The heated debate over voting rights in the United States is on full display in multiple venues. Senators clashed last week about the need for the major federal voting protections recently passed by the House. State legislatures across the country, meanwhile, are considering a range of proposals that ignore the positive lessons from the 2020 election.
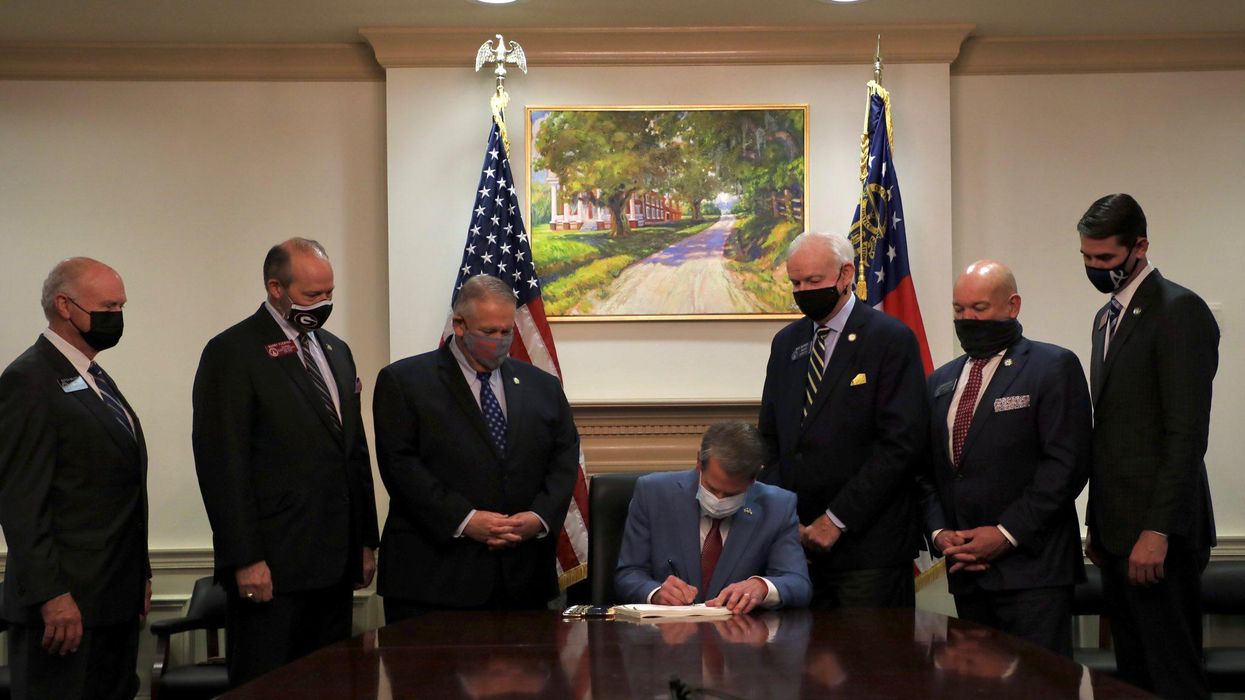
Georgia, having just emerged from close presidential and Senate elections, is ground zero in the voting rights debate. Last week Gov. Brian Kemp signed an election law overhaul passed by his fellow Republicans in charge of the General Assembly. Proponents see it as essential for ensuring ballot integrity. Voting rights activists see it as harkening to the spirit of the Jim Crow era.
While there has been an element of hyperbole in the vehement reaction of the law's critics, their response is understandable in light of the measure's origins in the highly partisan and baseless allegations of fraud in the November election. Those claims reflect a well-organized disinformation campaign and the conspiratorial delusions of a sore loser, former President Donald Trump, who is now under investigation in Georgia for possibly committing an election-related felony.
Furthermore, the new law falls short of international standards and democratic principles in several important ways.
First, these principles obligate governments to provide access for all eligible voters and to ensure the integrity of the process — making it simple to cast a ballot while making fraud or other malfeasance difficult and easily detectable.
Actions in recent years by Georgia's legislators and election officials had made improvements in attaining these goals. The state now allows voters to review their ballots on paper before they're cast and conducts the best available form of post-election audit to enhance confidence in the result. And it has increased access to the franchise with automatic voter registration.
Georgia has now undermined this positive record. Several provisions of the new law reduce access to the ballot necessary because our Election Day, unlike in many other countries, is not an official holiday. Early in-person voting and voting by mail effectively obviate the need for citizens to choose between work obligations and civic duty. And both alternatives already had ample security safeguards, including required verification of personal data before issuing an absentee ballot.
The new law requires vote-by-mail applications to include approved identification and sensitive personal information. The request must be submitted at least 11 days before Election Day. And drop boxes for the envelopes will only be allowed inside early voting locations. These changes do little to improve the integrity of the process. But they may well discourage Georgians without an approved ID, along with the elderly and others unable to access the more limited drop boxes.
Advocates for these restrictions repeatedly point to the 2005 report of a commission chaired by former President Jimmy Carter and former Secretary of State James Baker that encouraged further study of vote-by-mail practices. But given technological advances in the past 15 years, and the experiences of states conducting elections almost entirely by mail, Carter now says "voting by mail can be conducted in a manner that ensures election integrity."
A second principle that should guide election laws across the world is that people with a partisan or personal interest in the outcome should not be in position to influence an election.
Georgia's law falls far short here as well. It changes the makeup and authority of the State Election Board in ways that could allow undue influence by the political party in control of the state capital. The elected secretary of state is no longer chair of the board; instead, the official will be appointed by majority votes of the state House and Senate. Although commendable provisions encourage selection of a political independent, the likely outcome is four of the board's five members will be from one party and have no independence from the majority in the legislature.
Compounding this problem is a new provision granting the Election Board authority to temporarily replace election administrators in as many as four counties. Improving performance by subpar local election offices is a worthy goal. But the law is silent on the criteria for replacements, so this power could easily be abused for partisan ends. Taken together these provisions allow the majority in the General Assembly to control both the State Election Board and election administration in pivotal counties.
Rather than place these powers in the hands of partisan legislators, Georgia should establish an independent committee to shortlist candidates for the chair (and maybe all the members) of the Election Board and to find replacements for flawed local administrators. This follows the example of structures reducing partisan self-dealing in other areas of our democracy: the nominating commissions that find potential judges for courts in more than half the states, and the independent commissions that have a role in redrawing legislative and congressional boundaries in about one-fifth of the states.
Ultimately, repairing democracy in the United States requires a recognition that candidates and parties reliant on elections need to step back from how elections are run.
This guiding principle is behind much of the good government package known as the For the People Act, passed by the House as HR 1 and now before the Senate as S 1. For example, the bill would require independent redistricting commissions and automatic voter registration in every state — two reforms that do not favor either party and that have gained bipartisan support in state legislatures and state referenda.
While some of the consequences from the new Georgia law are not likely to be as dire as many claim, its enactment is a significant negative step for the country — a step away from democratic principles and toward a symbolic transformation of falsehood into law. Democracy has been ill-served by this development.