This weekly update summarizing legislative activity affecting voting and elections is powered by the Voting Rights Lab. Sign up for VRL’s weekly newsletter here.
The Voting Rights Lab is tracking 2,446 bills so far this session, with 573 bills that tighten the rules governing voter access or election administration and 1,088 bills that expand the rules.
Georgie and Arizona made changes on both fronts in recent days. Georgia. Gov. Brian Kemp signed legislation granting the Bureau of Investigation authority to investigate election crimes while the sate also restored automatic voter registration for drivers. Meanwhile in Arizona, it was a busy week for the Senate Rules Committee, with advance one bill that would mandate drop box monitoring as well as a voting rights restoration bill.
Looking ahead: New Hampshire’s bill placing new restrictions on voter ID is slated for a House floor vote this week.
Here are the details:
Florida secretary of state issues guidance on new voting restrictions. Shortly after Gov. Ron DeSantis signed S.B. 524 into law last week, Secretary of State Laurel Lee issued guidance concerning some provisions of the new law that may be subject to preclearance, pursuant to a federal court decision regarding another Florida bill, and therefore will not be enforced until further notice. The provisions on hold pending the state’s appeal of the district court ruling include the new restrictions on the use of drop boxes for mail-in ballots, increased penalties for third-party voter registration organizations and line warming.
Arizona’s rights restoration bill eligible for governor’s signature; Legislation restricting drop boxes advances. H.B. 2119 would allow people ineligible for automatic restoration to apply for their voting rights to be restored immediately upon discharge, instead of having to wait two years as they do under current law. The bill would also ensure that citizens convicted of or facing felony charges are notified about whether, when or how their voting rights will be restored. The bill has passed the Senate and passed a House vote on concurrence with the Senate amendments. It is now eligible for the governor’s signature.
Meanwhile, legislation restricting drop boxes ( H.B. 2238) passed out of the Senate Rules Committee. This bill would require drop boxes to be located in a facility at which election staff are present and monitoring the drop box. Otherwise, 24-hour video surveillance of the drop box would be required. Opponents have argued that these restrictions would be cost-prohibitive and threaten to eliminate drop boxes in many areas, especially on tribal lands.
Georgia governor signs criminal investigation law; officials restore automatic voter registration. Kemp signed S.B. 441 into law last week, expanding the authority of the Georgia Bureau of Investigations to independently investigate purported election crimes and issue relevant subpoenas. Georgia is one of 14 states to introduce bills that would escalate the investigation or prosecution of purported election crimes this year.
Last year voter registrations dramatically declined at the Georgia Department of Driver Services. The likely cause of the decline was a technical change making voter registration a confusing opt-in process, rather than offering eligible voters the opportunity to opt out of registration. This past week, following significant media coverage, Georgia officials announced they would restore the opt-out process to automatically register eligible voters.
New Hampshire’s strict voter ID bill passes the House Finance Committee. S.B. 418 passed the House Finance Committee despite a subcommittee’s recommendation to refer the bill to an interim study. This bill would make the state voter ID law more restrictive. Current New Hampshire law allows voters without ID to cast a regular ballot if they complete an affidavit affirming their identity, under penalty of perjury. This bill would eliminate that alternative, and instead rescind their vote from the count if they are unable to provide an ID. Most states with voter ID laws offer an alternative method of voting to ensure the identity of voters without ID can still be verified. This new bill would put New Hampshire in the minority of states. It is expected to face a House floor vote this week.
Oklahoma Legislature revives a bill that would allow interference in election litigation. The Oklahoma House adopted the most recent version of S.B 523 and sent it back to the Senate for concurrence. This bill would prevent litigants from changing election law by settlement or legal agreement and only permit state actors – including state courts – to alter election law to the extent authorized by statute.
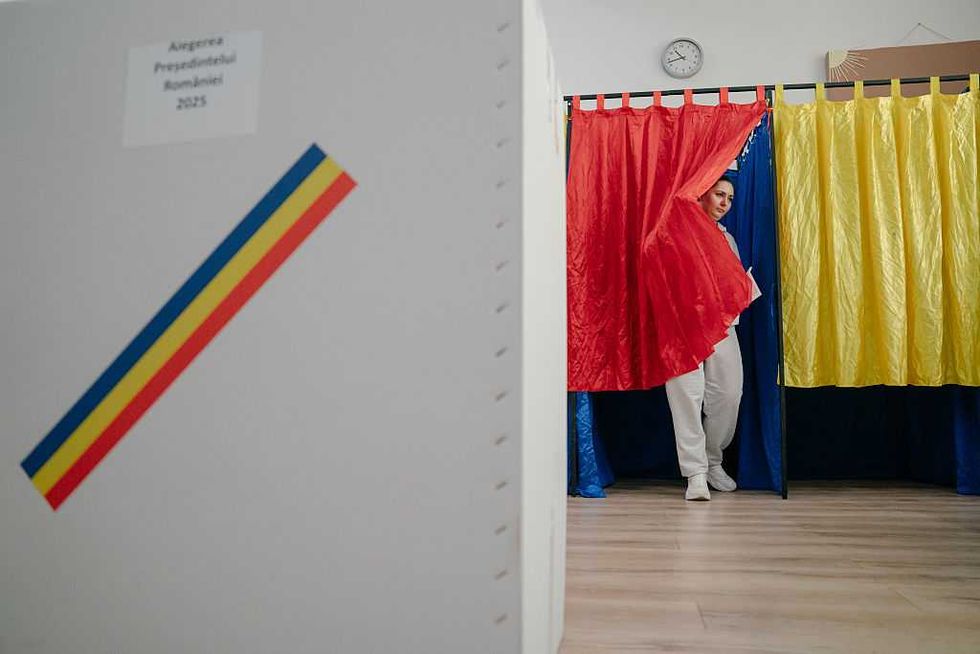

















 A woman prepares to cast her vote on May 4, 2025 in Bucharest, Romania. The first round of voting begins in the re-run of Romania's presidential election after six months since the original ballot was cancelled due to evidence of Russian influence on the outcome. Then far-right candidate Calin Georgescu surged from less than 5% days before the vote to finish first on 23% despite declaring zero campaign spending. He was subsequently banned from standing in the re-rerun, replaced this time round by George Simion who claims to be a natural ally of Donald Trump.Getty Images, Andrei Pungovschi
A woman prepares to cast her vote on May 4, 2025 in Bucharest, Romania. The first round of voting begins in the re-run of Romania's presidential election after six months since the original ballot was cancelled due to evidence of Russian influence on the outcome. Then far-right candidate Calin Georgescu surged from less than 5% days before the vote to finish first on 23% despite declaring zero campaign spending. He was subsequently banned from standing in the re-rerun, replaced this time round by George Simion who claims to be a natural ally of Donald Trump.Getty Images, Andrei Pungovschi
Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift