While much of the debate over election administration boils down to the left clamoring for “voting rights” and and the right demanding “election integrity,” there are some solutions that have proven attractive to both sides.
For example, let us introduce you to ERIC.
More formally known as the Electronic Registration Information Center, ERIC is a nonprofit organization that assists its members in maintaining accurate voter rolls by reviewing data provided by the states.
“Funded and governed by member states, ERIC is the most effective tool available to help election officials maintain accurate voter rolls. Using ERIC, members also provide voter registration information to potentially eligible individuals,” said Shane Hamline, the organization’s executive director.
Election officials from seven states – Colorado, Delaware, Maryland, Nevada, Utah, Virginia and Washington – formed ERIC in 2012. New Jersey became the most recent member earlier this year, bringing the current total to 32 states plus Washington, D.C.
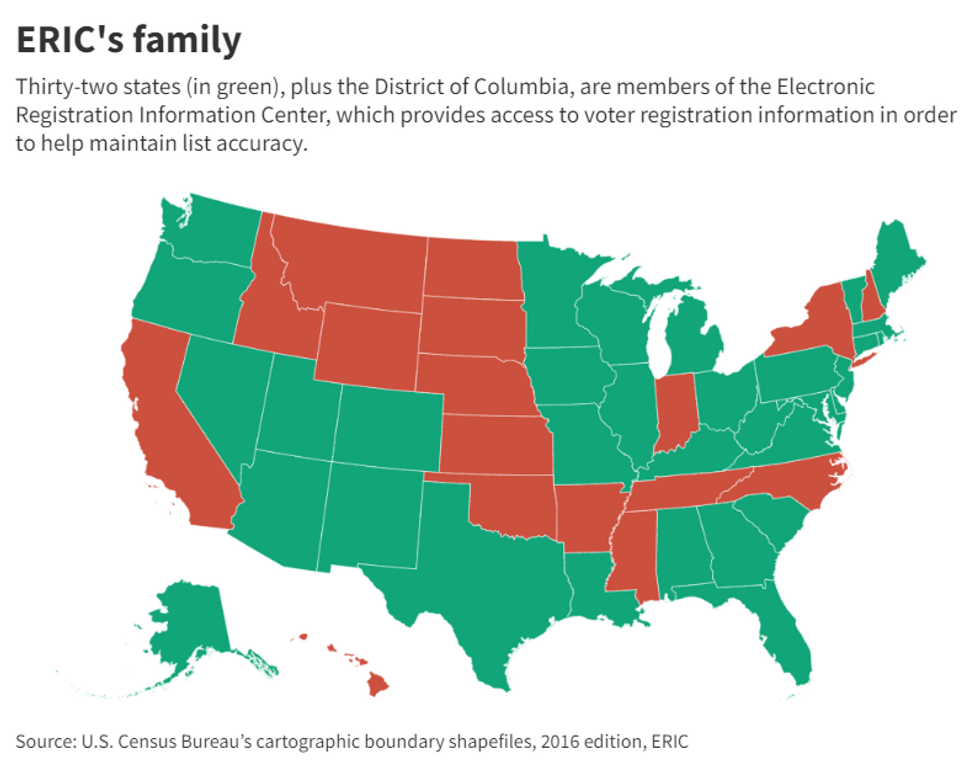
And those states now regularly share voter registration lists and data from motor vehicle agencies with ERIC, which also gathers Social Security death data. ERIC combines all the data to determine voters who have moved from one member state to another, voters who moved within a member state, voters with duplicate registrations in one state and people who have died.
States can then use those reports to properly update their voter registration lists. Members must request at least one of the reports at least once a year but may do so more often.
But it’s not just about removing people from the voter lists. ERIC also provides a report on people who are eligible to vote but remain unregistered, based on voter registration and motor vehicle data. Membership requires states to use that list to send out voter registration information at least once every two years.
Two additional reports further help with list maintenance. One uses U.S. Postal Service data to identify voters who have moved and another lists people who may have voted in more than one state or who may have cast multiple ballots in one state.
According to information provided by ERIC, four of the founding member states were led by Republicans and three by Democrats. As the organization has grown, its membership has remained about evenly divided.
Membership in ERIC may soon expand further. In early July, North Carolina enacted a law providing funding for the state to join ERIC for one year, but there are some restrictions.
States pay $25,000 to join ERIC and then annual dues based on size of the voting age population, ranging from $15,000 to $75,000. That money covers ERIC’s $1 million operating budget.
“We have witnessed repeated attacks on our democracy at the national level. The many states who are members of ERIC are working toward creating easy and equitable access to voter registration, and I am glad to join them,” New Jersey Gov. Phil Murphy said earlier this month in announcing his state had become the latest to join ERIC.




















Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift