Birdsong is a lecturer in political science at the University of Dayton.
Public opinion polls are ingrained in American politics. It seems like every day there is a new poll about the presidential election or impeachment or whether the public feels that the United States is on the right track.
As the presidential primary season begins in earnest in February, new polls will continue to come out. All polls can provide a wealth of information. But, as a political scientist, I think that if you want to better understand the American public, it would be good practice to look at state polls.
The Constitution created not only a system of shared power within the branches of the national government, but also a system of shared power between the states and national government.
So, one should not assume, like national polls often do, that social and political problems are national in scope and should be addressed by the national government. Many issues, like policing, school funding and mass transit, fall under the purview of the state and local authorities.
Additionally, social and political problems vary in their importance from national to state and from state to state.
For example, in October, Gallup found that 34 percent of Americans cited "the government/poor leadership" as the most important problem facing the country, 13 percent cited immigration and 11 percent said the economy.
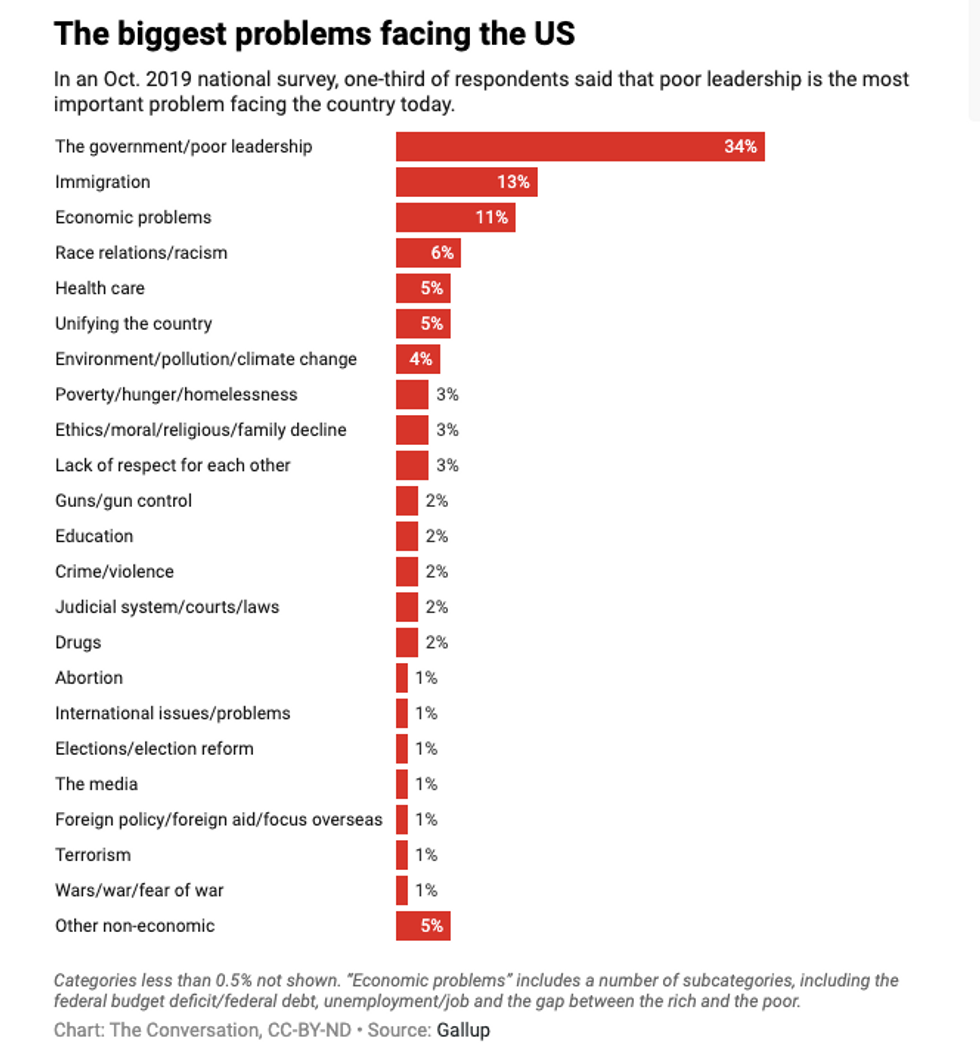
In Texas, however, immigration and border security ranked as the most important problems, whereas "political corruption/leader" was of less concern.
In Ohio, a third of voters cited the economy as the most important issue, followed by health care, social issues and the environment.
So, state polls can give a clearer sense of voters' priorities before and between elections.
Geography – and the changing demographics within the United States – is another reason why readers should pay greater attention to state polls.
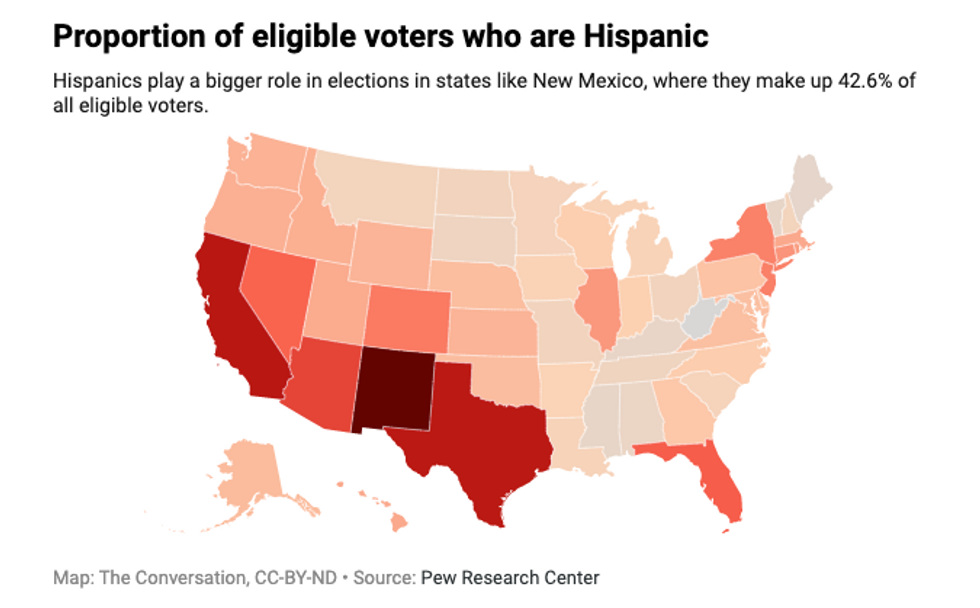
For example, the Census Bureau estimates that Hispanics make up about 18 percent of the population, and an estimated 29 million Hispanics are eligible voters. Hispanics and other nonwhite voters are projected to have greater power in upcoming elections.
But, since most Hispanics live in just a handful of states, their power in national elections is uneven.
More than half of Hispanics live in three states: California, Texas and Florida. Thirty percent of eligible voters in California are Hispanic, but only 2.6 percent of eligible voters in Ohio are Hispanic.While some argue that politics is national, electoral politics – how Americans select and elect leaders – remains local.
Consider the 2018 election and the "Blue Wave." An NPR/PBS NewsHour/Marist Poll found that 50 percent of registered voters would vote for a Democrat for Congress.
But the election results show that the "Blue Wave" washed across the states unevenly. In the Northeast and West, Democrats flipped 65 percent and 61 percent of seats respectively, but only percent and percent of the seats that were flipped in the Midwest and South.
State polls were better able to detect these differences than national polls, and are better suited to explain why, for example, in Michigan a Democrat won the governor's race and Democrats won two congressional seats previously held by Republicans – while, in Ohio, Republicans won every statewide race except for the Senate.
Finally, the electoral system is another reason why state polls are often better indicators of the political landscape.
The Constitution created an electoral system that separated elections by geography. Americans elect representatives for the House from districts based on population. Senators are elected statewide and the president is elected by the Electoral College.
By design, there is no single pool of voters that elects representation in the federal government.
In addition, unlike some other democracies, the United States has candidate-centered campaigning, where candidates are encouraged to promote themselves and their positions on the issues. To be sure, candidates run as Republicans or Democrats, but they mold their messaging to create their own image and to meet the needs of their target constituency.
This system of separated elections leads to the possibility of split-ticket voting like in 2016, where 35 House districts voted for the presidential candidate from a different party from the representative they elected.
Finally, national polls fail to account for the power of the Electoral College. A state's number of electors is equal to its total number of representatives and senators. With the exception of Maine and Nebraska, the candidate winning the most votes within a state receives all electoral votes from that state.
In 2016, the national polls showed an advantage for Clinton. The RealClear polling average showed Clinton ahead of Trump 46.8 percent to 43.6 percent.
Indeed, Clinton won the popular vote, but she lost close races in Michigan, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin. Consequently, Trump won the Electoral College and the presidency.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Click here to read the original article.
![]()