Usalis is a strategic partnerships manager for RepresentWomen.
Last month, Texas kicked off the midterm season with another batch of high-profile races going into a runoff — 23, to be exact.
Texas election law states that primary candidates must win with a majority, which becomes tricky when there are more than two candidates running. This results in an extraordinary amount of elections being forced into a runoff, where the top two candidates compete head-to-head in a second round of primary elections.
What’s so wrong with this? Two words: time and money. Both of which women candidates generally have less of.
 RepresentWomen
RepresentWomen
Money Cost
A March 3 article in The Fulcrum explained, “A 2021 analysis of election spending in Texas, conducted by FairVote and Third Way, estimated that each county had to spend hundreds of thousands of dollars to conduct the runoff, at least $6 million in total.” That is an additional $6 million beyond what is already being spent on elections. Every. Single. Year.
We also know that campaigning is expensive, especially for women candidates. RepresentWomen’s 2020 PAC Report found that individual donors are less likely to be women, that Republican women are the most underfunded candidates, and it simply takes more money to win as a woman. The report goes on to say, “women are underfunded by PACs and in turn are reliant on smaller donations from a larger network of donors (i.e.’grassroots fundraising’). Grassroots fundraising requires more time to raise the same amount of money putting women at a strategic disadvantage.”
Time Cost
The time cost of dragging out an election season is a serious burden for candidates, especially women. Our current culture dictates that women take on the majority of unpaid work at home, which means women who enter the workforce carry a dual burden that leaves them in major time poverty. The Pew Research Center found that working mothers in the United States spent an average of 25 hours per week on housework and chil dcare, compared to working fathers' 16 hours. And that’s on top of their full-time jobs. Imagine hearing that your race has gone into a runoff and you have to start all over again!
A twin-track solution
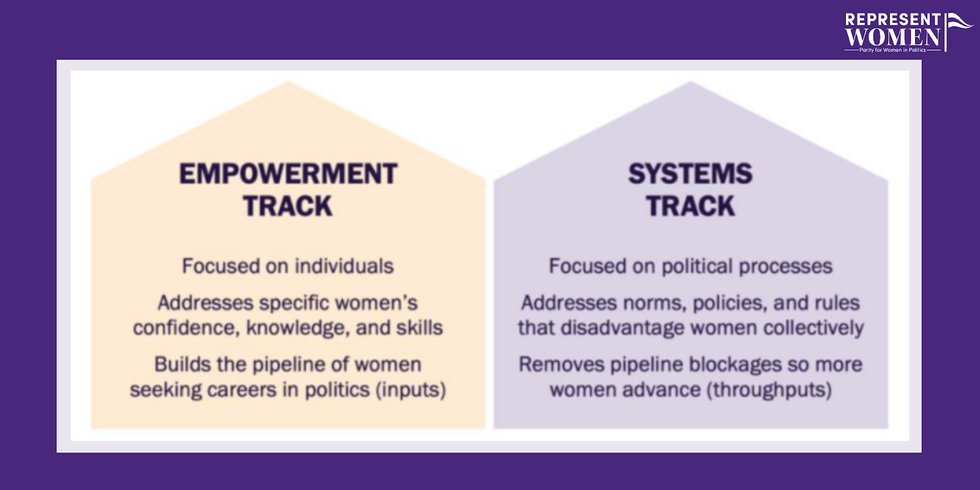
These systemic issues cause big problems for everyone involved, and these problems have a bigger impact on women. The situation for Republican women and women of color is even worse. To address challenges that are this multifaceted and deeply embedded, we need a twin-track approach.
 RepresentWomen
RepresentWomen
Empowerment track: Powerful factors like cultural beliefs about gender roles, “viability,” and who is traditionally seen as worth investing in all keep women from running and winning in U.S. politics. Because of the world we live in, women need a community to encourage, educate and empower them to participate in politics. They need a community to invest and believe in them, and often to help them address any self-stigma that has been absorbed from the world around them. This track is critical, but it’s not enough on its own.
Systems track. Electoral policies, gatekeeper norms, antiquated governance practices and other systemic barriers restrict the pace of change, no matter how many women run for office. So while organizations and groups are doing the work of investing in and empowering women to run, win, serve and lead, we need to also invest in systems change that removes the built-in barriers that keep women out.
Solutions like ranked-choice voting (also known as instant runoff) kill several birds with one stone by eliminating vote splitting and spoilers, incentivizing positive campaigning, rewarding issue-focused campaigns, and making elections more affordable. Since candidates in RCV elections always win with a true majority, RCV also eliminates the need for these costly runoff elections that are hard for everyone, but even harder on women candidates.
Why #RepresentationMatters
Representation is not just about fairness. It’s about better policy processes and outcomes. The United States is wading through a sea of challenges right now, and we need the best and the brightest at the table to successfully navigate these rough waters. Cutting women out of the equation severely limits that candidate pool and hamstrings our efforts to solve these pressing issues. To overcome powerful systemic barriers we need powerful systemic solutions.



















Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift