Optimism is growing that a new Bill in Connecticut will lead to the introduction of a statewide ban against female genital mutilation/ cutting (FGM/C). Thousands of women and girls across the state have undergone or are at risk of this harmful practice. Despite this, Connecticut remains one of just nine U.S. states that still lack state-level legal protections—something advocates hope this legislation will finally change.
Survivors and others from impacted communities, alongside women’s rights advocates and civil society organizations - including the U.S. Network to End FGM/C, Sahiyo, Equality Now, and the Connecticut General Assembly’s Commission on Women, Children, Seniors, Equity, and Opportunity - have long called for state legislation against FGM/C in Connecticut, citing how a law would help those at risk and their families resist cultural and social pressures to continue the practice.
Connecticut legislators have made five unsuccessful attempts to pass a law addressing FGM/C. Proposed bills in 2018, 2020, and 2021 aimed at criminalizing FGM/C or studying its prevalence did not progress beyond the committee stage, while in 2019, a Bill was rejected by the State Senate. In 2024, a drafted Bill failed to even be introduced.
FEMALE GENITAL MUTILATION/ CUTTING IN THE UNITED STATES
FGM/C is internationally recognized as a serious human rights violation involving partial or total removal or damage to healthy female genitalia for non-medical reasons. The procedure can lead to numerous immediate and long-term health issues, including severe bleeding which can result in death, chronic infections, psychological trauma, sexual dysfunction, and infertility. FGM/C can also cause childbirth complications and higher maternal and infant mortality rates.
At least 577,000 women and girls in 2019 were estimated to have undergone or be at risk of FGM/C in the U.S., according to the AHA Foundation. While there is some awareness about the practice occurring in some diaspora communities, there is far less recognition of it happening in other communities, including Christian communities in the U.S.
CONNECTICUT’S BILL TO PROHIBIT FGM/C AT THE STATE LEVEL
Connecticut now has the opportunity to ban FGM/C with the 2025 Bill, which has advanced to the second stage of the legislative process for committee review and hearing. If passed, Connecticut will become the 42nd state to criminalize the practice.
While the Bill’s exact language is still pending, previous versions of proposed anti-FGM/C legislation in Connecticut contained best practice provisions such as cross-departmental partnerships to develop and implement prevention and response activities, and education programs to raise awareness about FGM/C’s harms.
Advocates are calling for the Bill to mandate the development of specialized training for healthcare providers, enhanced collaboration between the state and non-governmental organizations, the right for survivors to pursue civil action cases for damages, and delay the start of the statute of limitations until survivors turn 18.
“We are closely monitoring the Bill as it moves through the legislative process and are hopeful that its language will reflect best practice provisions, including creating a civil right of action for survivors,” said Anastasia Law from Equality Now.
“Good legislation in other states incorporates a range of provisions, including robust education and awareness-raising programs, revoking medical licenses from healthcare practitioners who perform FGM/C, mandatory requirements to report FMG/C, and sanctions for “vacation cutting”, which is the practice of arranging for a person to be transported out of the state to undergo FGM/C,” she added.
While parties await the final language to be revealed, the introduction of the Bill marks a crucial step in the right direction.
NEED FOR COMPREHENSIVE STATE-LEVEL PROTECTIONS AGAINST FGM/C
Performing FGM/C in the U.S. or taking a girl out of the country for the purpose of being cut is already a federal crime. However, legislation outlawing FGM/C at the state level is crucial because state agencies and officials have far greater capacity than federal authorities to directly assist women and girls.
State laws govern local police, healthcare, social services, criminal justice, and schools. This makes local governments best placed to raise awareness about FGM/C at a community level, provide direct support to survivors and those at risk, and investigate and prosecute cases.
