Goldstone’s most recent book is "On Account of Race: The Supreme Court, White Supremacy, and the Ravaging of African American Voting Rights.
Recently, the Wall Street Journal, never shy about twisting language to maintain a status quo that serves its core audience at the expense of less wealthy or powerful Americans, ran an editorial taking new Supreme Court Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson to task. Her offense? Jackson had the temerity to object to the notion that the 14th Amendment, which guarantees “equal protection of the laws,” could not be used to protect Black citizens from unequal treatment because it would cause unequal treatment to white people.
The amendment, she noted, was not “colorblind,” but rather was created specifically to protect freed slaves, from whom most Black Americans descend. “The framers themselves adopted the equal protection clause, the 14th Amendment, the 15th Amendment, in a race-conscious way,” she said. Jackson further irritated the Journal by asserting that hers was the “originalist” interpretation of the amendment.
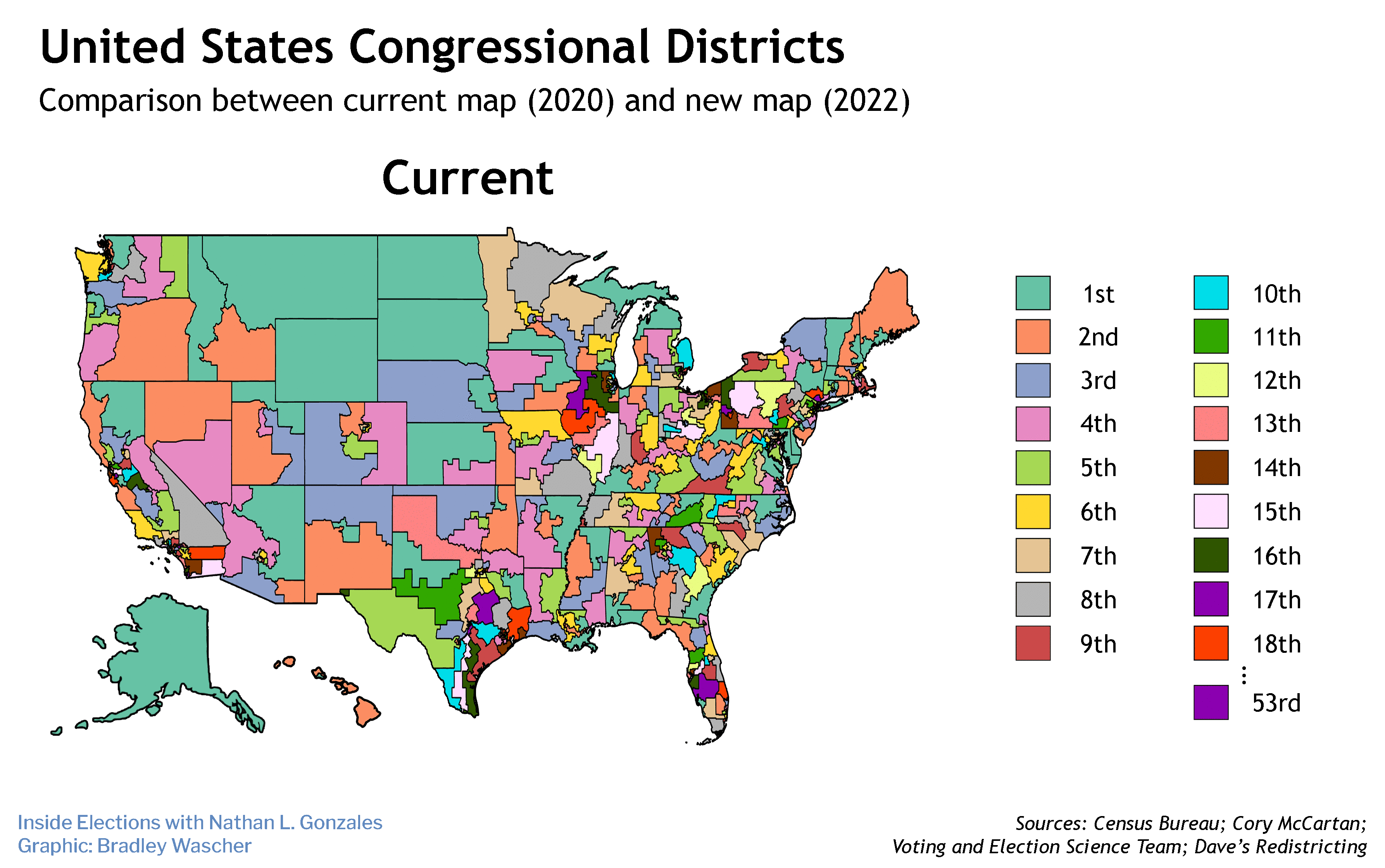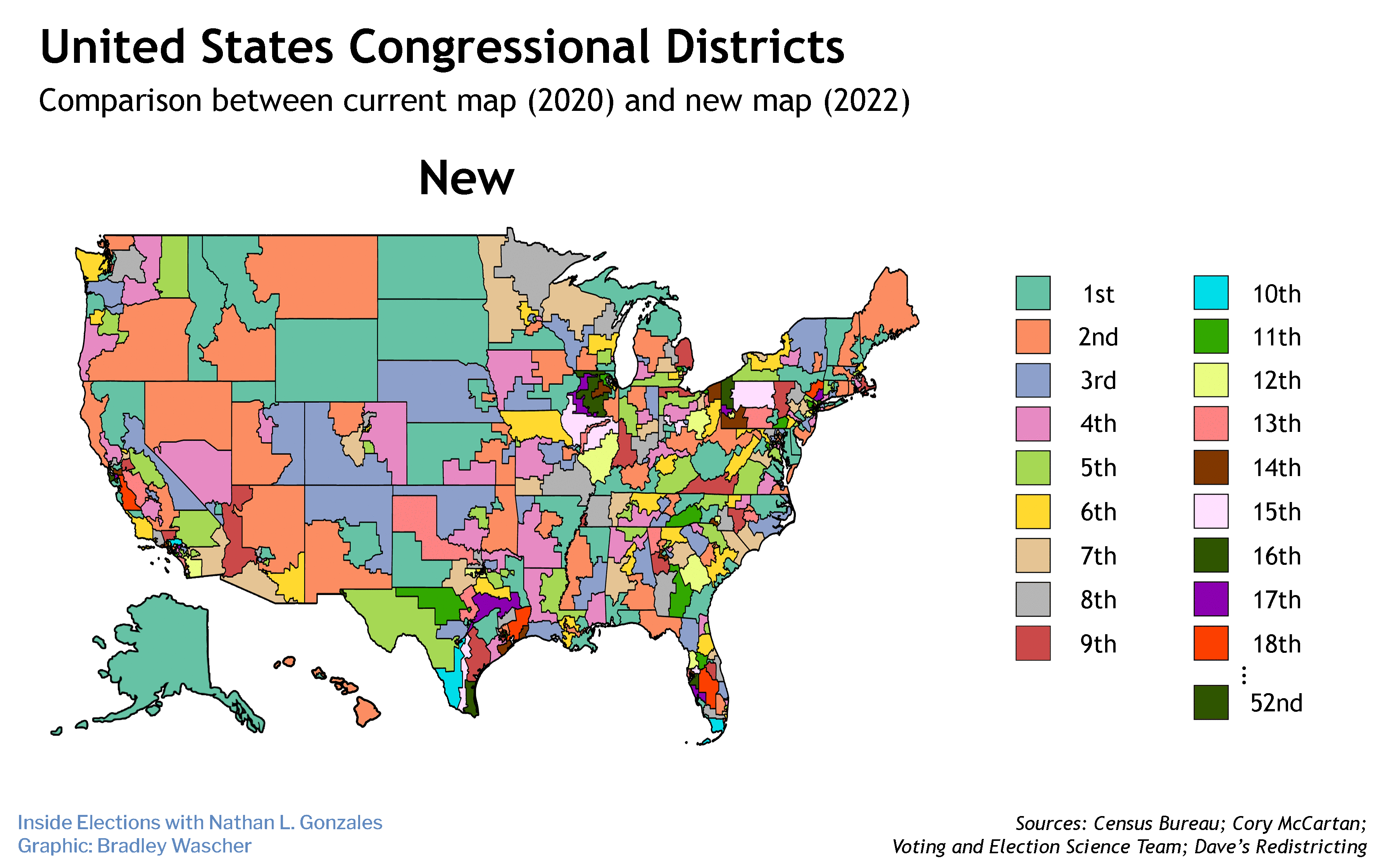
The case in question was Merrill v. Milligan, an equal rights challenge to Alabama’s 2021 congressional map that shoehorned Black voters into a single district, leaving six to be dominated by white voters – this in a state where more than one quarter of the population is African American. In January, the three judges on a District Court panel, two of whom were Donald Trump appointees, had ruled unanimously that Alabama’s plan violated Section 2 of the 1965 Voting Rights Act and ordered the state to draw a new map. In February, however, the Supreme Court (in a 5-4 decision) stayed the ruling until it could hear the case itself. This allowed Alabama to conduct primaries using the disputed district map. The court only took the case up in October, long after it could have any practical impact on the November midterms.
