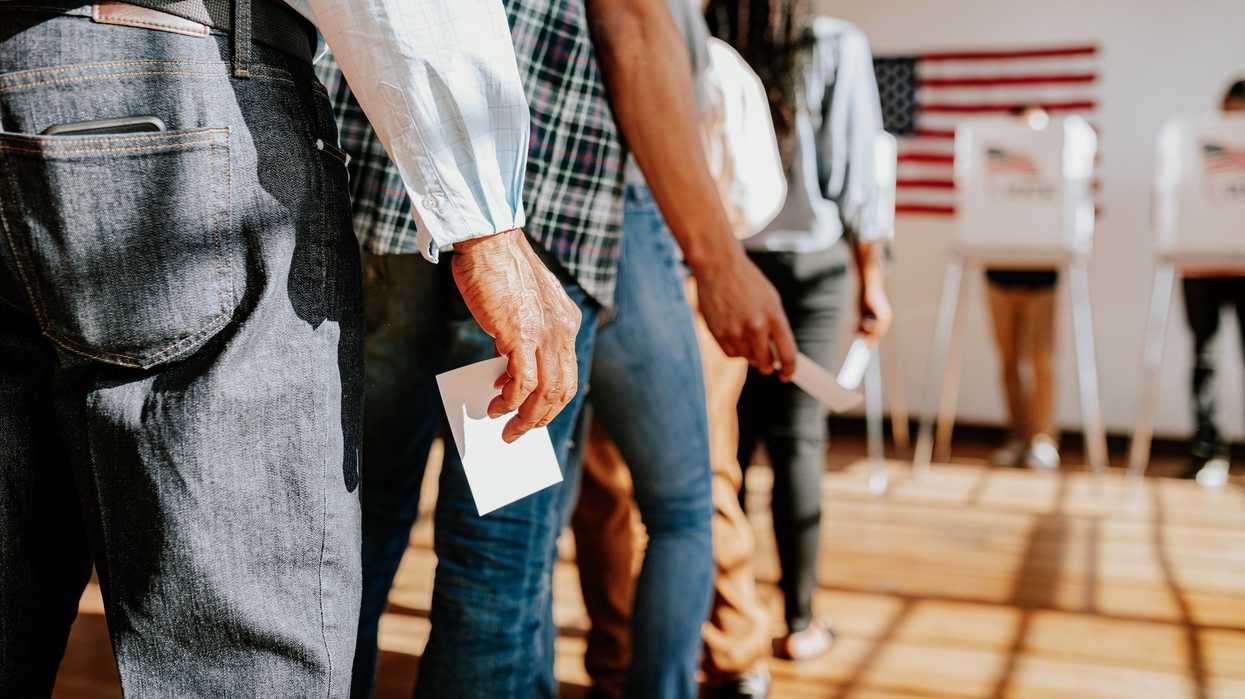
It wasn't just candidates on the ballot across the country this week — in some places, the method for casting those votes was under consideration as well.
Ranked-choice voting, the most popular alternative to traditional ballot-casting, was approved by voters in three cities on Nov. 2: Ann Arbor, Mich., Broomfield, Colo., and Westbrook, Maine. In addition, numerous cities that had previously authorized a switch to RCV used it for the first time this week.
The vote in Ann Arbor, where an overwhelming 73 percent of ballots were in favor of a switch to ranked-choice voting, is both the most significant and least consequential of the three victories. Ann Arbor, home to 124,000 people, is by far the largest of the three cities to vote on RCV. However, the new system cannot be instituted unless the Michigan Legislature grants its own approval to such a change. If state law is changed, voters in Ann Arbor will use RCV to elect the mayor and city council
"Ann Arbor voters demonstrated at about a two-to-one margin that they want RCV," said Deb Otis, senior research analyst for FairVote, a nonprofit election reform organization that specializes in ranked-choice voting. She explained that following such a strong victory, local advocates are working on a campaign, including an analysis of state law, so the city can institute a new elections system.
In Broomfield, a consolidated city and county of 70,000 people, the vote was far closer, as RCV passed with 52 percent of the vote. Ranked elections will be used to select the mayor and council members beginning with the 2023 balloting.
And in Westbrook (population 19,000), 63 percent of voters cast ballots in favor of using RCV to elect the mayor, city councilors and school committee members, joining Portland as the second Maine city to institute RCV for municipal elections. Ranked-choice voting is already used for all state and federal elections in Maine. In addition, Westbrook will use proportional representation for positions with multiple officeholders.
Voters in two other cities — Austin, Texas, and Burlington, Vt. — approved RCV measures earlier this year.
In a ranked-choice (or instant runoff) election, voters rank their preferred candidates in order. If no candidate receives a majority of the vote, then the person with the fewest votes is eliminated and their supporters' votes are distributed to the second option. This process continues until a candidate has a majority of the vote.
"Adopting ranked-choice voting in more towns, cities and states across the country will go a long way toward reducing the polarization that plagues our politics, and it's a way to end the two-party duopoly at the ballot box," said Josh Silver, CEO of RepresentUs, which also works across party lines to reform the political system. "RCV gives voters more choices, it ensures that the majority of voters approve of the eventual election winner, and it saves money."
According to Otis, 32 cities across seven states used ranked-choice voting this year, 22 of them for the first time. Local advocates, including Stan Lockhart of Utah RCV and Karl Landskroener of FairVote Minnesota, claimed their research shows ranked-choice voting is growing in popularity in their regions. Twenty Utah municipalities, including Salt Lake City, used RCV this year, joining five Minnesota cities: Minneapolis, St. Paul, St. Louis Park, Minnetonka and Bloomington.
"We're seeing midterm-level turnout for local races," said Landskroener, who also said RCV is having an impact on representation. He noted that for the first time, people of color will hold a majority of seats on the Minneapolis city council. In New York City, which debuted RCV primaries this year, a majority of the city council will be women for the first time following this year's elections.
Earlier this year, Virginia Republicans used RCV for the first time to select their candidates for the state's top three offices. Their nominees — Glenn Youngkin, Winsome Sears, and Jason Miyares — swept the elections for governor, lieutenant governor and attorney general.
"The big winners in Virginia and New York City were boosted after being nominated by ranked-choice voting, while voters keep saying how much they like it, whether in blue, red, or swing parts of the country," said FairVote CEO Rob Richie.


















 Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation ranking member Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-WA) (R) questions witnesses during a hearing in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill on February 10, 2026 in Washington, DC. The hearing explored the proposed $3.5 billion acquisition of Tegna Inc. by Nexstar Media Group, which would create the largest regional TV station operator in the United States. (Photo by Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images)
Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation ranking member Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-WA) (R) questions witnesses during a hearing in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill on February 10, 2026 in Washington, DC. The hearing explored the proposed $3.5 billion acquisition of Tegna Inc. by Nexstar Media Group, which would create the largest regional TV station operator in the United States. (Photo by Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images)
