Editor's note: This article has been corrected to show estimated data, not actual numbers, in regards to completed ballots.
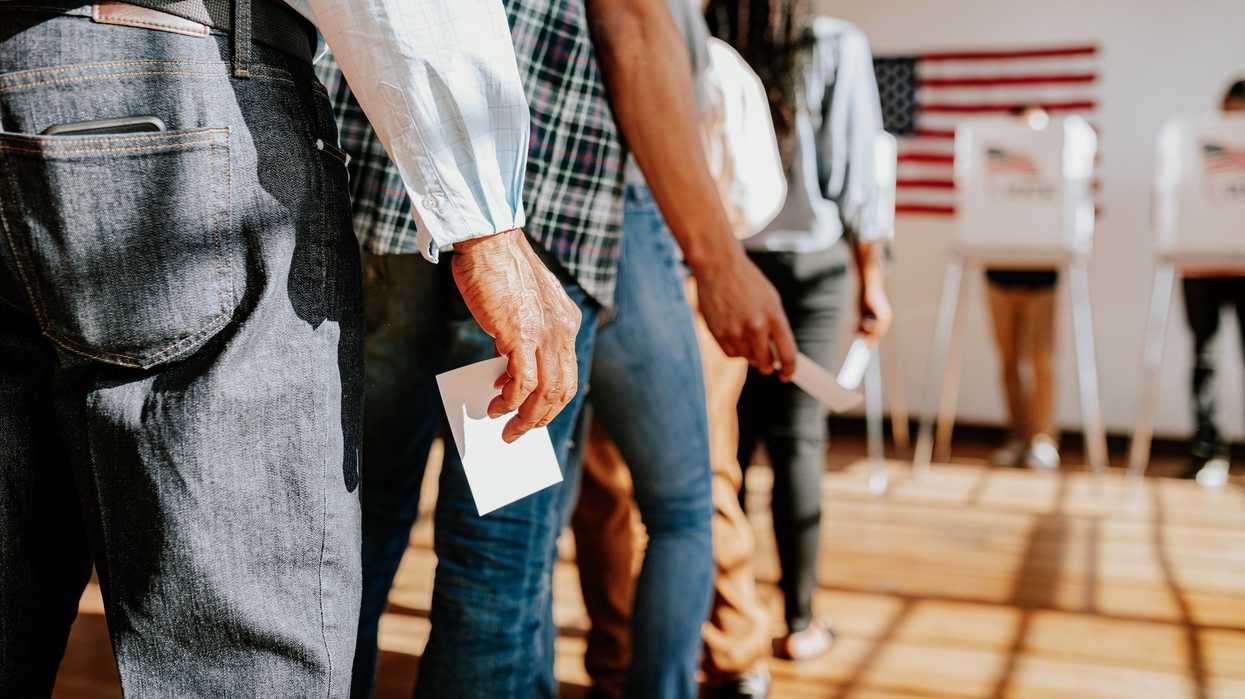
The number of people who vote by mail is expected to grow by 40 percent from the last midterm election and could nearly match the 2020 totals, according to data collected by advocates for remote voting.
In 2018, 30.4 million people voted by mail. The National Vote at Home Institute estimates that more than 42.6 million will do so this year – virtually the same completion rate (71 percent) as four years ago.
In 2020, amid the height of the Covid-19 pandemic with states making it easier to vote by mail (at least temporarily), 66.5 million used that option, according to Census Bureau data.
NVAHI is watching the numbers closely to see if the nation surpasses the 60-million mark this year.
“Hitting 60 million (or more) means that voting by mailed-out ballot has gone ‘mainstream’ beyond the few initial states in the Western third of the country,” said NVAHI’s director of research, Gerry Langeler. “Depending on total turnout, and return rates for those mailed-out ballots, about one-third of all U.S. votes or more will have been cast by a ballot the voter received in the mail, in a non-pandemic emergency rules year.”
Eight states proactively send all registered voters a ballot to be submitted by mail or dropped off at a designated location, including three – California, Nevada and Vermont – that are doing so for the first time this year. California alone accounts for 8 million more people voting from home.
Hawaii implemented its vote-by-mail system for the 2020 election and Utah expanded from a county-by-county to statewide program in 2019.
Colorado, Oregon and Washington were all running vote-by-mail elections in 2018. Washington, D.C, is continuing its temporary plan to mail ballots to all voters and may make it a permanent feature for the city’s residents. Vermont and D.C. are the only non-Western jurisdictions using such a system.
But some of the biggest increases are coming from places that are not pure vote-by-mail states, according to Langeler.
The highest rate of return, so far this year, can be found in the 21 states that do not proactively send ballots to all voters but also do not require people who request a mail-in (or “absentee”) ballot to provide an excuse. NVAHI estimates that 10.2 million of the 12 million requested ballots (85 percent) will be returned. (A number of states, including New York and Texas, have not yet made their data available.)
Drilling down into individual states, Langeler found that Michigan and Pennsylvania, which both moved to no-excuse absentee voting following the 2018 election, have seen significantly increased use of voting by mail – by 6 percentage points and 11 percentage points, respectively.
Among the eight vote-by-mail states, turnout is expected to reach 65 percent. Six states invite voters to register for permanent vote-by-mail status. In those half-dozen states, 74 percent of the 5.8 million mailed ballots are expected to be completed and sent back.
But Massachusetts has shown the biggest increase, going from 3.3 percent utilization of absentee ballots to 22.5 percent, now that the state is required to send all voters an application for mail-in balloting before every election.
“That undoubtedly accounts for a major portion of the differential lift between Pennsylvania and Massachusetts, as well as the fact that the Massachusetts legislators who were against this move stood down after they lost in court,” Langeler said.
And it’s not just about creating a system – implementation makes a difference, or as Langeler puts it: “There is a second-order potential impact – how the policy is rolled out.”
He pointed to examples in Massachusetts, which proactively mails applications, and Illinois which previously required voters to request a ballot each election but now allows people to sign up to be on a permanent vote-by-mail list. A similar proposal is on the ballot in Michigan this year.


















 Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation ranking member Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-WA) (R) questions witnesses during a hearing in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill on February 10, 2026 in Washington, DC. The hearing explored the proposed $3.5 billion acquisition of Tegna Inc. by Nexstar Media Group, which would create the largest regional TV station operator in the United States. (Photo by Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images)
Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation ranking member Sen. Maria Cantwell (D-WA) (R) questions witnesses during a hearing in the Russell Senate Office Building on Capitol Hill on February 10, 2026 in Washington, DC. The hearing explored the proposed $3.5 billion acquisition of Tegna Inc. by Nexstar Media Group, which would create the largest regional TV station operator in the United States. (Photo by Chip Somodevilla/Getty Images)