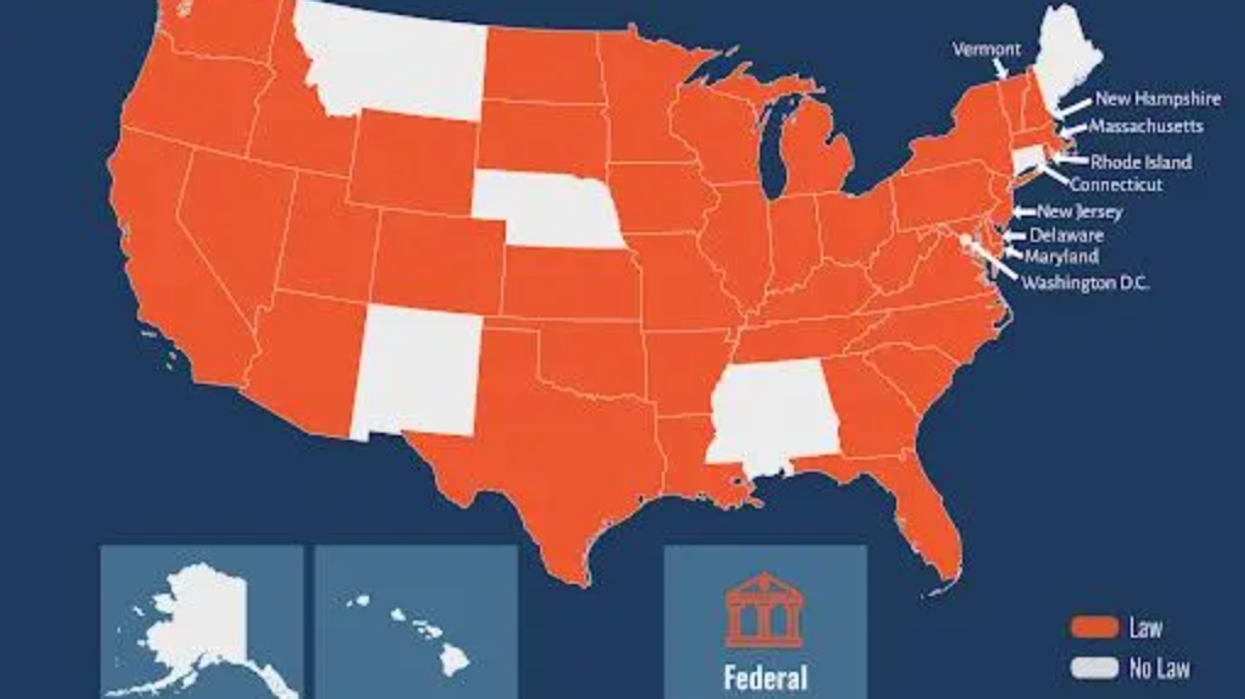
An interactive map by Equality Now and the U.S. End FGM/C Network shares FGM/C legal provisions and gaps in every state. Washington D.C. is the most recent district to pass legislation outlawing the practice, leaving just nine states without state-level legal protection against FGM/C - Connecticut, Alabama, Alaska, Hawaii, Maine, Mississippi, Montana, Nebraska, and New Mexico.
In 2023, Equality Now, the U.S. End FGM/C Network, and partners made a submission to the United Nations Human Rights Committee, highlighting the U.S.’s failure to protect women and girls within its borders from FGM/C and other human rights violations. The Committee recommended to the U.S. government that its federal legislation - the Stop FGM Act of 2022 (also known as Strengthening the Opposition to Female Genital Mutilation Act of 2020) - should be effectively implemented and states should be encouraged to pass legislation prohibiting all forms of FGM/C.
If passed, Connecticut will join the growing number of states taking a stand against FGM/C and affirming the right of every woman and girl to live free from this form of harm.
Connecticut lawmakers consider new bill to ban female genital mutilation/cutting was originally published by the Associated Press and is shared with permission. Mel Bailey joined Equality Now in 2022 as the Communications Officer for North America at Equality Now.



















Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift