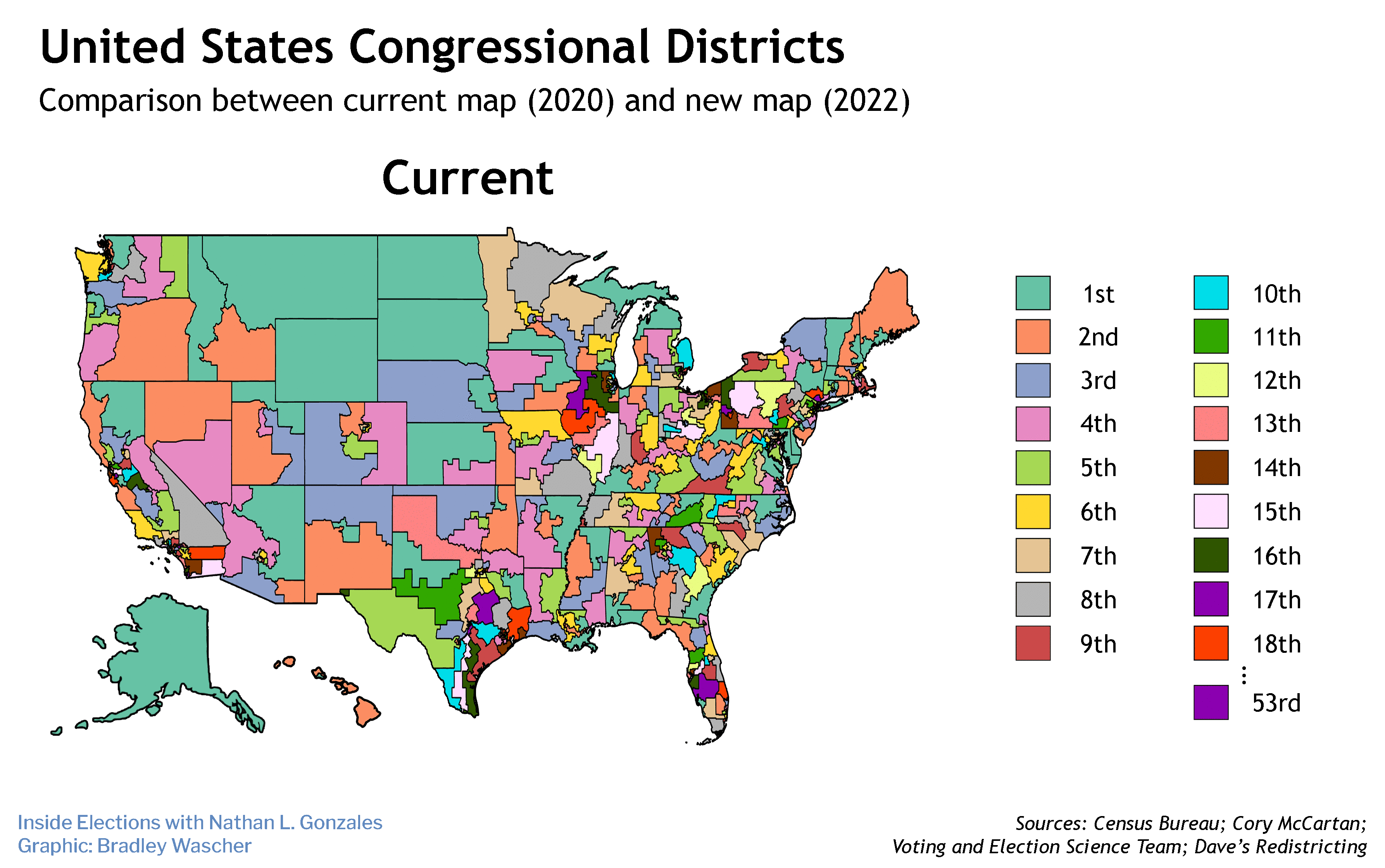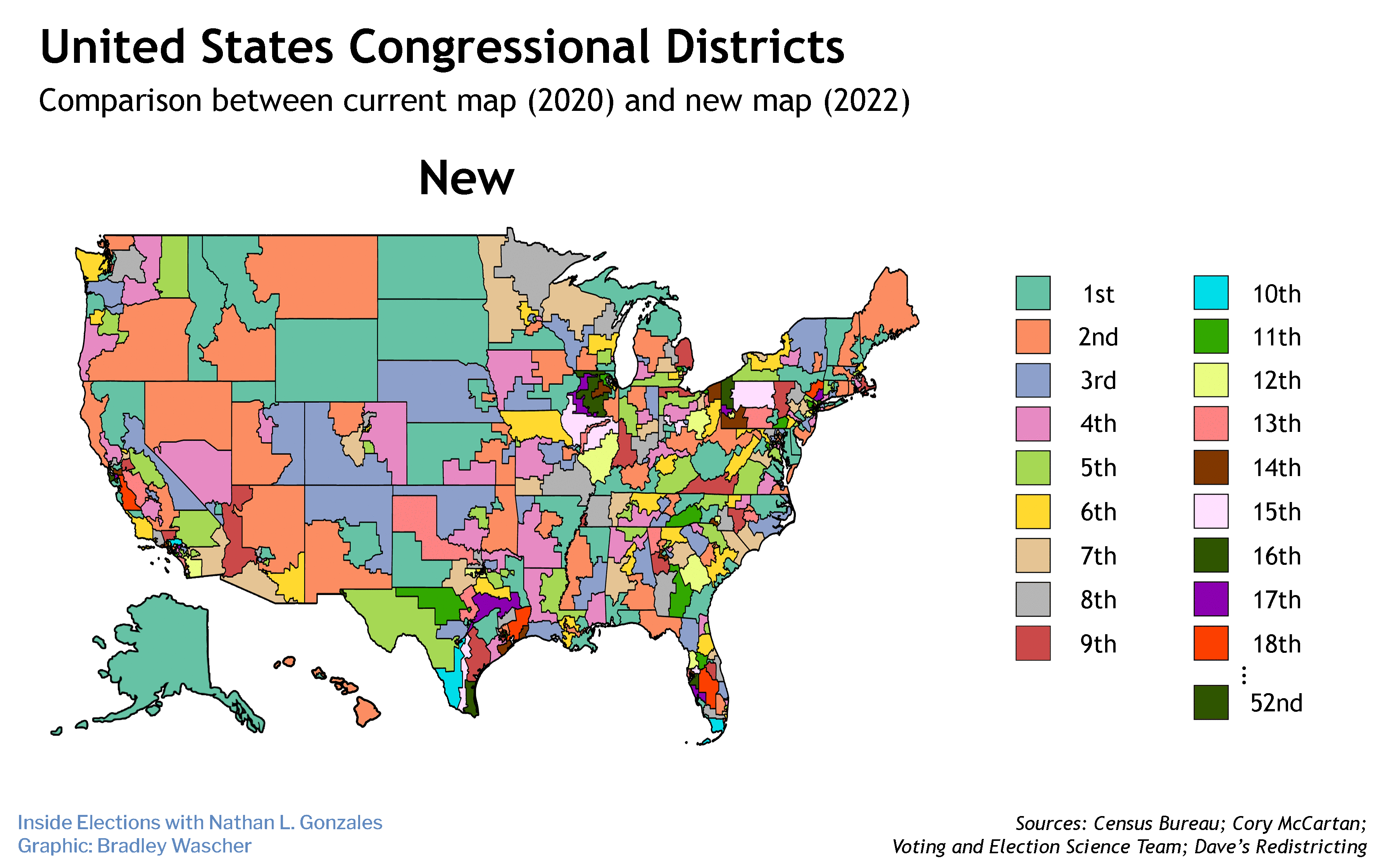
Wilson is an associate professor of political science at the University of Indianapolis and a public voices fellow at The OpEd Project.
Start your engines, organize your campaign and submit your filing paperwork, ladies, because now is the time to run. Women are critically underrepresented in government, regardless of the level or branch.
We are mere months away from the congressional midterm elections, which gives us the opportunity to vote on federal races, but there are many statewide elections that coincide with the Senate and House candidates at the top of the ticket. Even with the presidency not up for election this year, the Covid pandemic, rampant inflation, and Russia’s involvement in Ukraine give voters plenty of motivation to get to the polls.
Female candidates should be motivated, too. The last two election cycles marked record-breaking numbers of women running for office and ultimately winning. Research in political science (like the work of Jennifer Lawless and Richard Fox) shows that when women run, they win — but they do not run as often as men do. This disparity in declaring candidacies leads to the gender gap in politics.
Women are substantially underrepresented. At the federal level, women account for just 27 percent of members of Congress and are one-third of the Supreme Court. Though we have our first female (and person of color) vice president, our country still has never elected a female president. State government fares somewhat better in terms of women in public office, with 30 percent of state legislative seats occupied by women and nine states having female governors. Some politicians begin their careers in state government and then climb to the federal level, giving hope to the difference that could serve as a pipeline.
Sign up for The Fulcrum newsletter
If these numbers alone are unconvincing in the need to cultivate more diversity in public office, the statistics only get worse when racial and ethnic differences are added. Women of color comprise a much smaller subset of elected officials. According to the Center for American Women in Poltics at Rutgers University, there are three women of color currently serving in the Senate (and five ever historically), one woman of color is governor of her state (Michelle Lujan Grisham, the first Latina to hold that office) while four hold the office of lieutenant governor. A record-breaking number of women of color ran in 2020 and projections based on candidate declarations show that record will again be broken in 2022. But the disparity still remains.
This gap is often the topic of conversation immediately before and following the election itself. While there is never a bad time to analyze underrepresentation and consider the causes and consequences, nothing can be done then about attracting more candidates. Candidates need to file with their elections manager (usually the secretary of state) by their state deadline in order to be listed on the ballot. Write-in candidacies do not require filing but they are largely unsuccessful. Filing opened up across the country this month and the window to declare a candidacy is slowly closing, with most state deadlines set for February and March.
To file, a prospective candidate must meet state qualifications (usually including age minimums and residency requirements), organize a campaign committee (notably a campaign finance chair who will need to navigate complex but critical laws), and, in some cases, pay a filing fee. These fees were used historically as a way to deter candidates who weren’t serious in their pursuits, though “indigent” candidates who cannot afford the fee can collect signatures as dictated by state law to forgo the financial barrier.
Traditionally, parties and political organizations led the charge and still play a large role in the recruitment, training and campaign organizing for candidates. In an era of candidate-centered elections and where primaries, not conventions, select the names that will be on the ballot in November, prospective candidates should consider running, regardless of whether they are approached or groomed by a party. Waiting to be tapped on the shoulder is not going to cut it. If you are thinking about running, you can start by yourself.
In most arenas of public service, women are the minority. And, despite two great record-breaking cycles leading up to this election, they remain the minority. From a symbolic representation perspective, this can be harmful. But it is even more damaging when considering substantive representation, where differences of experience and perspective can have on an actual impact on policies. Research has shown that women contribute in different ways than their male counterparts, confirming the value of their presence in leadership. Having institutions that resemble the people they represent is essential to an effective democracy.
If our democratic institutions do not reflect their own constituencies, one has to question the extent to which they are truly democratic with regards to representation. After all, a government “of the people, by the people, for the people” must include the people who aren’t men.