Rozado is an associate professor of computer science at Te Pūkenga - The New Zealand Institute of Skills and Technology. He is also a faculty fellow at Heterodox Academy's Center for Academic Pluralism. McIntosh is the author of “Developmental Politics” (Paragon House 2020) and coauthor of “Conscious Leadership” (Penguin 2020). He is cofounder and lead philosopher at the Institute for Cultural Evolution.
Amid countless reports of how social media is exacerbating political polarization, many commentators worry that artificial intelligence will come to have a similarly corrosive effect on American culture. In response to these concerns, an innovative new tool has been developed to leverage AI technology to reduce polarization: Meet DepolarizingGPT, a political chatbot designed to tackle polarization head on.
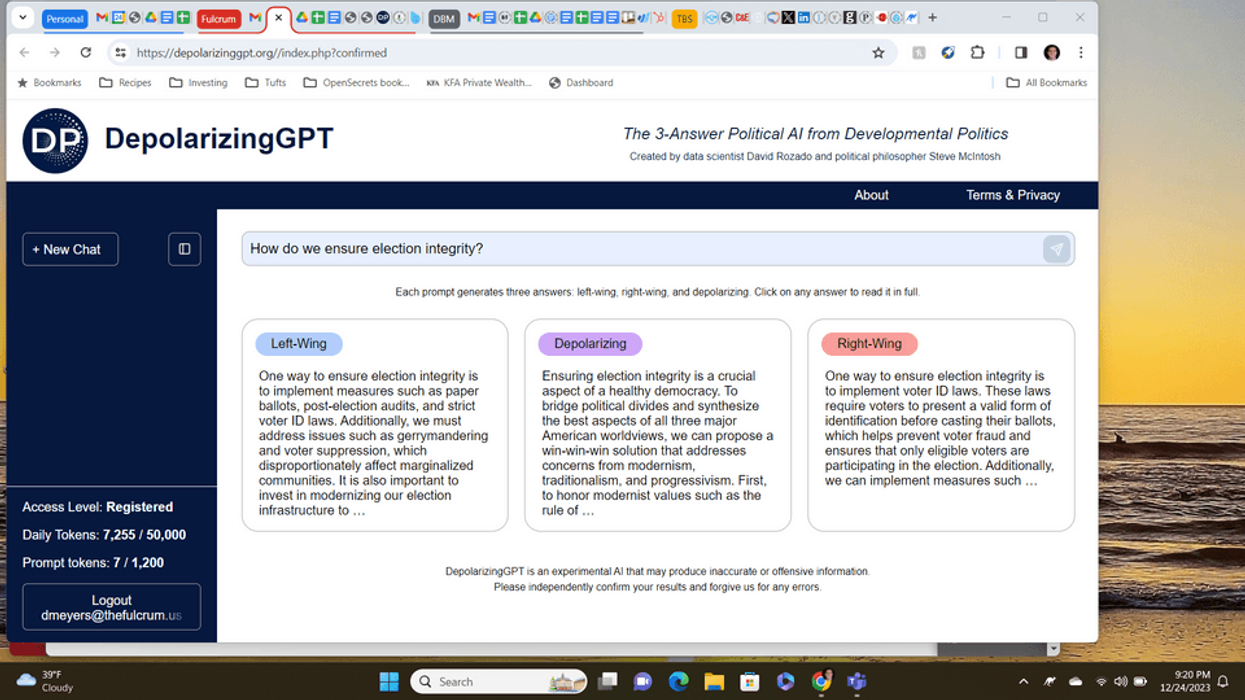
Unlike other AI models, DepolarizingGPT is focused specifically on political issues. It provides three responses to every prompt: one from a left-wing perspective, one from a right-wing perspective and a third response from a depolarizing or “integrating” viewpoint. We created this three-answer model to ameliorate political and cultural polarization by demonstrating a developmental approach to politics, one that synthesizes responsible perspectives from across the political spectrum.
The idea is to combine three models — LeftwingGPT, RightwingGPT and DepolarizingGPT — into one single system. Users are exposed to three perspectives simultaneously, moving beyond the echo chambers that often reinforce entrenched biases. Existing AIs, such as OpenAI's ChatGPT, claim to be unbiased, but this claim has been shown to be false. So rather than denying its bias, which always exists, DepolarizingGPT's three-answer model offers responsible perspectives from left, right and integrated positions. The goal is to foster a more diverse, nuanced understanding of differing political views, and to reduce the tendency to vilify the other side.
DepolarizingGPT's left-wing responses have been fine-tuned (within the fair-use provisions of copyright law) by using content from left-leaning publications such as The Atlantic, The New Yorker and The New Republic, and from numerous left-wing writers such as Bill McKibben and Joseph Stiglitz. The model's right-wing responses have been fine-tuned with content from publications such as National Review, The American Conservative and City Journal, as well as from numerous right-leaning writers such as Roger Scruton and Thomas Sowell. And the model's depolarizing responses have been fine-tuned with content from the inclusive political philosophy of the Institute for Cultural Evolution.
The model's depolarizing answers attempt to transcend centrism and avoid simply splitting the difference between left and right. When at their best, these depolarizing responses demonstrate a kind of "higher ground" that goes beyond the familiar left-right political spectrum. Admittedly, however, some of the model's depolarizing responses inevitably fall short of this goal.
This project stems from David Rozado’s academic research, which revealed the inherent left-wing political bias of ChatGPT. To address this issue, Rozado created an experimental AI model with an opposite kind of right-wing bias. His work attracted attention from The New York Times, Wired and Fox News. The intent in demonstrating the political bias of supposedly neutral AIs was to help prevent artificial intelligence from becoming just another front in the culture war.
After reading about Rozado's work, Steve McIntosh proposed that the two team up to create an AI model that could actually help reduce political polarization. Since cofounding the Institute for Cultural Evolution in 2013, McIntosh has been working to overcome hyperpolarization by showing how America can grow into a better version of itself. His institute offers a platform of "win-win-win" policy proposals, which integrate the values of all three major American worldviews: progressive, modernist and traditional. And this same method of integrating values used to build the institute's policy platform is now programmed into DepolarizingGPT's three-answer political chatbot.
Within conventional politics, people are often faced with win-lose propositions. But by focusing on the bedrock values that most people already share, it becomes possible to discover something closer to a win-win-win solution, even if such a solution does not completely satisfy all parties. This win-win-win strategy aims to accommodate the concerns of all sides, not just to get its way, but to make authentic progress through cultural evolution.
By synthesizing values from across the political spectrum, artificial intelligence promises to help American society grow out of its currently dysfunctional political condition.




















Will Trump’s moves ever awaken conservatives?