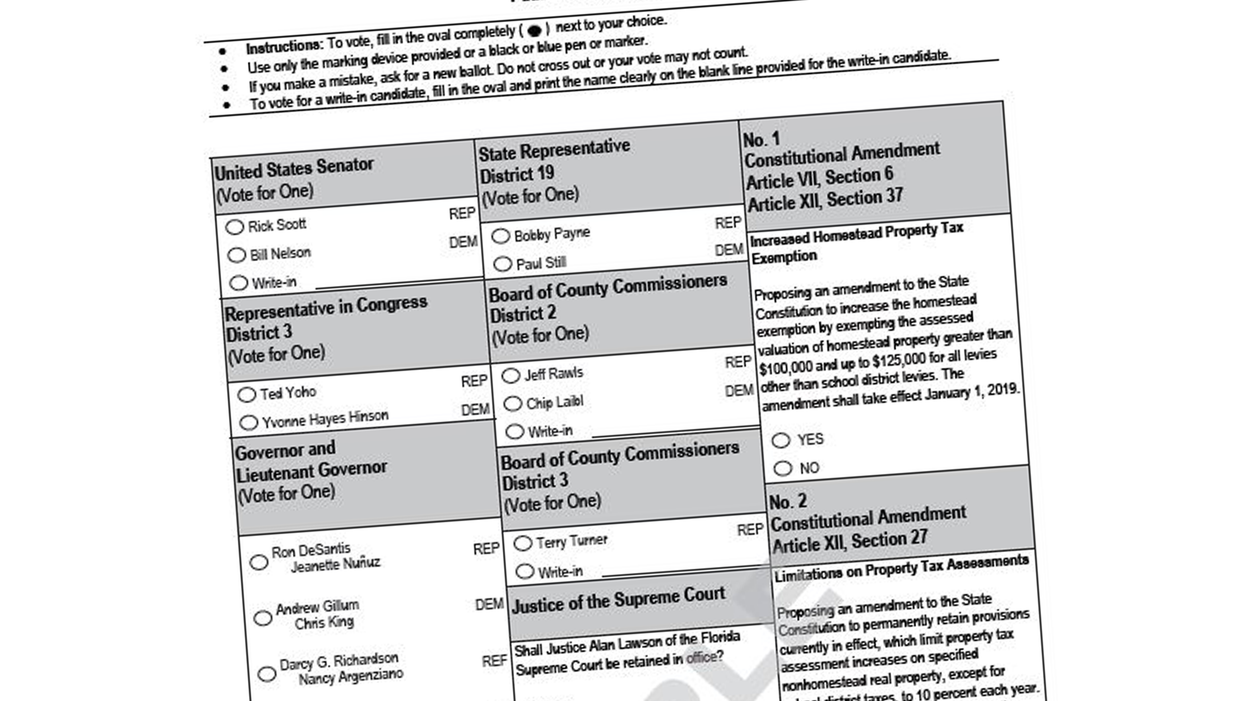
Florida has eight weeks to come up with ballots for November that abandon a central feature of the past seven decades: the candidates from the governor's political party getting listed first in every contest.
That system was held unconstitutional five months ago, a federal judge ruling it "imposes a discriminatory burden on plaintiffs' voting rights." On Friday that judge, Mark Walker of Tallahassee, said he was tired of watching the state slow-walk plans for an alternative while waiting for its appeal to play out.
Since Republicans have held the governorship since 1999, they've had the top ballot line for 10 elections in a row in the nation's most populous political battleground. Democrats think their shot at the state's 29 electoral votes will go up if the ballot design is changed by November.
That's because there's solid evidence the share of the vote for the party listed first generally gets an artificial boost of several percentage points — what political operatives have nicknamed the "primacy effect," the "windfall vote" and the "donkey vote."
"By systematically awarding a statistically significant advantage to the candidates of the party in power, Florida's ballot order scheme takes a side in partisan elections" in violation of the First and 14th Amendments, Walker wrote in November, declining to put his ruling on hold while Republican Secretary of State Laurel Lee has tried to get it reversed at the 11th Circuit Court of Appeals.
That court heard arguments in February but its proceedings have been slowed considerably because of the coronavirus pandemic, so there's no guarantee it will rule in the case any time soon. Also this winter, the Republican-majority Legislature rebuffed legislation that would have changed the system.
Walker set the June 1 deadline for a new ballot design proposal on Friday after hearing arguments by telephone. He said he needs time to review the plan in case he orders changes. The state says it needs to start printing ballots at the start of September to accommodate what's expected to be a surge in absentee requests because of the Covid-19 outbreak.
The lawsuit was one of the first filed by Democrats as part of a $10 million effort to improve voting rights in 2020 battleground states through litigation. The Republicans have promised to spend at least as much defending state laws and regulations that voting rights groups deride as aimed at suppression.
The party has since challenged ballot-primacy laws similar to Florida's in Texas, Arizona and Georgia. The latter lawsuit could be effectively decided by the ruling from the 11th Circuit, which also has jurisdiction over Georgia.
Florida has voted for the presidential winner six straight times, and the White House race will dominate the state's campaign this fall because there is no election for governor, U.S. Senate or state Senate this year and only two of the state's congressional contests are seen as even slightly competitive between the parties. The other major vote will be on a ballot referendum switching the state to an open, top-two-advance primary system.