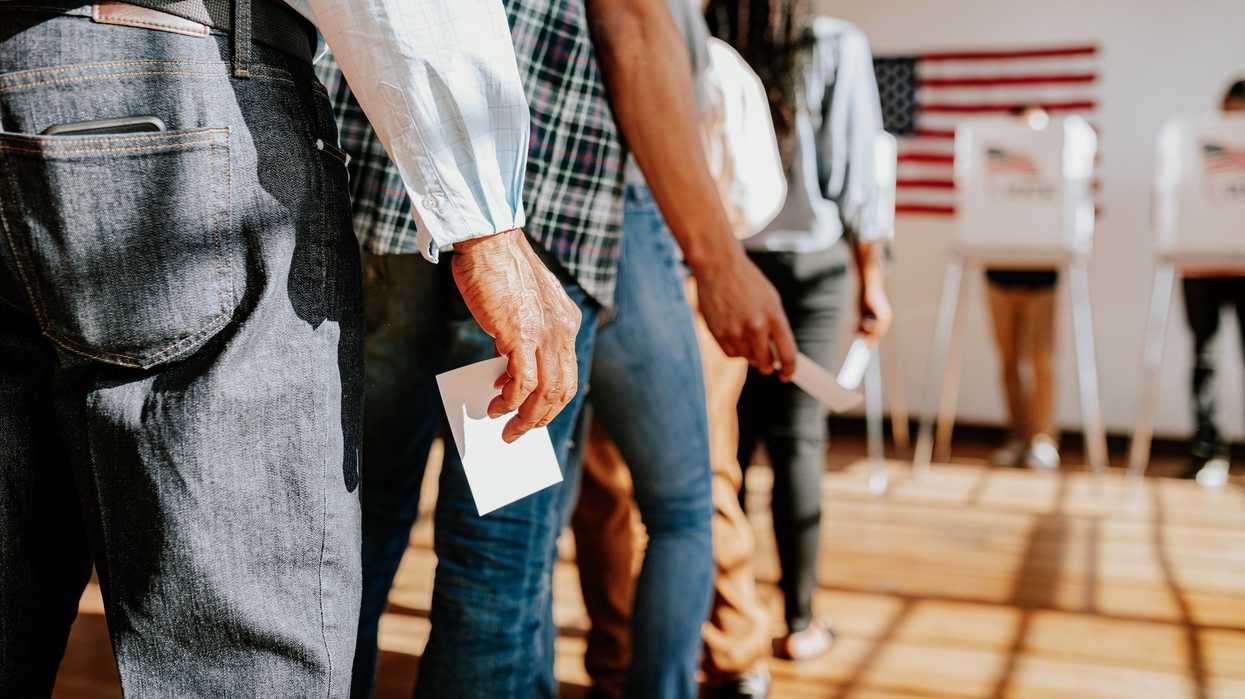
It wasn't the kind of test that you hope produces a perfect score. But hackers, technology geeks, academics and others were 100 for 100 this summer in their attempts to infiltrate and compromise an enormous array of voting machines using all sorts of technologies.
Their astonishing results will only boost the widespread anxiety among election security experts that American election systems remain widely vulnerable to hacking and Washington is not doing nearly enough to shrink the risks ahead of next year's presidential contest.
The total failure of voting hardware to ward off intrusion was revealed in a report last week summarizing the third Voting Machine Hacking Village, a three-day hack-a-thon held in Las Vegas in August as part of Def Con 27, one of the world's largest hacker conferences.
The participants either found new ways to break into the machines this year or replicated already published methods that could be used to alter stored vote tallies and change ballots displayed to voters.
"As disturbing as this outcome is, we note that it is at this point an unsurprising result," the report states.
The first such hacking village, in 2017, took on 20 types of voting devices. The second, last year, targeted more than 30 brands of equipment.
The equipment broken into included touchscreens, optical scan paper voting devices, paper ballot marking devices and electronic poll books — all the technologies that are currently in widest use by the more than 5,000 local jurisdictions that conduct our elections.
The volunteer intruders gained access in most cases through external interfaces accessible to voters or precinct workers.
Despite these vulnerabilities, the report's authors said some of the equipment is still viable for use in elections as long as there are "rigorous post-election audits." Legislation to mandate such audits is in a tall stack of election security bills that remains stalled in the Senate, where Majority Leader Mitch McConnell says none of those policy measures is necessary even though he has agreed to support $250 million in federal spending to protect the 2020 balloting from outside interference.
Attention has been focused on the vulnerability of the voting systems in the United States since Russian intelligence agents attempted to disrupt the 2016 presidential election.
Special counsel Robert Mueller's report on the Russian interference found that operatives attempted to hack into voting systems around the country and were successful in gaining access to a voter registration database in Illinois and to computers of some election officials in Florida.
The Voting Village report also includes a series of recommendations for improving security ahead of the 2020 elections, almost all of which are also being pushed by Democrats and some Republicans on Capitol Hill. They include mandating post-election audits and the use of machines that generate a paper trail, and increasing funding to help local election officials protect their IT infrastructure.