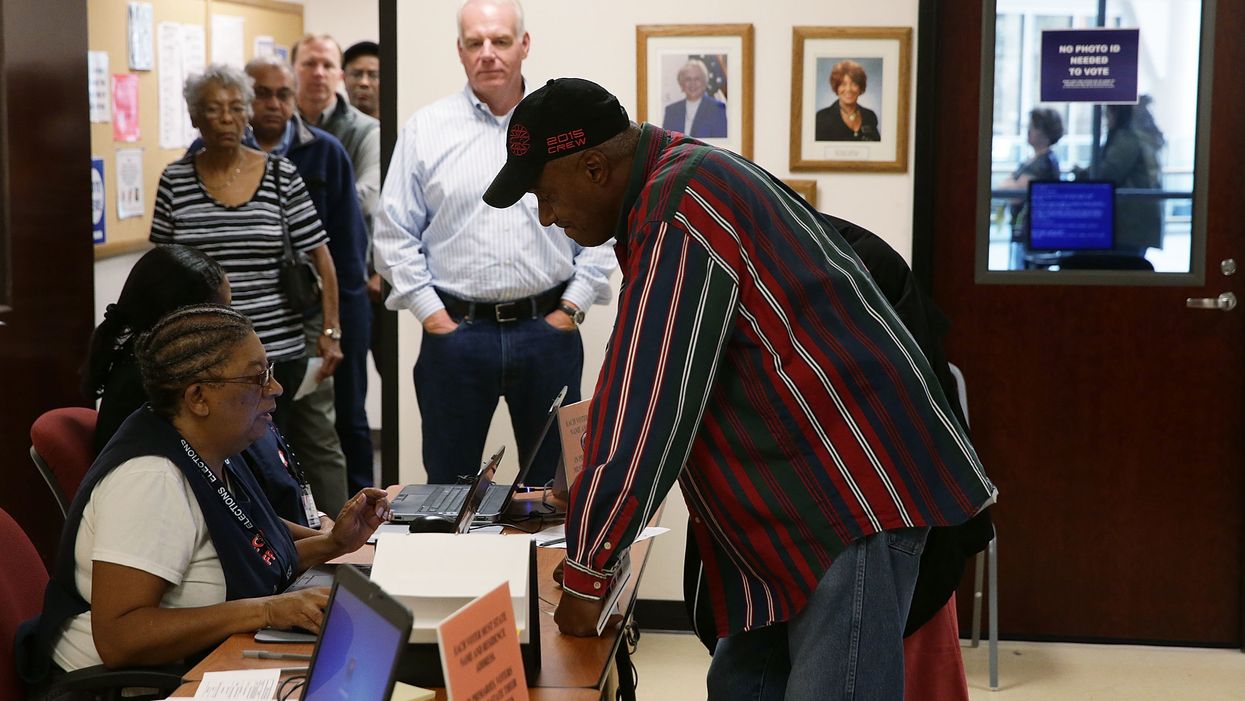
North Carolina's new voter ID requirements will be implemented during the 2020 presidential election.
A panel of three state judges dismissed much of a lawsuit alleging that black voters would face unconstitutional discrimination under the new rule, which requires voters to show photographic identification before entering the polls. A sliver of the lawsuit survives but the judges said the new requirement could be put into effect while the case proceeds.
The ruling is especially significant because winning North Carolina's 15 electoral votes will be critical to the electoral strategies of both President Trump and his Democratic challenger.
The requirement was approved by voters last fall. It was put on the ballot by the Republican legislature over Democratic Gov. Roy Cooper's veto.
"This is a huge win for the people of North Carolina who delivered a clear mandate last fall that they want common-sense protections against voter fraud," Senate GOP leader Phil Berger said after the judges' decision was announced Friday.
Voter ID laws have historically been used to disenfranchise black voters disproportionately, in part because many elderly African Americans in the South were not issued birth certificates. Three years ago a federal appeals court struck down an earlier photo ID law passed by the North Carolina Legislature as an unconstitutional targeting of "African-Americans with almost surgical precision."
The Republican authors of the new law say it is sufficiently different to survive such a voting rights challenge, in part because it allows for a wider array of IDs to be used at polling sites than before — including government worker identification cards — and provides a system for voters without a photo ID to explain why in writing and then cast a provisional ballot.