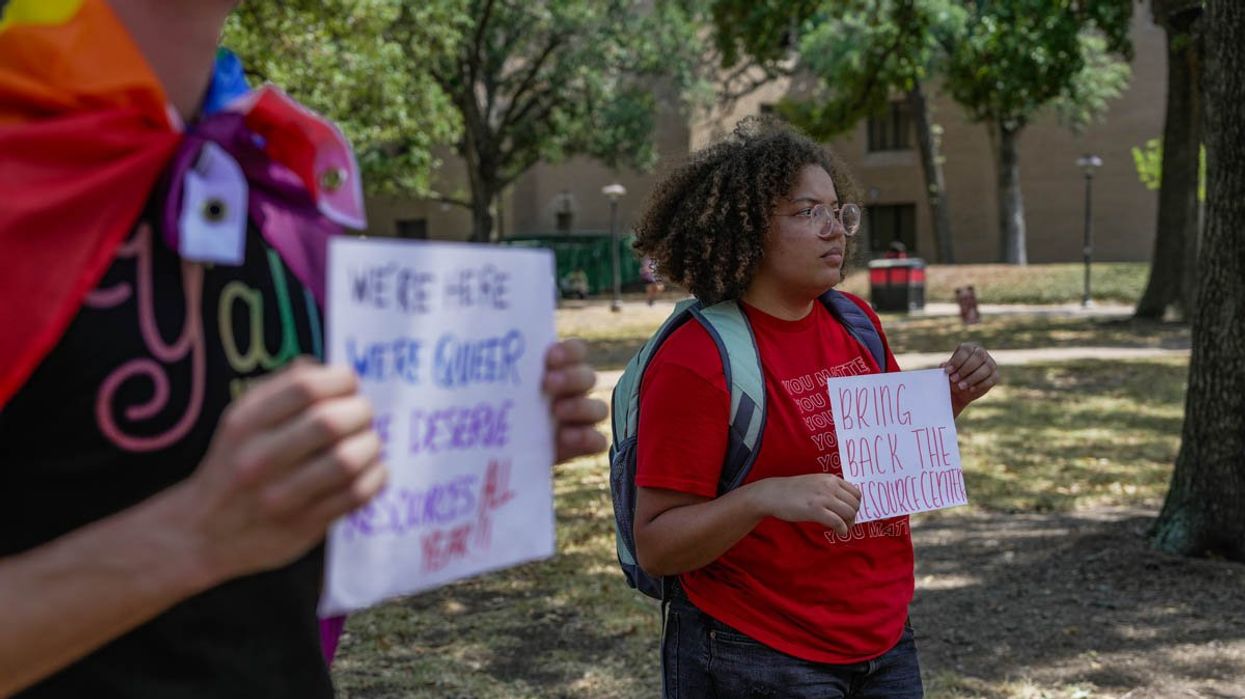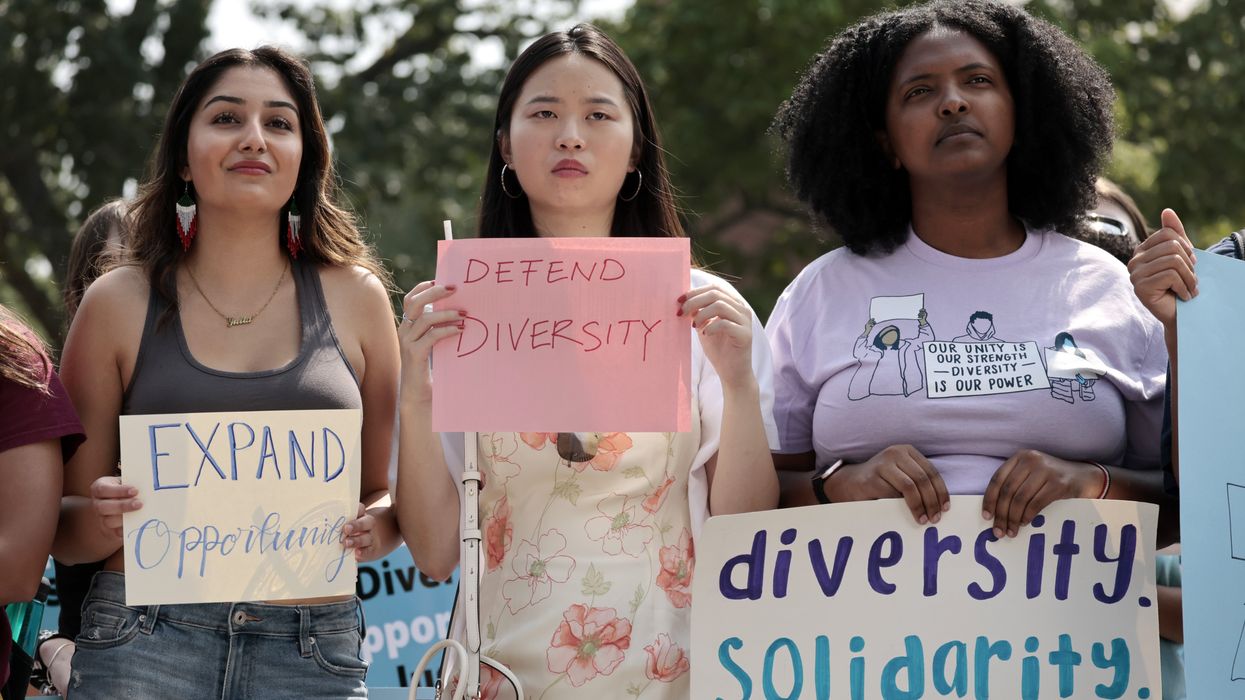Thiele Strong is a sociology professor at San José State University and a public voices fellow at the The OpEd Project.
Across the nation, campaigns to cancel, eliminate and marginalize the basic social science education that underpins diversity, equity and inclusion efforts have gained steam. Educational gag orders and DEI bans impact students from K-12 classrooms to college campuses.