Sign up for The Fulcrum newsletter
That during arguments the conservative justices pretended the redrawn districts were simply “politically” based, rather than racially discriminatory, was not at all a surprise. Since Oliver Wendell Holmes helped usher in Jim Crow with his 1903 opinion in Giles v. Harris, the justices have hidden behind separation of powers to avoid inserting themselves into the political process — except, of course, when it served their interests, as in Citizens United. As a result, by making Alabama’s redistricting political, the court will be able to invoke the 14th Amendment’s equal protection clause to avoid forcing Alabama to add a second Black-majority seat.
But Jackson was not about to let her conservative colleagues get away with it this time. To her, that Alabama’s plan was racially motivated was both obvious and indisputable and pretending otherwise was absurd.
This was too much for the Journal. The editorial writers claimed Jackson’s “aim was to refute the idea that the equal protection clause would be impinged if the Supreme Court requires Alabama to gerrymander by race to give the state a second majority-black House seat.” They conveniently chose to omit the fact that the Republican majority in the Alabama Legislature had already gerrymandered the district to prevent a second Black-majority district.
Incredibly, to buttress its argument, the Journal cited Justice John Marshall Harlan’s famous 1896 dissent in Plessy v. Ferguson. In that case, eight of the nine justices ignored 14th Amendment guarantees and upheld a blatantly racist Louisiana law forcing Black American citizens to ride in smoky, dirty, substandard railroad cars on the grounds that separate facilities were constitutionally acceptable as long as they were “equal.” Harlan was the only dissenter as he had been in another racially charged decision in the Civil Rights Cases 11 years before.
“Our Constitution is color-blind, and neither knows nor tolerates classes among citizens,” Harlan wrote in Plessy. “All citizens are equal before the law. The humblest is the peer of the most powerful. The law regards man as man, and takes no account of his surroundings or of his color when his civil rights as guaranteed by the supreme law of the land are involved.” The Journal acknowledged Harlan’s failure to convince his colleagues but declared “the principle is sound.” They added, “It doesn’t take a Harvard Juris Doctor to understand the phrase ‘equal protection of the laws,’ and to know that treating citizens differently based on race is the opposite.”
By this absurd rationale, no civil rights law would be permissible because all of them demand that, to redress discrimination, some citizens must be treated differently based on race. If the Journal wanted a more apt example to use as a parallel, it should have looked to Justice Stephen Field’s 1879 opinion in Ho Ah Kow v Nunan, where he wrote:
“When we take our seats on the bench we are not struck with blindness and forbidden to know as judges what we see as men; and where an ordinance, though general in its terms, only operates upon a special race, sect or class, it being universally understood that it is to be enforced only against that race, sect or class, we may justly conclude that it was the intention of the body adopting it that it should only have such operation, and treat it accordingly.”
Field was no liberal. He was a fierce defender of property rights and famously cantankerous, suspicious, vengeful, stubborn and convinced of his own rectitude. (He sometimes carried a gun in his judicial robes and most of his fellows assumed he would be happy to use it.) He had also gone on record many times with bigoted statements about Chinese immigrants.
But here, Field got it right. The point of the 14th Amendment was not to mandate faux equality, where those in power could profess that they were the ones being discriminated against, but rather to create a more fair and more just America. To postulate the reverse, as did the Journal and the conservative justices, is not so much colorblindness as willful blindness.
For the United States to approach the ideals we ascribe to those who drafted and ratified the United States Constitution, parsing language must not be allowed to overwhelm ideals. Without those ideals, democracy, already an extraordinarily difficult system to maintain, cannot survive.