How did American democracy get so broken and what are the paths forward to fix it?
These complex questions are explored with levity and clarity in a new nonfiction graphic novel. In "Unrig: How to Fix Our Broken Democracy," the campaign finance reform advocate Daniel Newman dives into gerrymandering, money in politics, voting rights and more — all through comics illustrated by author and illustrator George O'Connor.
Having worked in the democracy reform space for the better part of two decades, Newman says he saw a critical need for material that explained the issues plaguing American politics, while also providing optimism and inspiration for making the system work better. Sales of the books, which start next week, will suggest whether he was right.
"I've had so many conversations over the last 15 years where I'm explaining how the rules of political money and voting affect every other issue in the county, and a lightbulb goes on, so this book is meant to provide a lightbulb moment of clarity," said Newman, who created in 2005 and remains president of MapLight, a nonpartisan nonprofit group that chronicles the influence of money in politics.
Newman, who's based in Berkeley, Calif., has been working on the 290-page book for two years, using interviews with more than 100 advocates and experts, plus his own knowledge and experience, to inform his writing.
His artist partner O'Connor, based in Brooklyn, is best known for the "Olympians" series of Greek mythology graphic novels.
Throughout, their work highlights central problems with the political system and explains tried and tested solutions, while also weaving in real-life stories of democracy reform advocates. The book leaves the reader with potential next steps they could take to get involved in the fix-the-system movement.
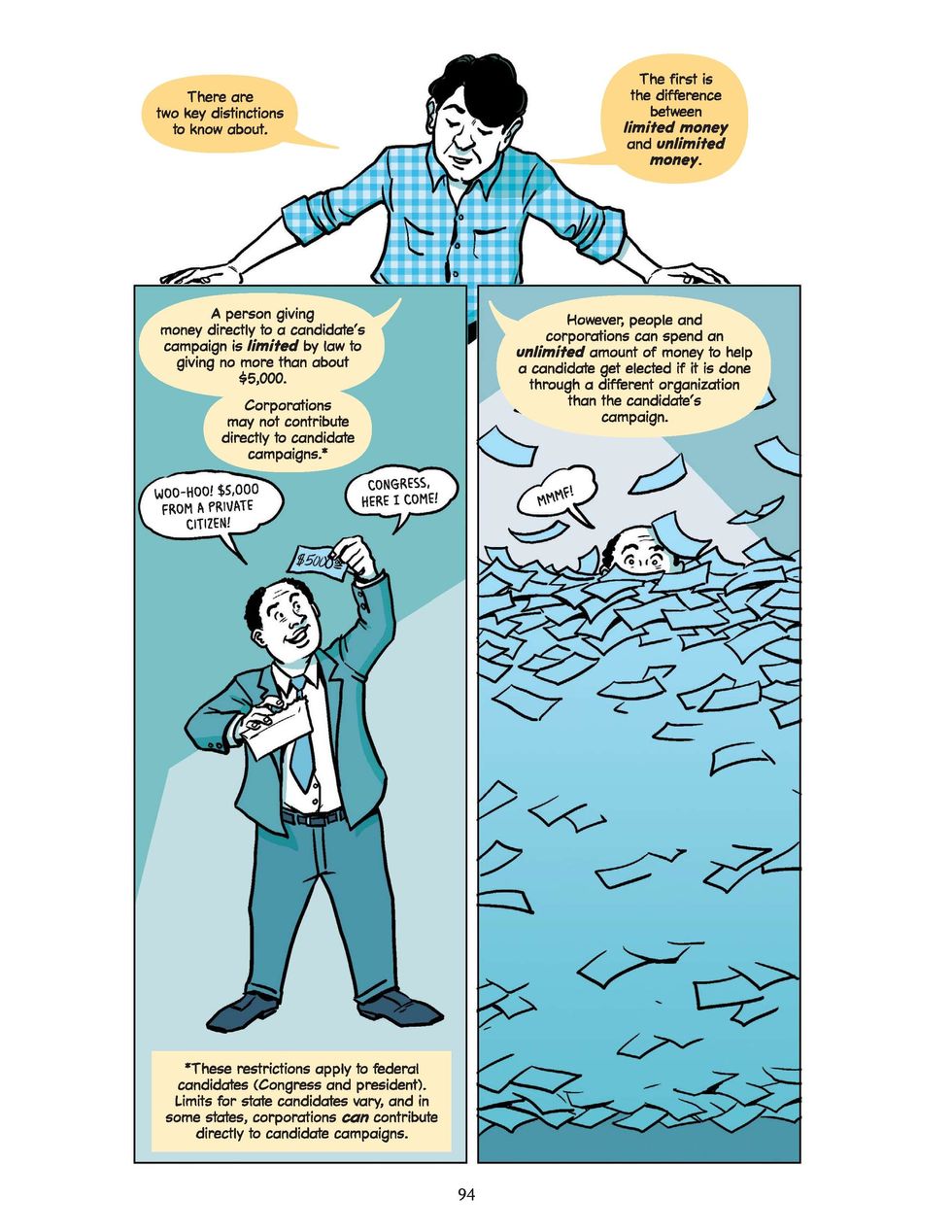
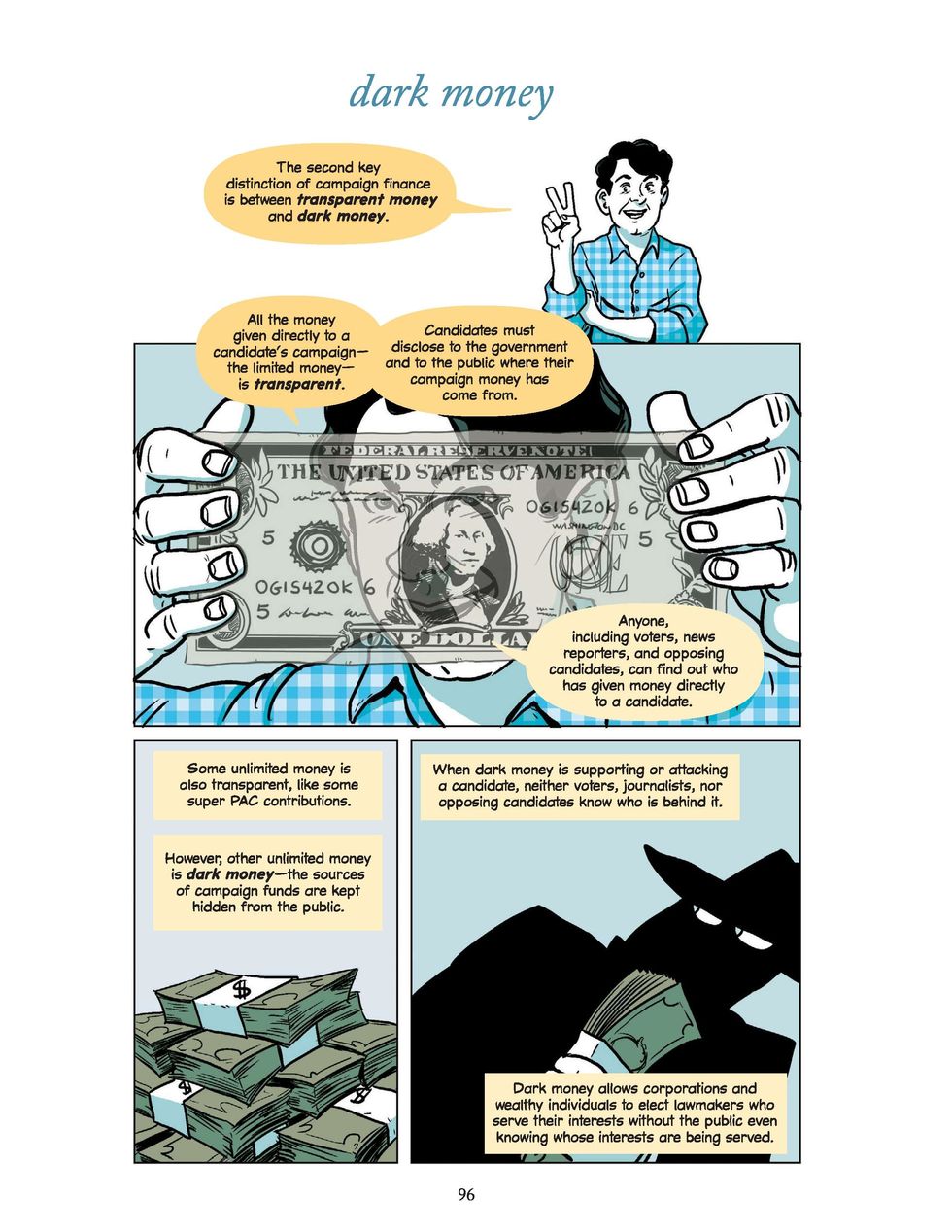
The chapter on political money — the topic Newman's most familiar with — explains how corporations and special interests are able to use their wealth to exert influence over politics, while remaining largely hidden from the public. One example is Republican John Ward, who lost his 2008 bid for the Montana Legislature by 25 votes following a last-minute ad blitz funded by entities whose identities remain hidden.
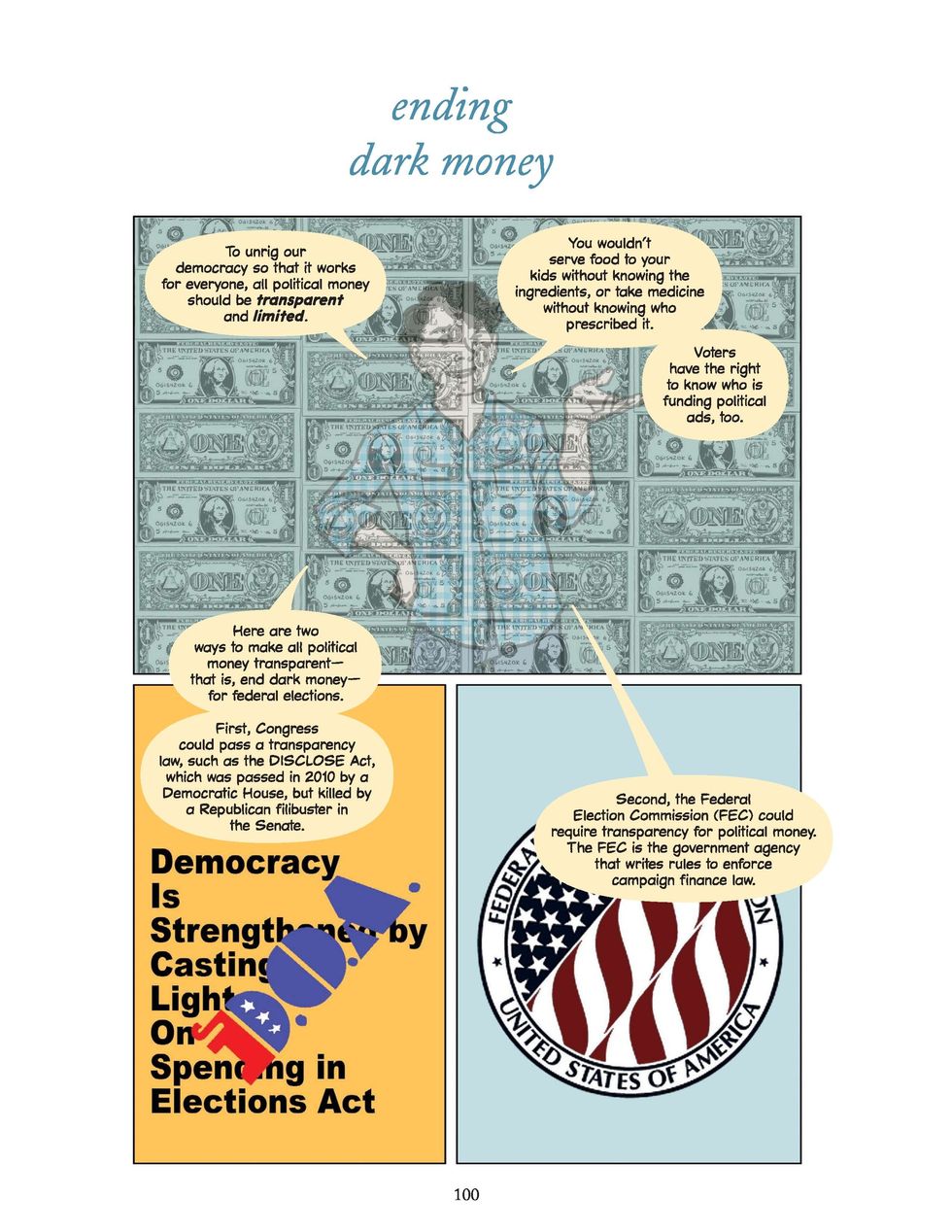
The chapter also points to solutions at the federal and state levels, including Congress bolstering disclosure rules for political ad spending online, the Federal Election Commission requiring greater campaign finance transparency and states adopting donor disclosure rules for political ads.
Democracy reform issues can often seem dry and complex, Newman said, but he hopes "Unrig" brings clarity and inspiration to readers.
"I hope people will be inspired to see that change is possible and is already happening — and how you can be involved, too," he said.
Here's an excerpt from that money-in-politics chapter of "Unrig."