Most central to the ire of those attacking are foundational sociological concepts. Sociology is the field which studies society. Sociologists analyze life chances and how we get them; how structures pattern our experiences and beliefs. Too often confused for its more celebrated sister science, psychology, sociology is the psychology of the people.
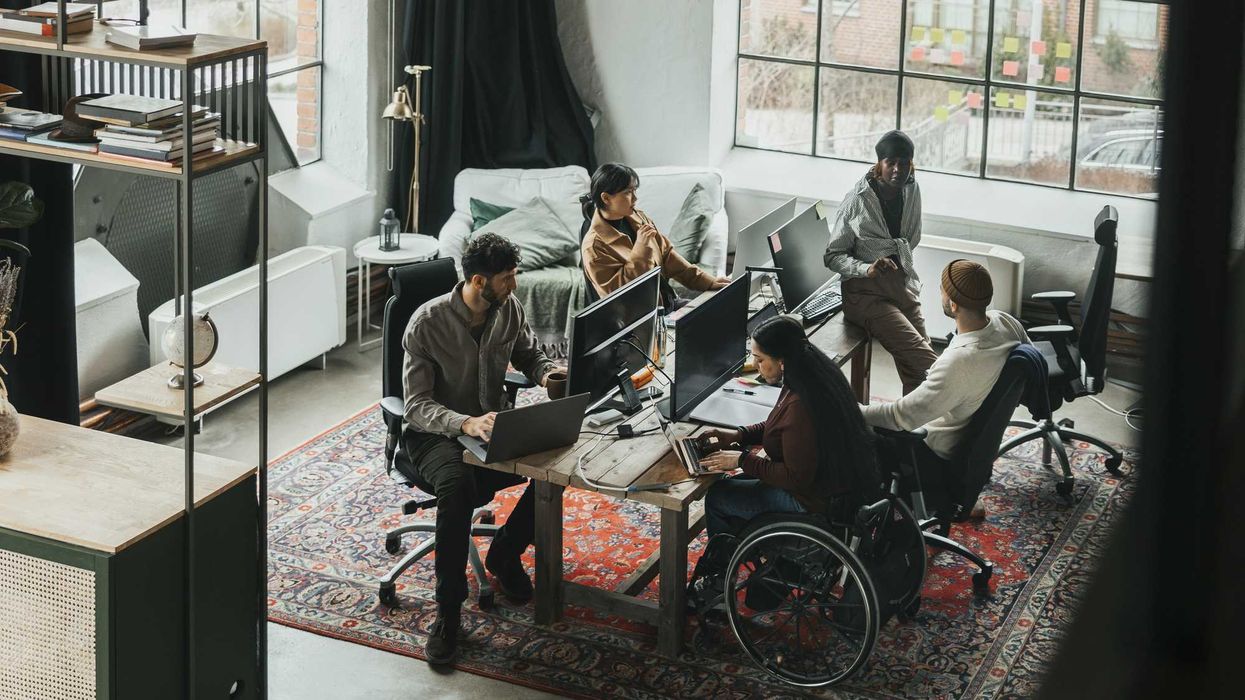
Sociologists explore how various aspects of our identity – gender, race, economic status, sexuality – show up and affect us in the world.
We discuss the “social construction zone” and how what has happened in the past affects people today. We examine power, who has which types of it — and, just as importantly, who doesn’t. As educators, we want students to learn about our social order, to reconsider and reimagine both it and their place in it.
Despite its centrality to understanding the collective human experience, sociology is marginalized in our schooling system. Sociology is not part of the core curriculum in K-12 education, and students can earn an undergraduate degree without taking a sociology class.
Becoming sociologically minded is not always easy. Quoting astrophysicist Neil DeGrasse Tyson, “In science, when human behavior enters the equation, things go nonlinear. That's why physics is easy and sociology is hard.”
As a normative sociologist, I encourage students to get curious and to use data to understand how we can learn from ourselves, what works and what doesn’t work, to build a better society for all people.
In recent years, I have felt incredulity for the ways in which the alt-right weaponizes the notion of freedom of speech. Conservative political pundits claim to be unable to speak freely, yet they have a platform to denounce social science fundamentals – and do so. Debating the theories of sociology is certainly acceptable but it is quite different from advocating the banning of sociological concepts from our schools.
As a tenured professor, I haven’t felt like I have full freedom of speech in my classroom; speaking without reservation about sociological content can feel risky. There are colleagues outside my department who dismiss sociologically driven insights. I worry a student in the class might record me, skewing content or taking what I say out of context to create a viral bit. I fear a public that does not value and will attack educated women talking honestly about our craft, which asks difficult, thorny questions with uncomfortable answers.
This negotiation to work within our current polemic political environment limits my ability to express freely. The notion of freedom of speech, and more specifically, the freedom of speech for whom, is at stake.
This hierarchy of “whose rights” is playing out across the nation and it plays out at the classroom level as well. Perversely, the ideal of freedom of speech has been commandeered by the alt-right as freedom to denounce legitimate and necessary social science knowledge. This shift has negative consequences for our youth, sociology educators, the public — all of us.
Nearly a dozen states have introduced bills directing what students can and cannot be taught about the role of enslavement in American history and ongoing racism. Florida lawmakers have proposed legislation that would prohibit classroom discussions about sexual orientation and gender identity. Labor history has long been absent from school curriculum.
At the root of the free speech debate is the fine line between speech that offends one’s sensibilities and speech that crosses the line into intolerance. Learning the reality of anti-Black racism, for example, may threaten some; however, antiracist curriculum is education, not hate speech.
In a highly polarized society, how do we keep ourselves and our school systems in contact with ideas that are enriching — and safe from ideas that are not so?
Sociology, because of the way it parses through, discerns and analyzes our collective ways, can help.
Sociology faculty, educators and students deserve to live out freedom of speech, both on- and off-campus. We need people and institutions to invest in sociology. We need parents to write letters to school boards and administrators asking for more sociology in schools. And we need a political system that will take seriously the work of those of us who study society. The ability to open our minds, perhaps to uncomfortable ideas, which could help us to envision a socially sustainable future, may indeed be vital for our collective well-being.