Turner Lee is a senior fellow and the director of the Center for Technology Innovation at the Brookings Institution. She has created a new AI Equity Lab at Brookings to interrogate civil and human rights compliance within emerging models.
The White House recently issued an executive order to ensure the safety, security and equity of artificial intelligence technologies in the United States and abroad. This call to action was reaffirmed when Vice President Kamala Harris spoke at the AI Safety Summit in the United Kingdom and she emphasized the need for expanded oversight, and possible AI regulation over machines and models that result in adverse consequences.
For decades, an increasing number of experts, including other Black women in AI, have generated research and policy recommendations around necessary civil and human rights protections, improved data quality, and the lawful compliance of AI and other emerging technologies. While the bold prominence of the vice president at the summit set the stage for more diverse voices, Black women are largely being excluded from these and other high-profile dialogues, which disadvantages any conversations on the design and deployment of more equitable AI.
Black women have led in AI policymaking before its growing popularity and interest. In 2019, Rep. Yvette Clarke (D-N.Y.) issued the first version of the Algorithmic Accountability Act with her colleagues to interrogate automated decisions driving housing, creditworthiness and hiring outcomes. In the same year, and after her former Speaker Nancy Pelosi was the subject of altered videos, Clarke also introduced the first version of her DEEPFAKES Accountability Act, which would go after video creators who falsified video content and contributed to disinformation, especially around the time of the 2020 election.
After presenting revised updates to her proposed legislation every year following, Clarke’s 2023 versions of both are up again for House consideration. Other Black women in policy like former White House official Alondra Nelson led the development of the first ever national Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights in 2022 that pushed the country closer to more equitable AI.
The indelible marks made by these women have not gone unnoticed. But they are joined by an increasing number of other Black women in AI, whose work includes formidable research and pragmatic policy proposals that bring lived experiences to AI design, deployment and oversight. Despite impressive backgrounds as computer and data scientists, criminologists, sociologists, curators, policy professionals, tech entrepreneurs, and social activists, many of these women are not prominently appearing in highly visible roles and conversations or being asked by policymakers to bring their findings to congressional hearings focused on AI regulation, technical cadences, or harms to consumers and democracy.
Between March 8 and Nov. 29, Congress held various hearings on AI that covered topics relating the workforce to AI’s role in modern communications. Black women were sparsely presented as witnesses to testify on the subject. Of the 125 witnesses who participated in the 32 hearings, only two were Black women, one of whom was me. Until recently, Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer has worked to increase the number of Black women participating in his recurring AI Insight Forum s, which will undeniably influence the direction of national AI self-regulatory policies, and more prescriptive regulation.
The reality is that when Black women’s voices are amplified, it is usually to discredit their contributions and achievements. AI pioneer Timnit Gebru, a former Google researcher, was terminated after announcing the company was silencing marginalized voices. Algorithmic justice advocate and bestselling author Joy Buolamwini exposed the racial inequities embedded in the design and use of facial recognition technology by government agencies. Yet, law enforcement continues to use it with little regard for the false arrests of Black people due to its technical misidentifications around skin color.
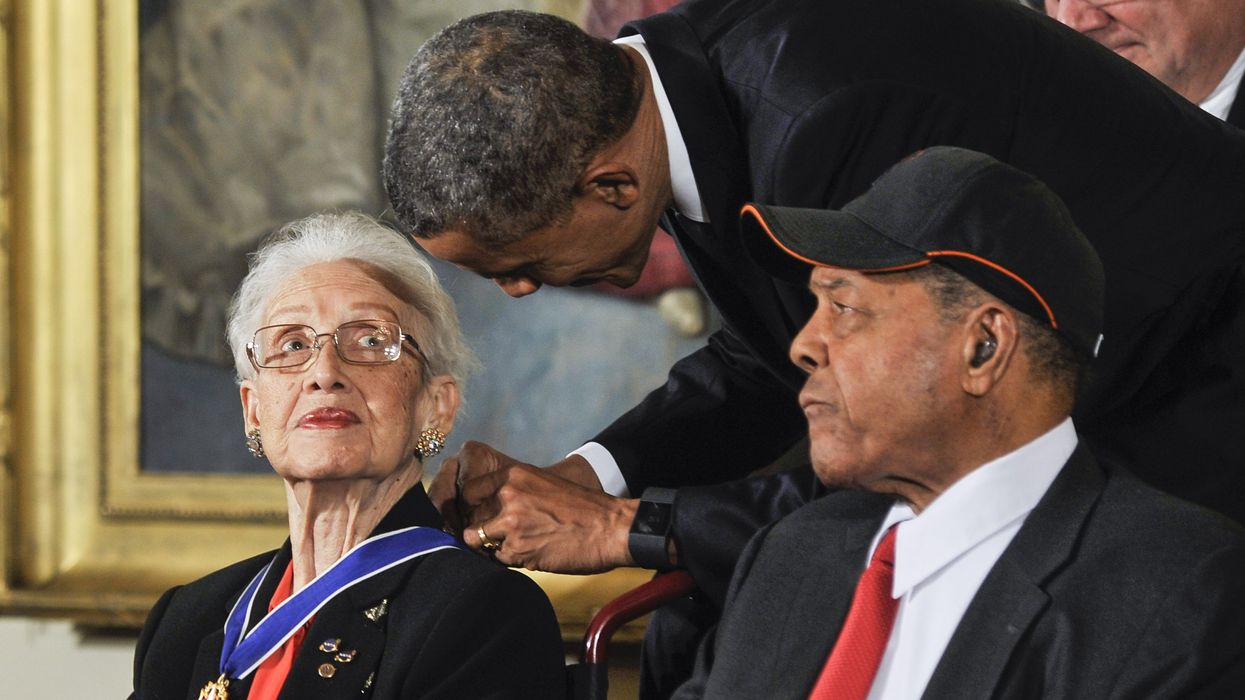
When Black women are not being attacked for their similarly poised expertise, they are relegated to the status of being hidden figures in science and technology – where they are more of an afterthought. In 2016, the world came to know the late Katherine Johnson, a retired NASA scientist and mathematician in orbital mechanics, through a bestselling book and movie both titled “Hidden Figures.” At the age of 96, Johnson’s expertise was finally recognized, especially her work on many critical space missions in her decades-long career, including the aversion of the near-fatal collision of the Apollo mission. Four years after we learned about her significant role in the country’s space programs, she died at the age of 102.
Black women in AI should not be attacked or become hidden figures where their ideas and concepts are invoked by others in privileged conversations and rooms.
If future AI is going to be responsibly designed and deployed, Black women must be included to stop and control how these technologies further racialize or criminalize certain communities. Their participation can motivate more inclusive design and products in AI that better serve and involve the public. As more corporations are dismantling diversity, equity and inclusion programs that will erode Black women’s visibility in board rooms, and other prominent leadership roles, this call for participation and input are both critical and timely.
Right now, it feels like Black women, whose thought leadership comes packaged in so many disciplines and work streams are largely invisible despite their established expertise. If the federal government, and the companies at the forefront of AI development, desire to achieve the goals of safety, equity and fairness in AI, then it must see and include Black women on Capitol Hill, in university research labs, in civil society organizations and think tanks, as well as in industry war rooms and boardrooms. We must not be memorialized later as hidden figures for the decisions that ultimately got made today about the governance, development and deployment of more ubiquitous AI.




















Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift