Griffiths is the editor of Independent Voter News, where a version of this story first appeared.
A whopping four out of five independents say the coronavirus pandemic has made partisanship in politics even clearer — and more critical to combat.
That's the top takeaway from the second nationwide poll conducted by Independent Voting, one of the main advocacy groups seeking to galvanize the two-fifths of Americans who don't identify with either major party and view their duopoly as one of democracy's major ills.
Pollsters for "Confronting A New Reality: Independents Speak Out" interviewed more than 3,600 independent voters over more than 100 days on the hot button issues of this campaign year, from the government's handling of Covid-19 to police reform to what being independent means to them.
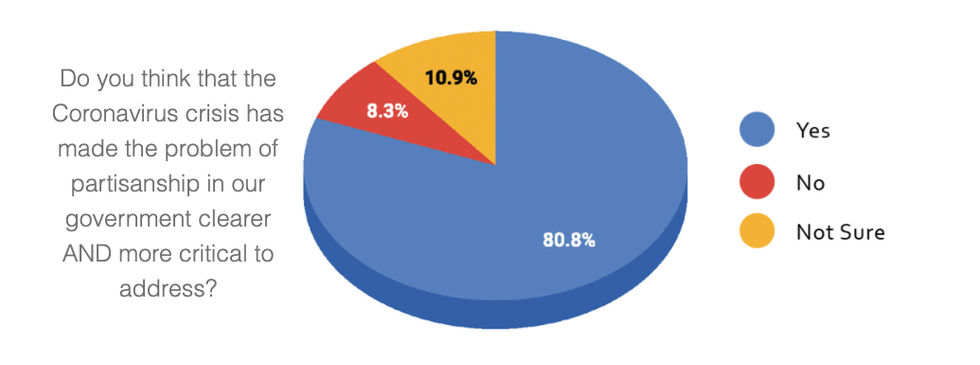
The most lopsided finding was the 81 percent who said they believed the public health emergency has only made the problem of partisanship more critical to address.
 Source: Independent Voting
Source: Independent Voting
Three-fourths of those surveyed said mistakes were made by both Republican and Democratic elected officials in handling the pandemic. And 63 percent said the main problem with partisanship remains the resulting policy paralysis, which prevents the country's needs from being addressed.
A majority also agreed a root problem is the partisanship and divisiveness that dominates the electoral process — with 62 percent complaining that a main problem with this year's election landscape was that independents in many states were locked out of the primary process.
A third of those surveyed said they sometimes register with one of the major parties just so they can vote in the primaries — and that's a condition to voting most would like to see changed.
This data is important because it punctures the narrative that independent voters are a myth. Ultimately, they will choose a Republican or a Democrat, this theory goes, and so there is little point focusing on how four in 10 Americans refuse to identify with a political party.
Independents, though, make clear in the poll that they want change. They want an equal and meaningful voice in the process. They want a competitive and fair system. And, the more frustrated these voters get with the status quo, the more active they become in seeing a transformation in the American political process.
"Independent voters are optimistic that if we open up the electoral system and make it more democratic for everyone, we will start to see less partisanship and more cooperation for the good of everyone," wrote Tiani Coleman and Randy Miller, who supervised the survey.
Their polling also found 61 percent of independent voters want to explore the idea of a nonpartisan nominating process for the next presidential election, while 80 percent believe leaders of election and political reform groups should join forces and collaborate.
"If our country is to free itself from the clutches of partisanship, independents will have to lead the way." said the organization's president, Jackie Salit.