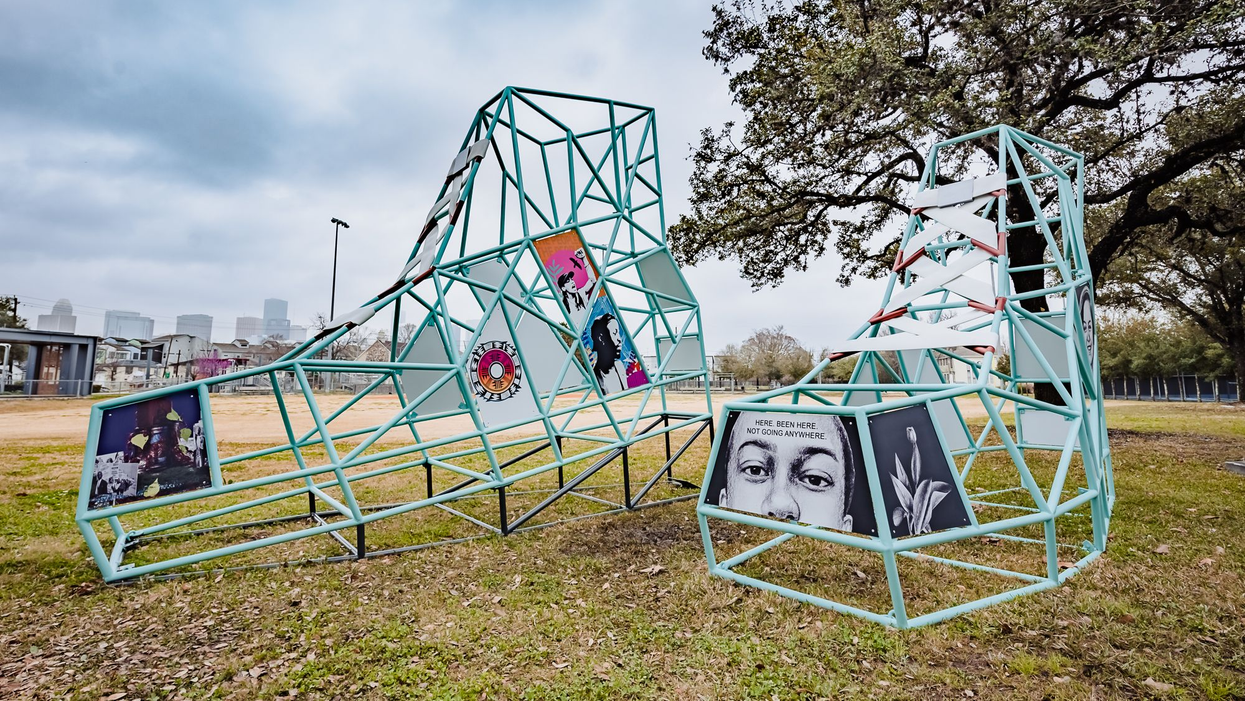
Mack is a member of Black Lives Matter Houston. Escobar is a member of United We Dream. Those organizations released "Move Into The Future," a public art installation celebrating Houston’s Black and Brown youth power.
We are in a critical moment in the state of Texas, where narratives that center the voices of Black people and other people of color are being eliminated from our curriculum. As a Black, same-gender-loving/queer man and an undocumented young woman in Texas, we know this is largely because some people in our state — and across the country — don’t want to face the hard truths about the atrocities committed against Black people in our country, from slavery to Jim Crow to the resulting systemic oppressions that continue to disproportionately impact Black people.
This is happening as the 2020 Census revealed that people of color make up 95 percent of the population growth in Texas and in 2019, the state was third in growth of Black immigrants. It’s clear that the fear of white erasure prompted Texas Republicans to attempt to pass laws that would ban schools from teaching about the state’s anti-Black and anti-Native founding.
Our communities fear that the police and deportation agents are one and the same, rooted in a culture of violence that harms people of color. In 1823, a predecessor of the Border Patrol was formed — they were known as the Texas Rangers. The Texas Rangers were white men who volunteered to uphold slavery in Texas by catching and lynching runaway enslaved people seeking freedom in Mexico.
By 1924, after the abolition of slavery in the United States, the Border Patrol was formed to maintain the southern border and keep out Chinese people after they had been banned by the United States’ first-ever immigration law known as the Chinese Exlusion Act. The same Border Patrol that just last year was thrust into the national spotlight for its abuse of Black migrants from Haiti, and which in 2017 was actively separating parents from their children at the border under the Trump administration.
These are examples of the histories of our communities that some in our state seek to hide from us. When we see the arguments against teaching about racism and other cultural experiences, we are told it makes white students feel bad. But, for Black students, our history is often overlooked. For Black and Brown students, we are denied the opportunity to learn about the history and continued reality of racism and anti-Blackness. How would you feel if your communities’ contributions were never acknowledged? The fight to ban books and control what parts of history we are taught is centered on white people and their feelings.
We should all have the opportunity to see that it is possible for all of us to achieve greatness. That is why we need to make sure that we learn about one another. This belief united Black Lives Matter: Houston and United We Dream to release "Move Into The Future,: a public art installation celebrating Houston’s Black and brown youth power. When we build spaces to learn with and about each other, we ultimately build ties that strengthen our collective power.
As young Black and Brown people fighting for racial justice, we are clear that we need to be learning all of our histories, to push for racial justice and build across movements to create a spirit of abundance and joy, and not allowing white supremacy to tell us that resources are limited. Not allowing those in power to try to limit our ability to care for ourselves.
We are committed to radical racial solidarity, and the idea of abundance is what will shift us away from systems of harm and punishment to systems of holistic care. An abundance mindset stands in direct defiance of the fear and scarcity that employees of government agencies such as the Border Patrol and the police need in order to continue terrorizing our communities.


















Why does the Trump family always get a pass?