Summary
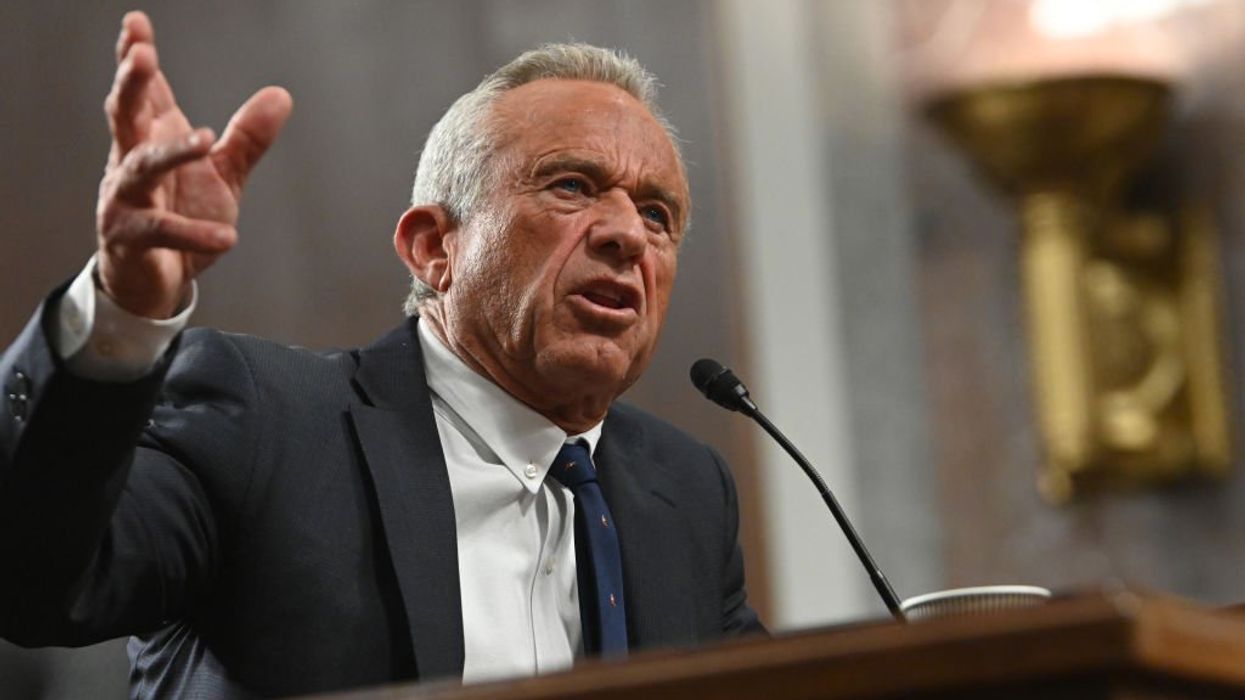
On June 9, 2025, Robert F. Kennedy Jr., the Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS), dismissed all 17 members of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). Secretary Kennedy claimed the move was necessary to eliminate “conflicts of interest” and restore public trust in vaccines, which he argued had been compromised by the influence of pharmaceutical companies. However, this decision strays from precedent and has drawn significant criticism from medical experts and public health officials across the country. Some argue that this shake-up undermines scientific independence and opens the door to politicized decision-making in vaccine policy.
Background: What Is ACIP?
The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) is a federal advisory group that helps guide national vaccine policy. Established in 1964, it has over 60 years of credibility as an evidence-based body of medical and scientific experts. ACIP makes official recommendations on vaccine schedules for both children and adults, determining which immunizations are required for school entry, covered by health insurance, and prioritized in public health programs. The committee is composed of specialists in immunology, epidemiology, pediatrics, infectious disease, and public health, all of whom are vetted for scientific rigor and ethical standards. ACIP’s guidance holds national weight, shaping both public perception of vaccines and the policies of institutions like schools, hospitals, and insurers.
Departure From the Typical Appointment Process
The standard appointment process for ACIP members is designed to ensure transparency, expertise, and independence. Members are nominated through a public call for applications and are evaluated by a CDC-appointed panel for qualifications, scientific credibility, ethical standing, and the absence of financial conflicts of interest. The process includes interviews, background checks, and a public comment period before final approval. This rigorous, multi-month process has long protected the panel from political or commercial influence and upheld its role as a science-driven authority.
In a sharp departure from this traditional process, Secretary Kennedy abruptly dismissed all 17 sitting members of ACIP and appointed eight replacements within 48 hours. There was no public call for nominations, no CDC oversight, no background vetting, and no opportunity for public comment. This bypassed the usual protocols designed to ensure balanced, evidence-based decision-making. Critics argue that this move severely undermines the committee’s credibility and violates established norms for appointing federal health advisers.
New Appointees
The new panelists include several individuals who have publicly questioned vaccine safety and efficacy. Among them is Martin Kulldorff, a biostatistician and co-author of the Great Barrington Declaration, which opposed COVID-19 lockdowns and mass vaccination. Robert Malone, who has claimed to be the original inventor of mRNA vaccine technology, has become a leading voice against COVID vaccines. Retsef Levi, an MIT professor, has criticized vaccine risk assessment methodologies, while Vicky Pebsworth has questioned the necessity of the HPV vaccine. These appointees have ties to vaccine-skeptical organizations and have frequently voiced positions that contradict scientific consensus. Their appointment has raised concerns about the objectivity and reliability of ACIP’s future recommendations.
New Panel Agenda
Since taking over, the new ACIP members have launched a series of controversial initiatives. They recommended removing thimerosal, a mercury-based preservative, from all flu vaccines, despite longstanding evidence confirming its safety. The panel also announced a review of the cumulative effects of the childhood vaccine schedule, echoing concerns often promoted by anti-vaccine activists but widely dismissed by the scientific community. Additionally, panelists have called for renewed investigations into vaccine ingredients and side effects, many of which have already undergone extensive scrutiny and review. These agenda items signal a shift away from long-established science and toward revisiting topics long considered settled.
Policy and Legal Implications
Under the new panel’s guidance, several COVID-19 vaccines are no longer recommended for children and pregnant individuals. Researchers at Harvard University expect this change to have far-reaching effects, such as slowing research that has the potential to reduce illness. Insurance companies may no longer be obligated to cover vaccines that are no longer officially recommended, creating new financial barriers to access. Public health experts warn that vaccination rates may decline, leading to resurgences of preventable diseases such as measles and bird flu. There is also an ongoing lawsuit involving multiple medical professional societies to determine whether his appointments were unlawful, specifically in terms of the Federal Advisory Committee Act (FACA), a federal law that ensures advisory committees remain balanced and free from improper influence.
Conclusion
The dismissal and replacement of ACIP’s full membership by RFK Jr. has triggered a national debate over the future of vaccine policy in the United States. Critics argue that the move undermines the scientific independence of public health decision-making and threatens to erode decades of progress in immunization coverage and disease prevention. ACIP’s next formal votes in the fall of 2025 will provide an early indication of how the new panel approaches vaccine recommendations, coverage, and distribution. Legal proceedings and the panel’s actions in the coming months will help shape public perception of this significant shift in advisory leadership.
Understanding the Debate on Health Secretary Kennedy’s Vaccine Panelists was first published on the Alliance for Civic Engagement and was republished with permission.
Vaidehi More is an undergraduate student at The Ohio State University pursuing a dual degree in Public Policy and Biology on the pre-med track.

















 Native American women face higher rates of death than other demographics. (Oona Zenda/KFF Health News)
Native American women face higher rates of death than other demographics. (Oona Zenda/KFF Health News)
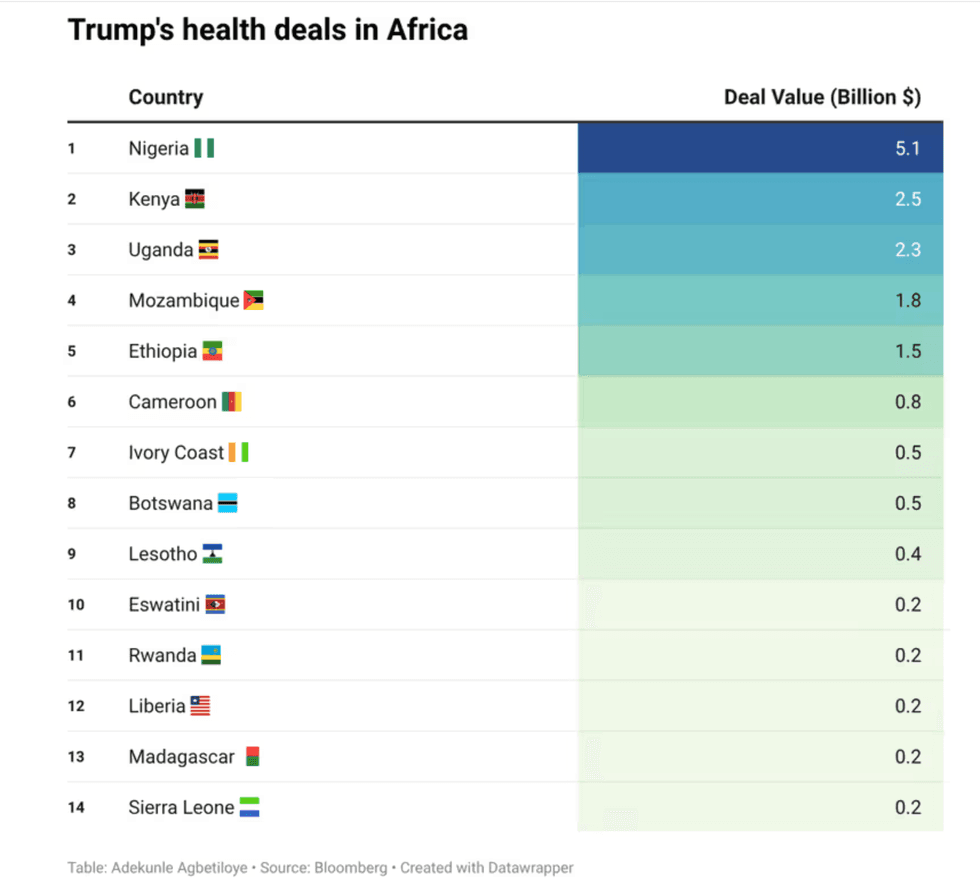
Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift