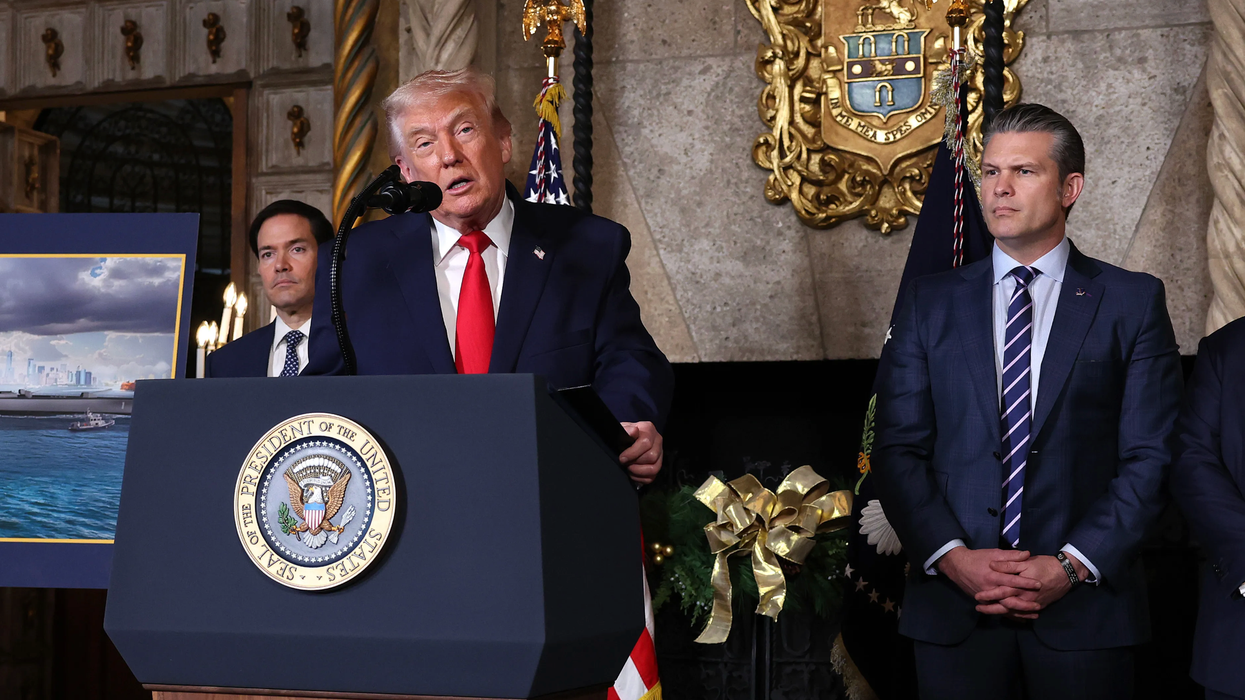
President Donald Trump signed into law this month a measure that prohibits anyone based in China and other adversarial countries from accessing the Pentagon’s cloud computing systems.
The ban, which is tucked inside the $900 billion defense policy law, was enacted in response to a ProPublica investigation this year that exposed how Microsoft used China-based engineers to service the Defense Department’s computer systems for nearly a decade — a practice that left some of the country’s most sensitive data vulnerable to hacking from its leading cyber adversary.
U.S.-based supervisors, known as “digital escorts,” were supposed to serve as a check on these foreign employees, but we found they often lacked the expertise needed to effectively supervise engineers with far more advanced technical skills.
In the wake of the reporting, leading members of Congress called on the Defense Department to strengthen its security requirements while blasting Microsoft for what some Republicans called “a national betrayal.” Cybersecurity and intelligence experts have told ProPublica that the arrangement posed major risks to national security, given that laws in China grant the country’s officials broad authority to collect data.
Microsoft pledged in July to stop using China-based engineers to service Pentagon cloud systems after Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth publicly condemned the practice. “Foreign engineers — from any country, including of course China — should NEVER be allowed to maintain or access DoD systems,” Hegseth wrote on X.
In September, the Pentagon updated its cybersecurity requirements for tech contractors, banning IT vendors from using China-based personnel to work on Defense Department computer systems. The new law effectively codifies that change, requiring Hegseth to prohibit individuals from China, Russia, Iran and North Korea from having direct or indirect access to Defense Department cloud computing systems.
Microsoft declined to comment on the new law. Following the earlier changes, a spokesperson said the company would “work with our national security partners to evaluate and adjust our security protocols in light of the new directives.”
Rep. Elise Stefanik, a Republican who serves on the House Armed Service Committee, celebrated the development, saying it “closes contractor loopholes … following the discovery that companies like Microsoft exploited” them. Sen. Tom Cotton, the GOP chair of the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence who has been critical of the tech giant, also heralded the legislation, saying it “includes much-needed efforts to protect our nation’s critical infrastructure, which is threatened by Communist China and other foreign adversaries.”
The legislation also bolsters congressional oversight of the Pentagon’s cybersecurity practices, mandating that the secretary brief the congressional defense committees on the changes no later than June 1, 2026. After that, such briefings will take place annually for the next three years, including updates on the “effectiveness of controls, security incidents, and recommendations for legislative or administrative action.”
As ProPublica reported, Microsoft initially developed the digital escort program as a work-around to a Defense Department requirement that people handling sensitive data be U.S. citizens or permanent residents.
The company has maintained that it disclosed the program to the Pentagon and that escorts were provided “specific training on protecting sensitive data” and preventing harm. But top Pentagon officials have said they were unaware of Microsoft’s program until ProPublica’s reporting.
A copy of the security plan that the company submitted to the Defense Department in 2025 showed Microsoft left out key details of the escort program, making no reference to its China-based operations or foreign engineers at all.
This summer, Hegseth announced that the department had opened an investigation into whether any of Microsoft’s China-based engineers had compromised national security. He also ordered a new third-party audit of the company’s digital-escort program. The Pentagon did not respond to a request for comment on the status of those inquiries.
Trump Signs Defense Bill Prohibiting China-Based Engineers in Pentagon IT Work was originally published by ProPublica and is republished with permission.


















Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift