Voting in the presidential election ends in 40 days, and states are still making adjustments to their rules and procedures.
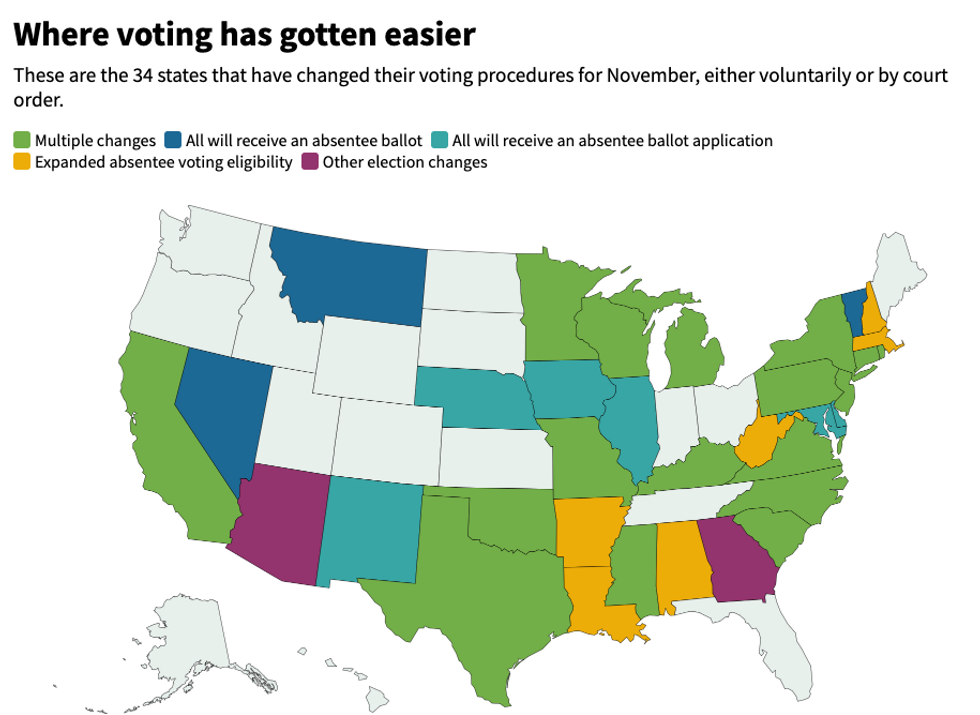
The coronavirus pandemic, along with a wave of litigation from voting rights groups and Democrats, has resulted in 34 states deciding to make it easier to cast a ballot this fall — either voluntarily or as the result of a lawsuit. Most of the changes encourage voting by mail and ease the rules governing the completion and tabulation of absentee ballots.
More developments are virtually certain. Many will be prompted by fresh judicial rulings, or appeals upholding or reversing voting easements now in place. And appeals in some of those cases could reach the Supreme Court in the final days before Nov. 3.
But here are the current plans in the two-thirds of states where the rules have already been altered this year:
Four states (and also Washington, D.C.) will soon send all active registered voters an absentee ballot while also providing in-person voting options: Reliably Democratic California, New Jersey and Vermont along with purplish Nevada, where the Trump campaign unsuccessfully sued to block the one-time switch to a mostly vote-by-mail election. And Montana has given discretion to its 56 counties, all but nine of which have decided on proactive ballot mailings.
Source: Ballotpedia • Changes as of Sept. 24
These states will join the five that planned to be primarily vote-by-mail even before the pandemic made voting in person a potential health risk: Colorado, Hawaii, Oregon, Utah and Washington.
A dozen states have relaxed for this fall their normal requirements that voters provide a specific reason for using an absentee ballot instead of making an in-person appearance.
Four have eliminated the excuse requirement altogether. Three are sure to vote in favor of the re-election of President Trump: Alabama, Missouri and South Carolina. Former Vice President Joe Biden can count on Massachusetts.
Eight others have temporarily expanded the definition of "illness" to cover worry about exposure to Covid-19. New Hampshire is the one presidentially competitive state on this roster. The others are solidly blue Connecticut and New York and reliably red Arkansas, Kentucky, Oklahoma and West Virginia.
(Tennessee was on this list for two months. But in August the stateSupreme Court struck down a blanket relaxation of the excuse rules, after state officials said people could decide for themselves what sort of "underlying health condition" made it necessary for them to vote by mail.)
Louisiana is under a federal court order to relax its excuse rules slightly and send mail ballots to people who say they have Covid-19, are quarantined or are caring for sick people.
Ten states have decided to send absentee ballot applications to all active registered voters. Three are presidential battlegrounds with a combined 32 electoral votes: Michigan, Wisconsin and Iowa. Six of them are reliably blue — Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Maryland, New Mexico and Rhode Island — leaving Nebraska as the sole red state encouraging mail-in voting this way.
Several more states have made other easements to their election and voting procedures.
