Nicole Norman is a graduate student at Medill in the Politics, Policy & Foreign Affairs specialization. She covers the politics beat for Medill News Service. Norman received a B.S. in Journalism from Loyola Marymount University in the spring of 2023 and has interned at news organizations such as NBC and CNN
Juliann Ventura is a graduate student at Northwestern University’s Medill School of Journalism and a reporter at Medill News Service, where she covers social justice.
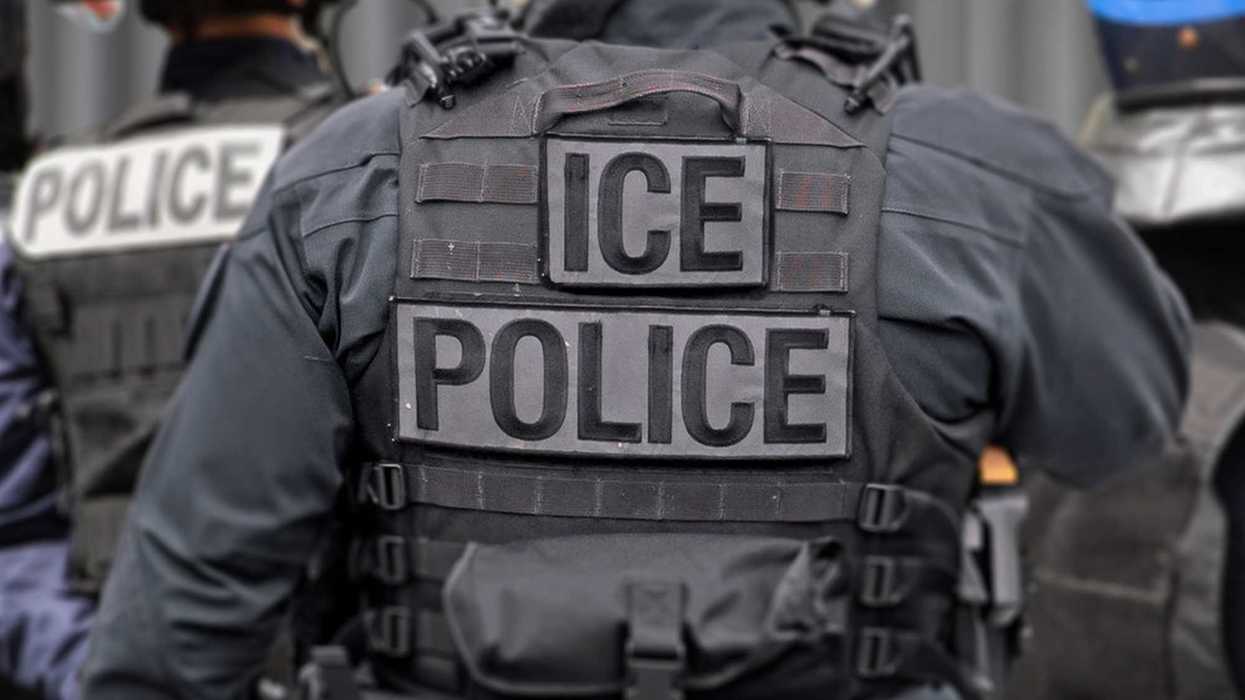
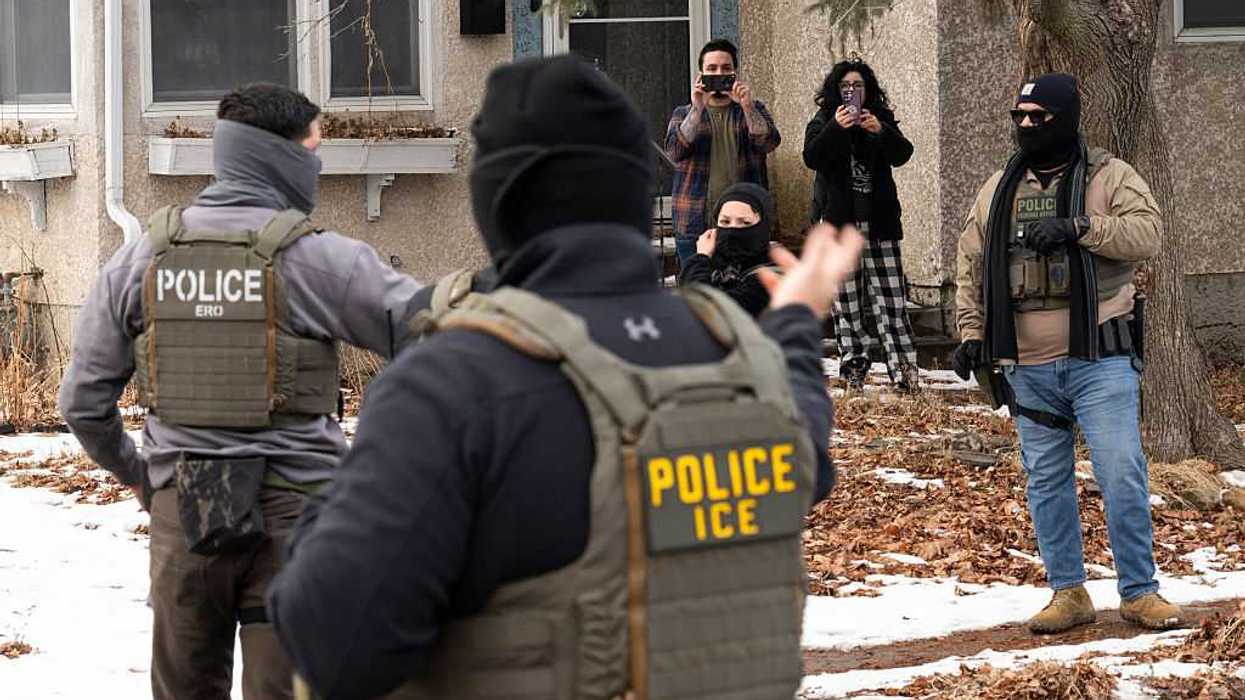
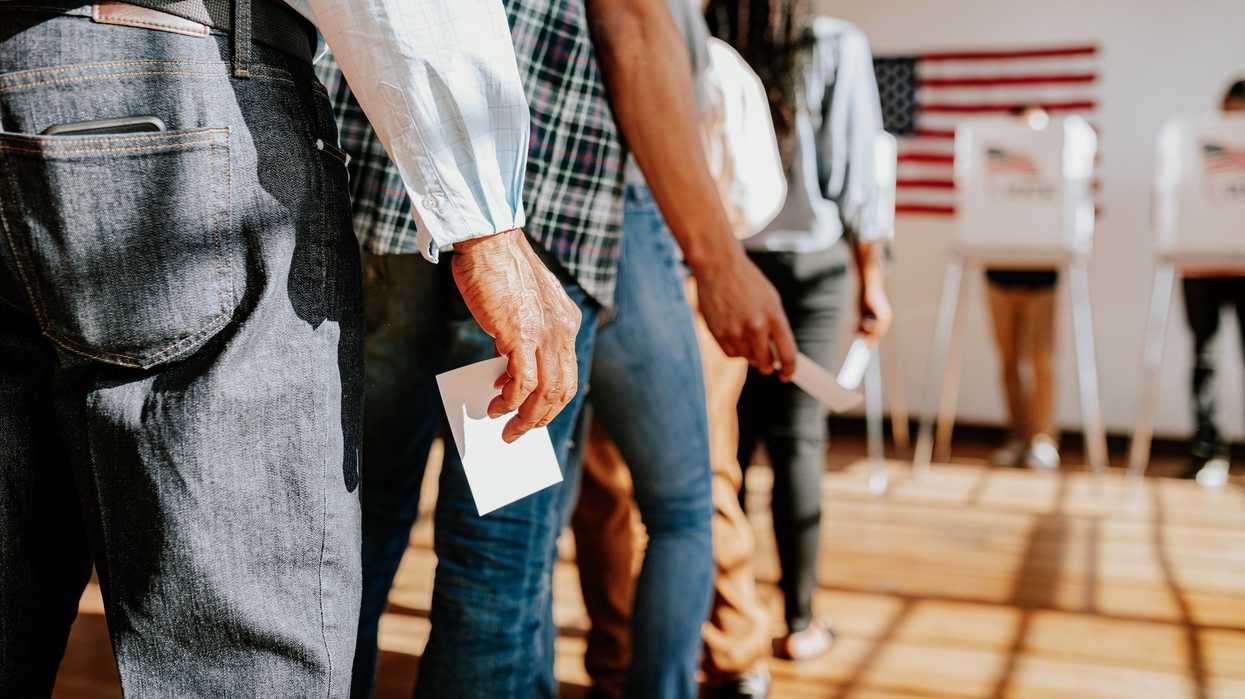
Voters in Virginia will have a chance to elect new lawmakers to all 140 seats in the General Assembly when they head to the polls today, potentially shifting control of the state legislature.
Virginia will vote under new district maps for the first time since redistricting reform was approved in December 2021. These new districts, which many experts say more fairly represent the population, have created new competitive districts that have the potential to affect the political power in the commonwealth.
Virginia’s state legislature is currently split, with Democrats holding the majority in the Senate and Republicans holding the governorship and the majority in the state’s House of Delegates. Republicans will be looking to flip the Democrat-controlled state Senate. If this happensit would be likely that conservative policies will be passed on issues like abortion and K-12 education. Conversely, if Democrats win more seats, Republicans will have a more difficult time passing conservative policies.
Voters approved the Redistricting Commission Amendment in 2020, which gave powers to a group of Virginia legislators and citizens, allowing them to draw the congressional and legislative districts.
Prior to the amendment, state legislators heavily gerrymandered the state in a manner that heavily favored incumbents of both parties and did not accurately reflect the state’s racial and political demographics.
“For our organization, we wanted communities to decide who their leaders are. Not the other way around,” said Brian Cannon, former executive director of OneVirginia2021, an organization that led Virginia’s bipartisan redistricting reform.
The Virginia Supreme Court appointed the two mapmakers, Sean Trende and Bernard Grofman, after the newly created redistricting commission failed to submit the maps by the deadline. The Republican mapmaker, Sean Trende, is a senior elections analyst for RealClearPolitics, a political news company. The Democratic nominee, Bernard Grofman, Ph.D., is a political scientist at the University of California at Irvine. The maps were then unanimously approved by the State Supreme Court
Today, experts are mostly pleased with the new map. Dr. Sam Wang, founding director of the Electoral Innovation Lab at Princeton University, said that whichever political party receives more votes should end up with more seats in the legislature because there is no partisan lean on the map.
“In this case, the work of these two special masters, Grofman and Trende, created almost level playing fields for both Democrats and Republicans,” said Wang.
The Electoral Innovation Lab gave both legislative maps passing grades, judging based on partisan fairness, competitiveness, and geographic features. However, most seats will not be competitive.
“There are places in Virginia that are just 80% Republican or 80% Democrat and they should be that,” said Cannon. “It would be a gerrymander to artificially draw them to be some sort of fifty-fifty competition.”
However, experts have identified five Senate races and ten House of Delegates races that will be highly competitive. Experts hope that this will lead to a body of legislators that accurately represent Virginia.
“What you're going to see next week is probably– and I’m not even sure ‘probably’– almost guaranteed, will be the most diverse General Assembly ever elected in Virginia,” Cannon said. “And it will be elected for the first time under these new maps.”

















 Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation ranking member Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-WA) (R) questions witnesses during a hearing in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill on February 10, 2026 in Washington, DC. The hearing explored the proposed $3.5 billion acquisition of Tegna Inc. by Nexstar Media Group, which would create the largest regional TV station operator in the United States. (Photo by Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images)
Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation ranking member Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-WA) (R) questions witnesses during a hearing in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill on February 10, 2026 in Washington, DC. The hearing explored the proposed $3.5 billion acquisition of Tegna Inc. by Nexstar Media Group, which would create the largest regional TV station operator in the United States. (Photo by Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images)
