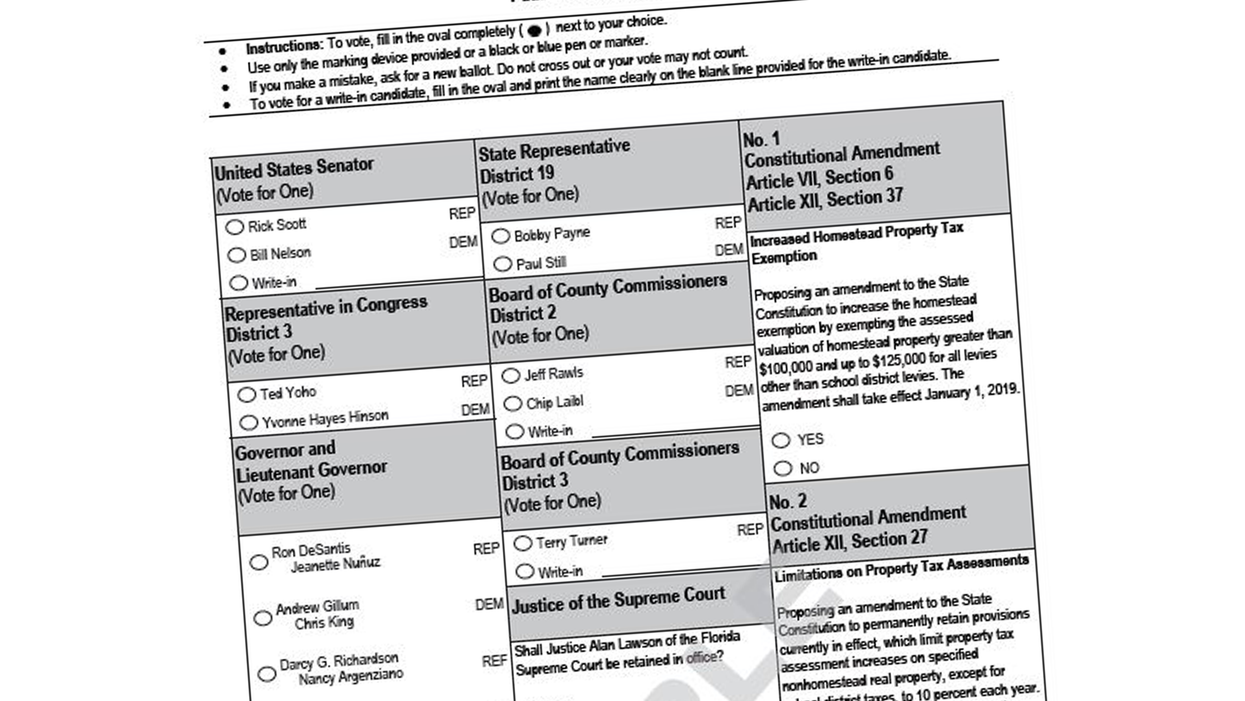
Does the order in which the names of the two major political parties appear on the ballot effectively discount the votes of half of Florida's electorate? That's the question at the heart of the latest in the long list of legal fights over election fairness in the nation's most populous purple state.
The dispute is being heard in a trial this week before Judge Mark Walker, the chief jurist at the federal district courthouse in Tallahassee. Walker has become the pivotal figure in several voting rights lawsuits that could tip the state off its partisan razor's edge.
Florida last fall reaffirmed its status as the biggest electoral prize in the country that both Republicans and Democrats can realistically hope to win, when the GOP held on to the governor's mansion by four tenths of 1 percent of the vote and claimed a Senate seat by an even closer margin.
The Democratic Party and progressive groups are working on several fronts to tilt things their way in time for 2020, when winning the state's 29 electoral votes will be central to the strategies of both President Trump and his challenger.
In the latest case, they're hoping the federal courts strike down as unconstitutional a 68-year-old Florida law giving pole position on every ballot line to the federal, state and local candidates who are from the governor's party.
Because only Republicans have been governor since 1999, the Democrats say this has put them at a decided disadvantage, as voters are more likely to pick the candidate whose name they see first.
"There's no secret in politics that where a candidate appears on the ballot matters," Abha Kanna said in her opening arguments Monday on behalf of the Democrats. Their case will emphasize a study of seven decades' worth of Florida election returns by Stanford University political scientist Jon Krosnik, who found GOP candidates had a 5.4 percentage point advantage in elections when their names came first and Democrats a 4.6 point edge when they were listed first.
"People vote for all sorts of reasons and no reasons at all," countered Florida's attorney, Mohammad Jazil. "The statute, at the end of the day, doesn't keep a single voter from casting a ballot."
Democrats have proposed having the party with the top ballot line alternate by county, a system used in several states
Walker, nominated to the federal bench by President Obama in 2012 after four years as a state judge, had refused Democrats' request to suspend the ballot position law before the midterm election. Burt he also ruled against the GOP state elections administrator to require more widespread use of Spanish language ballots. And, before the voters approved the restoration of voting rights to felons, Walker had issued a ruling that could have eventually resulted in the same outcome.
Now, in addition to the ballot position case, the same judge is also overseeing several other election-related lawsuits — including those prompted after GOP Gov. Ron DeSantis this summer signed a sweeping elections package including new limits on felons' voting rights and requirements that college students say will make it much tougher for them to vote.