The Fulcrum strives to approach news stories with an open mind and skepticism, striving to present our readers with a broad spectrum of viewpoints through diligent research and critical thinking. As best we can, we remove personal bias from our reporting and seek a variety of perspectives in both our news gathering and selection of opinion pieces. However, before our readers can analyze varying viewpoints, they must have the facts.
How has Trump's first 100 days compared to previous presidents, with respect to congressional legislation?
In the first 100 days of his second term (2025), President Donald Trump signed only five bills into law, marking the lowest legislative output for a new president in over 70 years. This is a significant decline from his first term in 2017, during which he signed 28 bills within the same period.
Trump's second-term legislative record, so far, is notably sparse compared to his predecessors.
- Joe Biden (2021): Signed 11 bills into law in his first 100 days.
- Barack Obama (2009): Signed 14 bills, including the landmark American Recovery and Reinvestment Act.
- George W. Bush (2001): Signed seven bills, including tax cuts and education reforms.
- Bill Clinton (1993): Signed 24 bills, including the Family and Medical Leave Act.
How many executive orders has Trump signed to date in his second term and how does this compare to previous presidents for their first 100 days in office?
While legislative activity was limited, President Trump issued a record-breaking number of executive orders in his first 100 days of the second term, totaling 124. This surpasses the previous record held by Franklin D. Roosevelt, who issued 99 executive orders in his first 100 days, and far surpasses the number of executive orders issued in the first 100 days in both his first administration (which was 33 executive orders) and his predecessor’s term.
- Joe Biden (2021): 42
- Barack Obama (2009): 19
- George W. Bush (2001): 11
- Bill Clinton (1993): 13
The executive orders focused on various areas, including federal budget cuts, regulatory rollbacks, and immigration policies. Notably, President Trump declared multiple national emergencies to implement policies without congressional approval, a move that has raised concerns among legal scholars about the balance of powers.
How many pardons has President Trump issued so far in his second term and how does this compare to previous presidents in their first 100 days?
Trump has issued over 1,500 pardons so far in his second term, including a controversial mass pardon of individuals involved in the January 6, 2021, Capitol attack. This is an unprecedented number, compared to previous presidents in their first 100 days. None of the past five administrations (including the first Trump administration) made any pardons or commutations in their first 100 days in office. Note that this is not to say that there have not been many pardons and commutations made throughout their full administrations, just the first 100 days.
Trump's approach to pardons has been far more aggressive than his predecessors, particularly in granting clemency to political allies and controversial figures. His actions have sparked significant debate over the use of presidential pardon power.
How many legal actions have been filed against the Trump administration in the first 100 days and how does this compare to previous administrations?
As of April 23, 2025, President Donald Trump's administration has faced over 200 legal challenges during the first 100 days of his second term. This marks a significant increase when compared to previous administrations; the current number of legal challenges is also largely proportionate to the increased number of executive orders issued by Trump.
- Biden (2021): Approximately 20 lawsuits were initiated by states and organizations, focusing on environmental and public health COVID policies.
- Trump (2017): There were around 50 legal actions, notably against the travel ban and immigration enforcement measures.
- Obama (2009): There were fewer than 10 significant legal challenges, mainly concerning early executive orders and regulatory changes.
- Bush (2001): Minimal legal opposition in the initial 100 days, with most lawsuits emerging later in his term.
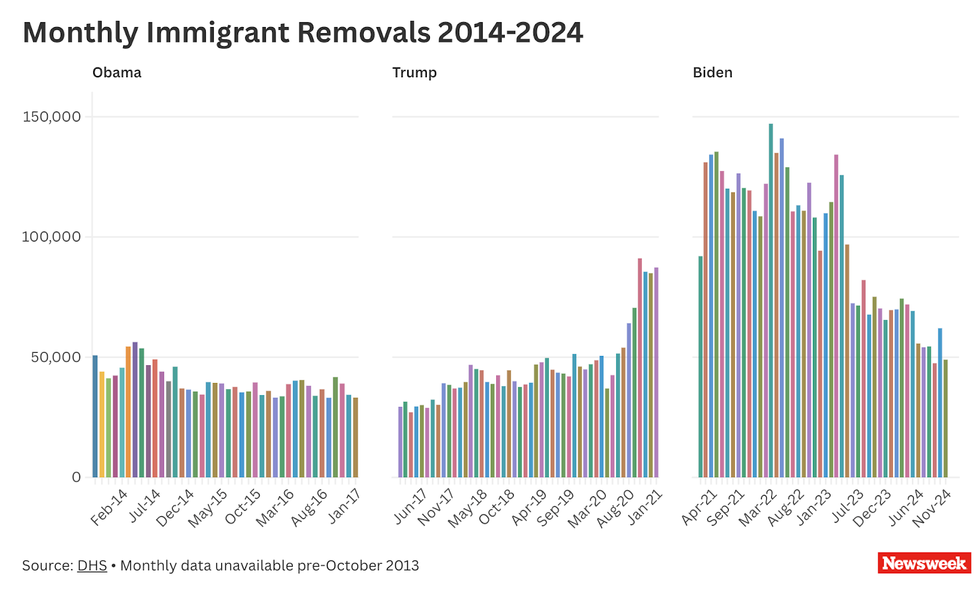
How many deportations have there been during the Trump administration so far and how does this compare to previous presidents?
Despite campaign promises of mass deportations, the administration's first-month deportation figures were lower than those during the same period in Biden's final year and the lowest monthly level since 2000. Legal challenges and international resistance have complicated enforcement efforts.
Data on deportations for previous presidential terms during their first 100 days could not be found. However, given the priority President Trump has put on mass deportation, comparisons of the total number of deportations within entire presidential terms are already being made with previous administrations—the numbers are there for those who care to keep track in the next three (plus) years of the Trump administration.
- Biden (2021-2024): 4.6 million deportations
- Trump (2017-2020): 2.1 million deportations
- Obama (2009-2016): 5.3 million deportations (note two terms)
David Nevins is co-publisher of The Fulcrum and co-founder and board chairman of the Bridge Alliance Education Fund.




















Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift