Lamendola is the research director at RepresentWomen, which advocates for political reforms it believes would result in more women holding elective office.
Over the last few years, more women have been running for office — and winning — than ever before. But women hold less than a quarter of all elected positions in the country, and large representation gaps remain across ideology, identity, age and geography.
The problem is systemic. And as important as it is to recruit and prepare more women to run, these efforts will yield disproportionate outcomes if we continue to rely on antiquated systems to determine the outcome of elections.
At the national level, the United States follows a single-winner plurality system, otherwise known as the "winner take all" system, which permits candidates to win elections with less than majority support. This system further protects incumbents who remain mostly white and mostly male, rewards negative campaigning — and is often subject to expensive, low-turnout runoffs in the event of a close race.
What's more, the system incentivizes party leaders to ask "spoiler" candidates, who are often women of color, to "wait their turn" so as not to risk splitting the vote.
An election system that actively discourages women from running, and then systematically reduces their odds of success, will not ever produce a reflective democracy. Systemic issues demand systemic solutions, which is why the United States needs to adopt ranked-choice voting.
In a ranked-choice election, voters rank candidates for each position in order of preference. Those listed as first-choice on a majority of ballots win their race. Otherwise, the candidate named first on the fewest ballots is eliminated, and those ballots are redistributed to the second choices. The process continues until a candidate has secured majority support.
This election method has a long and tested history in this country, with proven benefits for increasing the representation of women and minorities. Research has shown so-called RCV mitigates some of the barriers to representation that prevail in single-winner, plurality-wins systems. Specifically:
- It eliminates vote splitting. That way multiple women can run without having to worry about "spoiling" the election.
- It incentivizes positive campaigning. Anecdotal evidence suggests that women are more likely to run in a positive campaign environment.
- It rewards issue-focused campaigning. That provides women candidates with more space to connect with voters on the issues they care about.
- It produces more efficient elections. Runoffs are automated, eliminating the need for people to cast a second set of ballots, so elections cost less. This can be particularly important for women running for local positions for the first time.
- It ensures representative outcomes. Officials elected in RCV contests report that they govern better, knowing they have majority support.
Ranked-choice voting was first introduced in at-large districts in Ohio in 1912. From there, it spread to New York City in the 1920s and was implemented in 1941 in Cambridge, Mass. As cities began electing women and people of color for the first time, the system became a victim of its own success; white men, concerned with the future of their two-party duopoly, began repealing ranked choice procedures. By the 1960s, Cambridge was the only jurisdiction using multi-winner RCV.
In the 1990s, grassroots movements and support for ranked-choice contests fomented. In just the last decade, single-winner and multi-winner RCV election systems were used for local elections in 19 cities and counties. Maine has used the system for statewide elections since 2018. And, at present, there are 62 bills in state legislatures proposing the implementation of ranked-choice voting.
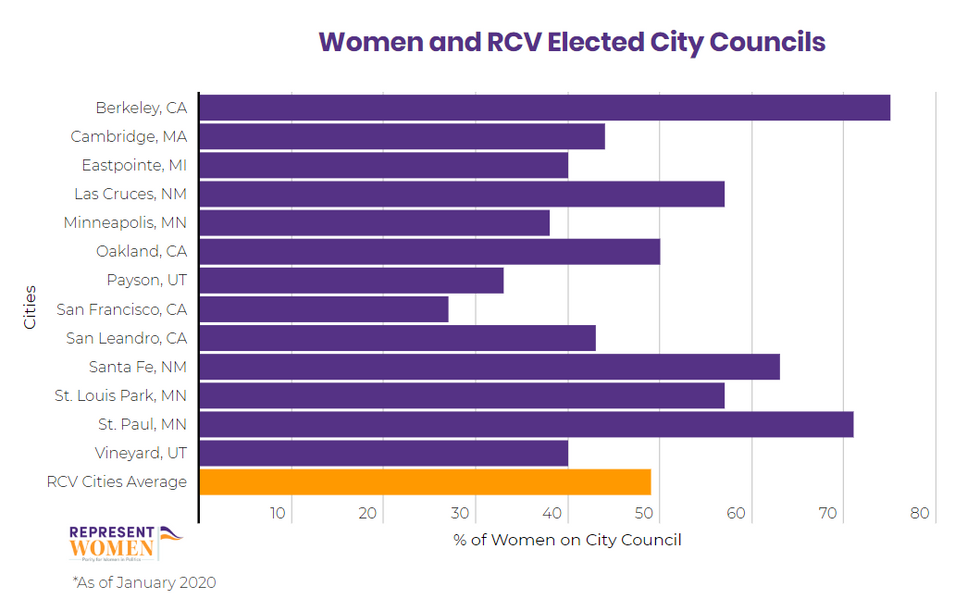
In the previous nine years, there have been 156 local ranked choice elections among three or more candidates — and women have won 48 percent of them. Of those winners, 38 percent were women of color. At the start of this year, women were half of all mayors and 49 percent of all city council members elected by RCV. As more cities, and now states, begin adopting and implementing ranked-choice voting, it will be worth noting if these positive outcomes continue to grow.
Many activists for RCV believe the country is an election cycle away from its widespread acceptance as the national system of choice. This year it was used in the Democratic presidential primaries of four states and has been adopted for both Republican and Democratic party leadership contests in several states.
This November, Maine will be the first state to use ranked-choice voting to award its presidential electors.
RCV is a tried and tested, nonpartisan electoral reform which would not only help elect consensus candidates, but would also increase the number of women and people of color who run, win, serve and lead in our government.




















