Generative AI could save hundreds of thousands of lives, make healthcare affordable for every American, and let clinicians spend more time with their patients. But this won’t happen unless our nation embraces the opportunities this technology makes possible.
The need for swift and bold action has never been greater. With average medical costs now topping $14,000 per person, U.S. healthcare is both unaffordable and unsustainable. Employer health-insurance premiums are expected to rise 9% this year, approaching $30,000 for a family of four. Yet despite spending far more than other wealthy nations, the United States ranks last in life expectancy, maternal mortality, and childhood deaths.
Generative AI can help reverse these trends. Here are five ways this technology could make care safer, smarter and more affordable:
1. Closing Medicine’s Knowledge Gap
Every 26 seconds, a new medical study is published, more than 5,000 a day. No clinician, no matter how diligent, can keep up. Generative AI can.
By scanning and synthesizing the entire body of medical literature in seconds, it can surface the latest evidence and help clinicians make faster, more accurate decisions. Already, three in five healthcare professionals use GenAI regularly, and among medical students and residents, adoption is nearly universal.
Consider one case: a teenager’s rare autoimmune illness baffled experts at five major health centers. At the sixth, a physician entered the symptoms into a large language model. Within seconds, the system generated three possibilities. The correct, extremely rare diagnosis topped the list.
Soon, patients won’t worry when their clinicians consult generative AI for guidance. They’ll expect it.
2. Empowering Patients Everywhere
American medicine is built on a 20th-century model that assumes the best place for care is a doctor’s office or hospital. That worked when most illnesses were short-term and acute. But today, 60% of Americans live with at least one chronic disease such as diabetes, hypertension, heart failure — and 42% have two or more.
These lifelong conditions can’t be effectively managed through brief office visits every few months, as is the current standard.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that better control of chronic diseases could cut heart attacks, strokes, cancers, and kidney failures by up to 50%, saving $1.5 trillion each year. Generative AI offers a way to get there.
When connected to wearable devices, GenAI would analyze blood pressure, glucose, and oxygen levels in real time, alerting patients and clinicians to early signs of trouble. For those with heart failure, it would identify fluid buildup days before an emergency, allowing for timely treatment. And as millions of Americans turn to home tests to detect infections or screen for cancer, GenAI would help interpret results, guide next step,s and potentially schedule telehealth visits when needed.
3. Preventing Medical Errors
Even when clinicians know the right steps to take, the pace and pressure of modern medicine make it hard to follow every safety protocol every time. The result is predictable and devastating: medication errors, wrong-site surgeries, and preventable hospital-acquired infections that kill an estimated 371,000 Americans each year.
Generative AI can close the deadly “knowing-doing” gap. Using multimodal capabilities — vision, speech, and text analysis — it could observe care in real time and compare clinician actions to nationally accepted safety protocols. When a critical step is missed, the system would alert the clinician before the patient is harmed.
This isn’t about replacing medical judgment. It’s about increasing patient safety and sparing clinicians the moral injury that follows a preventable tragedy.
4. Delivering Smarter, More Personalized Care
In medicine, “treating everyone the same” sounds fair, but it often produces worse outcomes for everyone. Patients who need close attention get overlooked while those recovering well are awakened in the middle of the night for unnecessary checks. Rather than discovering a patient’s status is deteriorating after a bedside monitor signals a life-threatening crisis, this technological approach would notify them hours earlier.
Using bedside data (heart rate and rhythm, blood pressure, oxygen levels), GenAI would continuously calculate the rate of change for each. The information would allow nurses to focus on those patients who need immediate help and let others rest undisturbed. The result: earlier interventions, faster recoveries, and better sleep.
The same principle applies outside the hospital. By training GenAI systems on real (and anonymized) patient-clinician conversations, families everywhere could receive accurate and personalized medical guidance whenever symptoms arise.
Worried parents would receive instant, evidence-based advice about a child’s fever. And people living with chronic illness would get personalized coaching anytime, thereby improving control and reducing complications.
5. Unlocking Medicine’s Hidden Data
American medicine is drowning in data yet starving for insight. Every bedside monitor, surgical procedure, and clinical interaction generates more information than any human could possibly retain or understand.
In a typical hospital, bedside monitors alone produce about a terabyte of data each year (that’s a one followed by 12 zeros). An estimated 97% goes unused.
It’s a vast, untapped gold mine that could accelerate discovery and improve patient care. Generative AI could investigate all that data to identify which diagnostic and treatment approaches deliver the best results.
It could also examine technical details from surgical robots and cardiology labs to determine how top-performing clinicians remove tumors or reopen arteries most effectively. In time, GenAI could even replicate their precision.
Research that once took years to conduct and interpret could soon be completed in weeks, accelerating medical progress.
For decades, America has tried to fix its broken healthcare system through small, incremental changes. It hasn’t worked. During that time, costs have tripled, clinical outcomes have stagnated, and access has eroded.
Generative AI offers a way forward. If fully embraced in clinical practice, it would help clinicians deliver safer, smarter, more affordable care for all Americans.
Robert Pearl, the author of “ChatGPT, MD,” teaches at both the Stanford University School of Medicine and the Stanford Graduate School of Business. He is a former CEO of The Permanente Medical Group.

















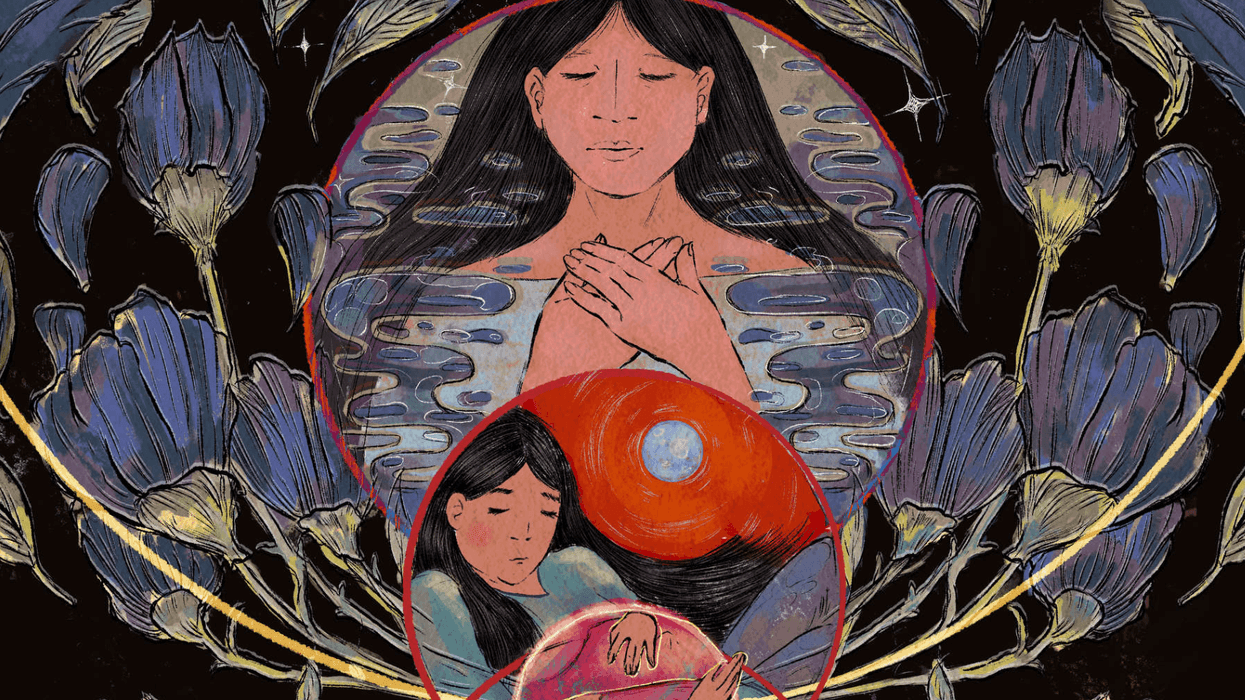
 Native American women face higher rates of death than other demographics. (Oona Zenda/KFF Health News)
Native American women face higher rates of death than other demographics. (Oona Zenda/KFF Health News)