A growing chorus of congressional Democrats are saying that enacting a new Voting Rights Act is the best way for Congress to honor John Lewis, the civil rights icon and veteran Atlanta congressman who died last week.
The Republicans running the Senate have signaled no interest in debating the bill, designed to revive the racial discrimination protections enshrined in the original 1965 landmark law. The Democratic House passed the measure in December, with Lewis wielding the gavel during the vote.
Many of his colleagues now say the measure should be dubbed the John R. Lewis Voting Rights Act. There's talk of pushing it through the House a second time this summer, perhaps with election assistance aid to the states tacked on.
The legislation is a response to the Supreme Court's 2013 decision invalidating a central provision of the law, which then required places with histories of discrimination to get Justice Department permission for any changes to election laws or processes. Nine states and parts of five others were subject to such "preclearance" at the time, but the court said the formula for deciding which jurisdictions made the list was unconstitutionally outdated.
Since that ruling, in Shelby County v. Holder, almost every one of those places has tightened voting rules.
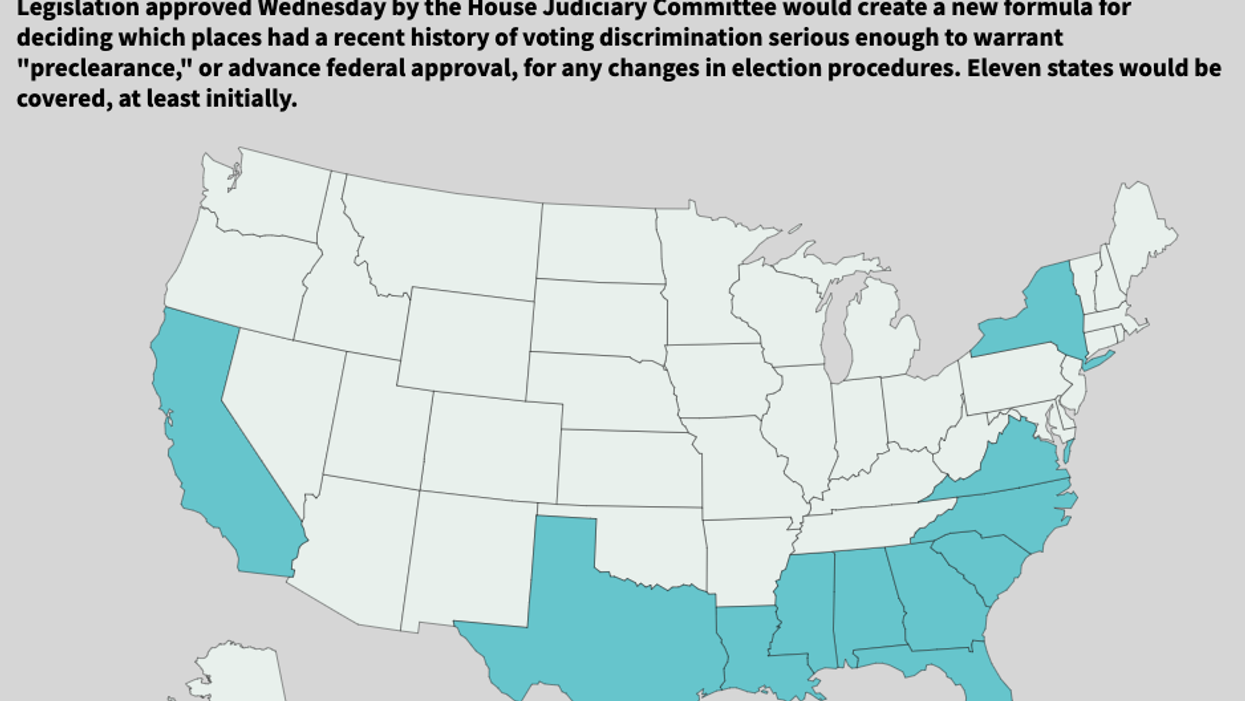
Under the updated formula now stuck in Congress, the four most populous states would be subject to preclearance along with seven others, according to analysts at the Institute for Southern Studies, a progressive policy group:
- Alabama
- California
- Florida
- Georgia
- Louisiana
- Mississippi
- New York
- North Carolina
- South Carolina
- Texas
- Virginia



















Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift