CORRECTION: The previous version of the story and accompanying map incorrectly omitted Florida, Iowa, Maryland, New Jersey and Texas from the states allowing early tabulation. It wrongly included Connecticut, Kansas, Kentucky and Ohio.
The coming flood of absentee ballots is headed for a bottleneck on Election Day.
Thanks to the coronavirus pandemic, half or maybe more of all votes for president this year are expected to be cast remotely, then deposited in drop boxes or sent in the mail. Good-government groups, partisan operatives and the Postal Service are all urging people who choose to vote this way to complete their civic responsibility as soon as they can as a way to assure their envelope arrives in plenty of time to be counted.
But in two-thirds of the states — including most of the battlegrounds — the rush of voting early will not translate in any way into a rush of early returns the night of Nov. 3. That's because election officials can't start tabulating mailed ballots until Election Day, or in some cases until after the polls close. This means those millions of votes won't get counted as soon as the millions of votes cast in person — and Election Day will stretch into Election Week, or longer, if contests are too close to call.
Some of the 33 states may relax their rules in the final weeks before the election.
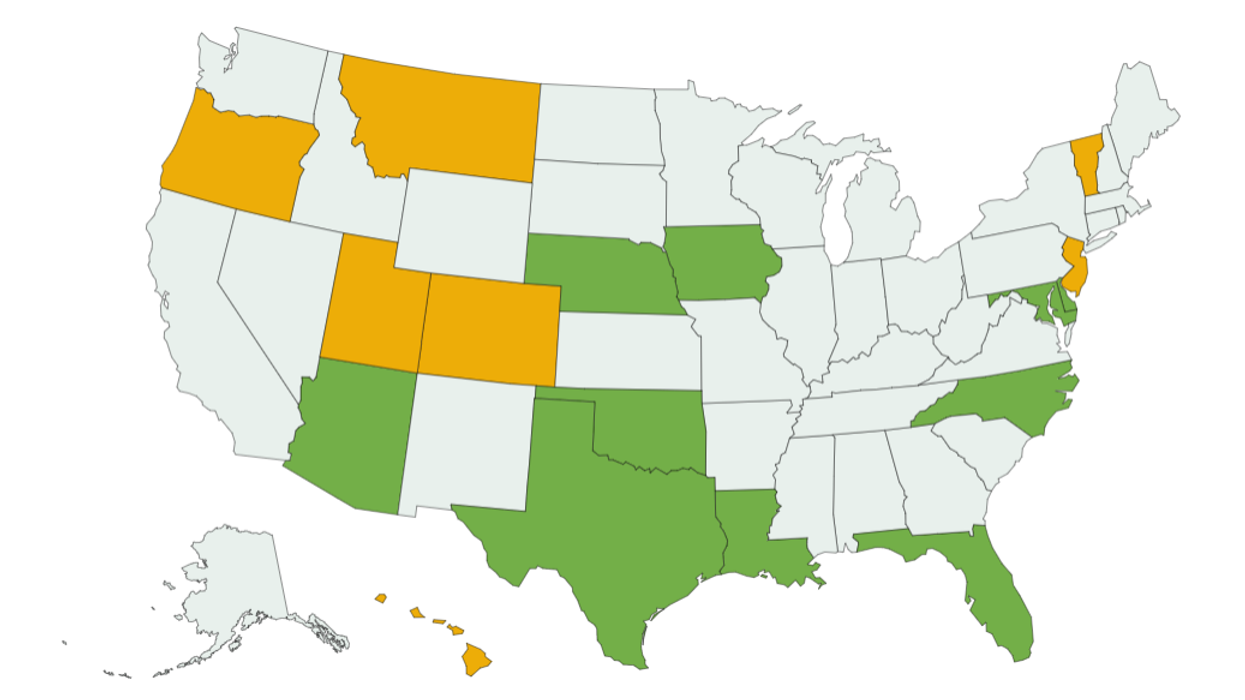
But for now, just 17 states allow for officials to begin counting ballots before Election Day. Among them, Arizona, Florida, Iowa, Nebraska's 2nd District, North Carolina and Texas now look to be competitive between President Trump and former Vice President Joe Biden. (There are also highly competitive Senate races on the ballot in several of those states.)
Because counting votes before the polls close is allowed in seven of the states where the election is being held almost entirely by mail, look for some of the fastest returns in the country to come from Colorado, Hawaii, Montana, New Jersey, Oregon, Utah and Vermont.
Louisiana and Texas are the only states out of the 17 where an excuse other than fear of Covid-19 infection is required before voting absentee.



















Trump & Hegseth gave Mark Kelly a huge 2028 gift