Kentucky will offer early in-person voting more expansively, Monday through Saturday beginning Oct. 13. North Carolina added two weekends for such early voting, while Texas extended its period by six days, to 19.
New Jersey, Pennsylvania, South Carolina and Virginia will cover the cost of postage for returning absentee ballots.
Minnesota, Missouri, Rhode Island, South Carolina and Virginia have waived the notary or witness signature requirement for absentee ballots. North Carolina now says just one witness is sufficient, instead of the usual two. And Oklahoma is allowing absentee voters to send a copy of a photo ID instead of finding two witnesses.
Eight states are extending the time for ballots (so long as they're postmarked by Election Day) to arrive at local election offices and still be counted — reducing the number of disenfranchisements but extending the timetable for knowing the results of close races.
Georgia and Pennsylvania have the shortest deadline extensions, at three days. Mississippi will count ballots that arrive five days after the polls close. Wisconsin and New Jersey will accept ballots delayed in the mail up to six days after the election. (For ballots without a postmark, New Jersey says they need to be received within two days.) Minnesota will give ballots to a week to arrive, and North Carolina will accept them even nine days late.
California has granted by far the most leniency. Ballots will still be counted if they arrive Nov. 20, or 17 days after the election.
Michigan will also count ballots arriving two weeks after the election — but they must be postmarked by Nov. 2. The state will also allow anyone to get assistance or assist others in returning ballots to local clerks, starting Oct. 30. Normally, only immediate family members and election clerks are allowed to help.
Minnesota residents can also provide, and receive, an unlimited amount of help from others when voting absentee. And Mississippi will allow people in quarantine, or caring for someone in quarantine, to vote in person before Election Day.
Arizona, New York, North Carolina and Texas will give voters the opportunity to address errors, such as a missing signature, and "cure" their ballot.
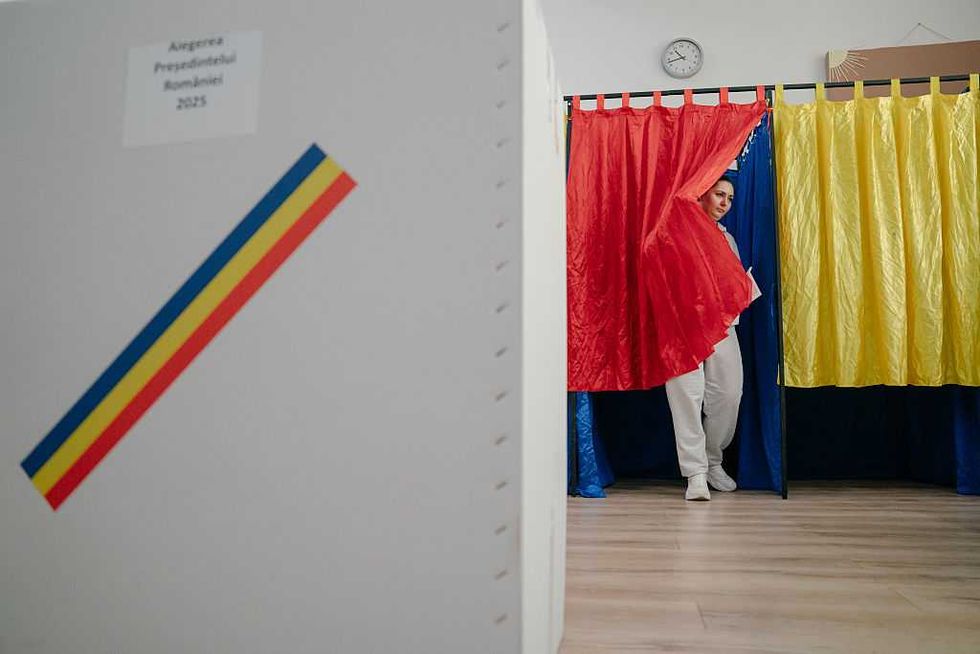


















 A woman prepares to cast her vote on May 4, 2025 in Bucharest, Romania. The first round of voting begins in the re-run of Romania's presidential election after six months since the original ballot was cancelled due to evidence of Russian influence on the outcome. Then far-right candidate Calin Georgescu surged from less than 5% days before the vote to finish first on 23% despite declaring zero campaign spending. He was subsequently banned from standing in the re-rerun, replaced this time round by George Simion who claims to be a natural ally of Donald Trump.Getty Images, Andrei Pungovschi
A woman prepares to cast her vote on May 4, 2025 in Bucharest, Romania. The first round of voting begins in the re-run of Romania's presidential election after six months since the original ballot was cancelled due to evidence of Russian influence on the outcome. Then far-right candidate Calin Georgescu surged from less than 5% days before the vote to finish first on 23% despite declaring zero campaign spending. He was subsequently banned from standing in the re-rerun, replaced this time round by George Simion who claims to be a natural ally of Donald Trump.Getty Images, Andrei Pungovschi
Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift