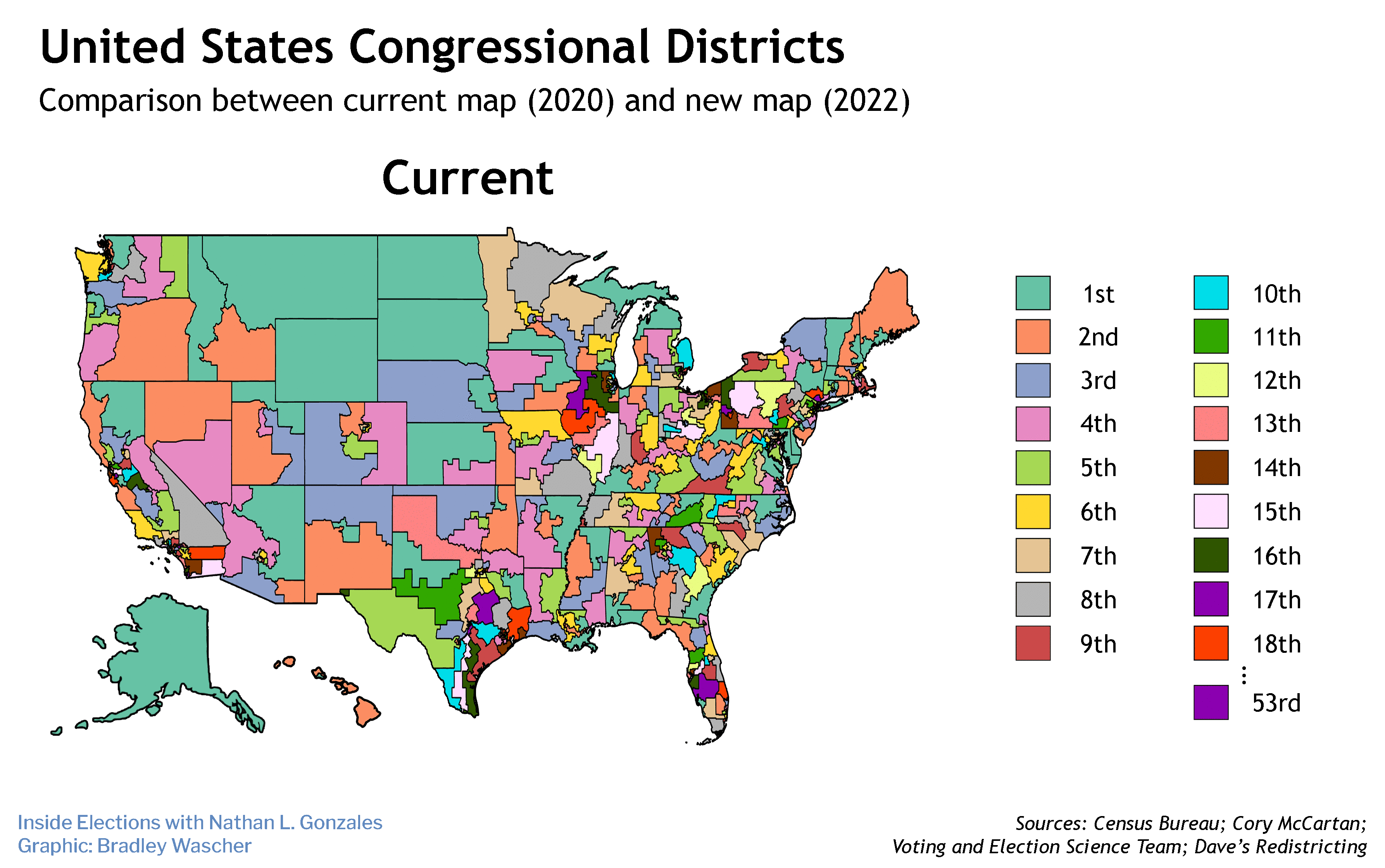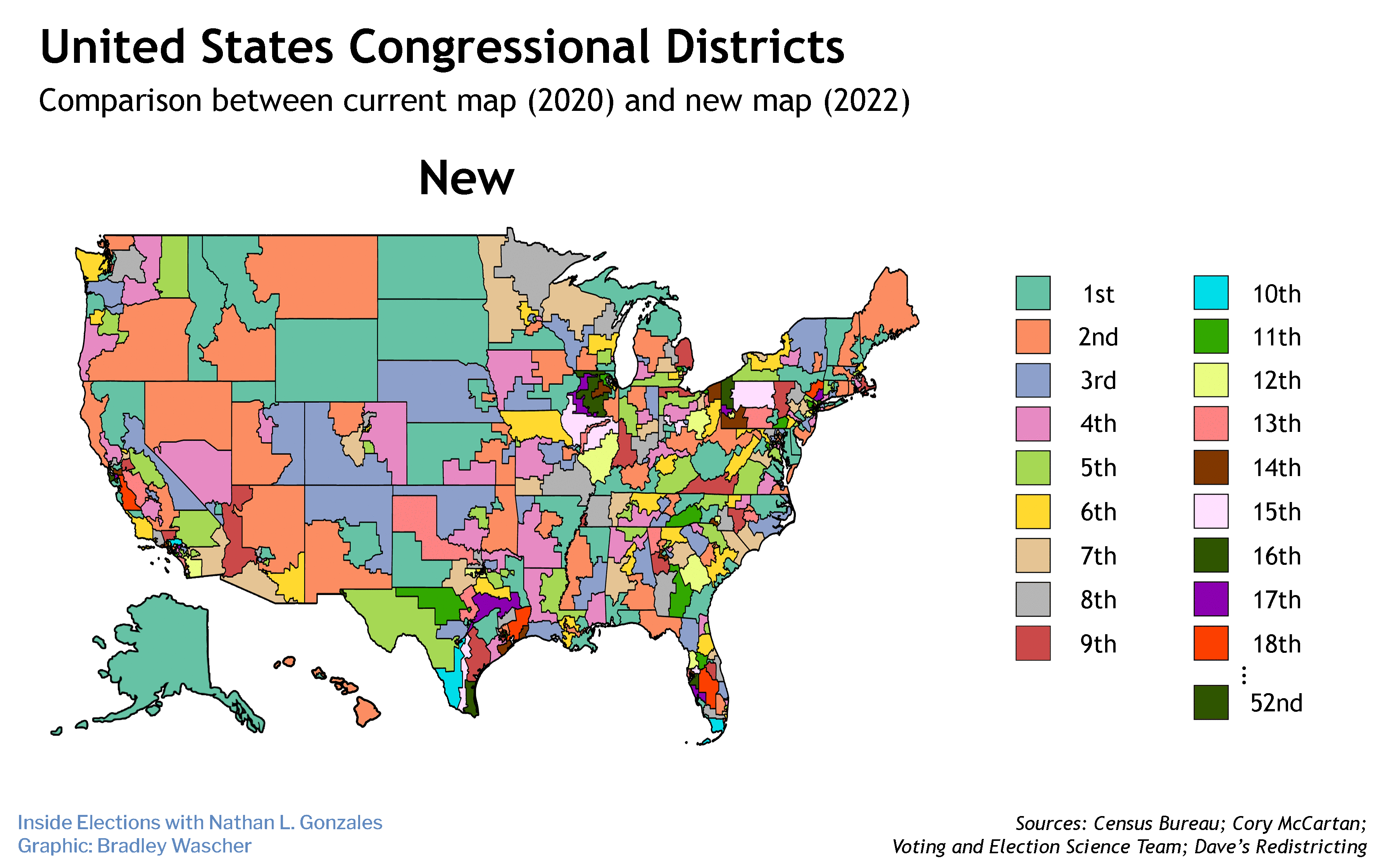
Advocates for ranked-choice voting announced Monday the freshest step in their effort to build a national movement around the form of voting that allows people to support more than one candidate.
Democratic Rep. Jamie Raskin, who represents Maryland suburbs north of Washington, said he would introduce a bill in the House this week to mandate all federal elections be conducted using ranked-choice voting.
At least in the short term, however, the legislative drive will be entirely about political messaging and raising awareness of RCV. The bill stands no chance of enactment by the currently divided Congress. And advocates of this form of voting almost always frame their cause as persuading the other 49 states, one at a time, to embrace Maine in applying this process to congressional and presidential contests.
"People will be able to vote for exactly who they want," Raskin said at a news conference with his primary co-sponsor, Democratic Rep. Don Beyer, who represents suburban Virginia just outside D.C.
The two also introduced a bill in July that included ranked-choice voting but had other reform provisions, including establishing independent commissions to draw the legislative district maps after the decennial census.
Under RCV, voters list candidates in order of preference and, if no one secures an outright majority of No. 1 votes, a sort of automatic runoff takes place. The candidate with the fewest first place votes is eliminated, those ballots are re-allocated to others based on their second place markings, and that process continues until someone has a majority.
Sign up for The Fulcrum newsletter
Raskin said this has three advantages, because it would:
- Guarantee the winners enjoy support from a majority of their constituents. Now, in races with multiple candidates, the victor may secure much less than 50 percent of the vote.
- Reduce negative campaigning, because candidates would have an incentive to try to be an acceptable second choice for voters who rank someone else as No. 1.
- Eliminate the need for in-person runoffs elections, which are costly and usually have far lower turnout than the original election.
Critics of ranked-choice voting fear the system would confuse voters and make balloting vulnerable to fraud.
Beyer said he was skeptical of the idea at first but is now a "true believer."
He described his frustration with a Congress that has less than a 20 percent approval rating and has a hollowed-out political center because of partisan politics.
Rob Richie, president of FairVote, the nonpartisan group most responsible for pushing for expanded use of ranked-choice voting, used the news conference to tout other developments going on at the state and local level across the country.
Among the highlights: New York City will vote on a ballot initiative this fall that would implement ranked-choice voting in municipal elections, and organizers in Massachusetts are attempting to collect 120,000 signatures to get a ranked-choice voting referendum on the ballot in 2020.
Democrats in several states — including Hawaii, Alaska, Kansas and Wyoming — are planning to use ranked-choice voting in their 2020 primaries, although the Democratic National Committee has yet to sign off on states' voting plans.
Plans for the presidential debut of ranked-choice voting in the crucial first-in-the-nation Iowa caucuses have been scrapped for now.