Shannon is the founder of Negative.vote, which is promoting statewide ballot initiatives to allow voters to register firm opposition to one candidate in each race.
Beneath the 2020 campaigns, a different battle is brewing between two wonky factions to replace America's plurality voting system — sometimes called first-past-the-post, which means the most votes wins.
Advocates lobby in different cities, online and on social media for instant-runoff voting and approval voting.
Maine, San Francisco, Minneapolis and New York have adopted instant-runoffs for municipal elections, while Fargo and St. Louis are considering approval voting.
Instant runoff and approval voting advocates agree that plurality voting is deeply flawed. The problem is vote splitting. If there are more than two options, similar candidates dilute each other's support. Vote splitting multiplies with each additional candidate on the ballot.
In college, a handful of similar fraternity members were vying to preside over the fraternity system, so I entered the race. I was less interested in fraternity affairs than election odds. It was like a "Revenge of the Nerds" movie, and my uniqueness prevailed.
However, the two-party duopoly is far more sophisticated than fraternity row. Democrats and Republicans cooperate to nominate just one candidate in their primaries.
They are used to self-endorse two ideological minorities as perpetual rulers over an unaffiliated majority.
One alternative, instant-runoff elections, is marketed as ranked-choice voting in order to make it easier to explain. After voters rank the candidates, instant-runoff means a series of (still flawed) plurality elections where the last-place finisher in each runoff is removed. This is followed by subsequent recounts after votes for the last-place finisher in each round are redistributed to candidates still left standing. Runoffs continue until one candidate obtains majority support. You may notice that ranking your favorite candidate first is not always the best strategy.
A rival faction favors approval voting, where voters are instructed to vote for as many candidates as they wish. It has a shortcoming. Enlightened parties will train their supporters to vote for their nominee only and for no one else. With approval voting, a constituency should never risk boosting even another friendly candidate's vote total. If you vote for more than one, then you're the sucker.
As you can see, voting systems add layers of strategy and complexity.
And despite each group's claims to the contrary, neither will disrupt the powerfully dysfunctional two-party system. Do you think that's a good thing? It's not.
Ask yourself if you have a least-preferred candidate. Most people do. Then ask why you are prohibited from expressing that.
Introducing a disapprove option brings any ballot into "balance."
If voters could express disapproval we could punish negative propaganda campaigns and stop aspiring autocrats like President Trump — as well as extreme leftists like Sen. Bernie Sanders — in their tracks. This is not a matter of opinion. There's a mathematical proof.
These truths may be counter-intuitive: positive votes equal negative politics. And negative votes compel pragmatic politics.
Future candidates would be forced by the math to moderate their positions toward compromises in order to avoid the wrath of our thumbs-down votes.
Our board member Paul Cohen has a favorite ranked-choice scenario: Imagine an instant-runoff among five candidates of which you know only your favorite and least favorite.
In this scenario, with ranked-choice voting you may find yourself inventing arbitrary reasons to rank the three unfamiliar candidates. That experience would leave you feeling uncertain. Such reckless voting may inadvertently swing an election to a candidate you were indifferent about. Instead, rank your priorities on this balanced ballot:
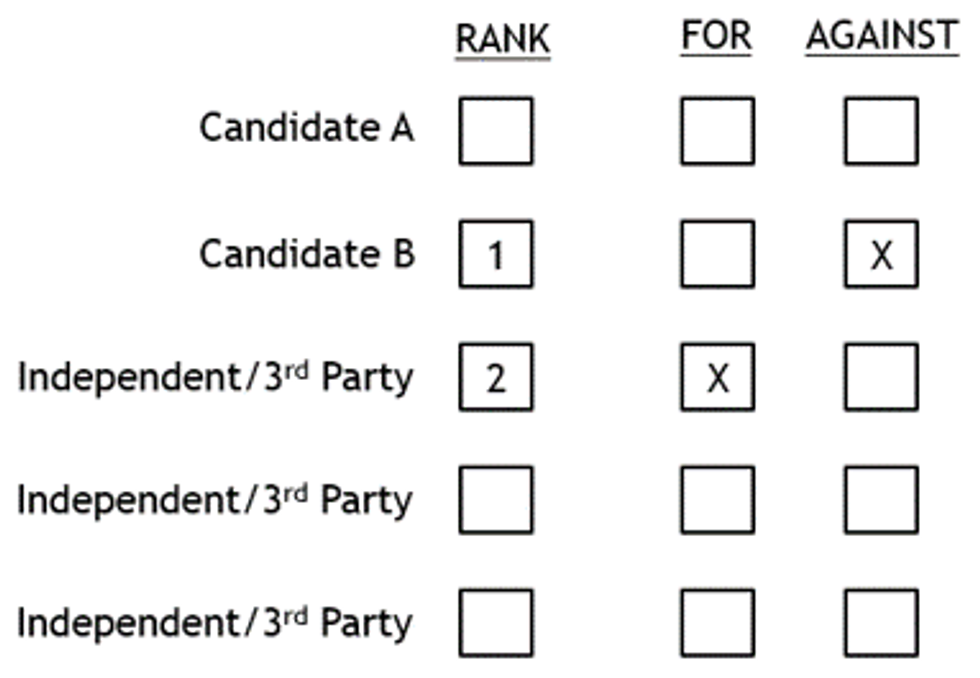
Above, your top priority is a disapproval vote against your least-preferred candidate in each runoff until that person is eliminated. After that, your second priority may be a vote for your favorite candidate — or maybe vice-versa. Why bother ranking those that you're indifferent about when you could just abstain? This experience would leave you feeling empowered and satisfied.
To supplement approval voting, the disapprove option enables you to distinguish between candidates that you are indifferent about from those you do not want to win. Here's a sample:
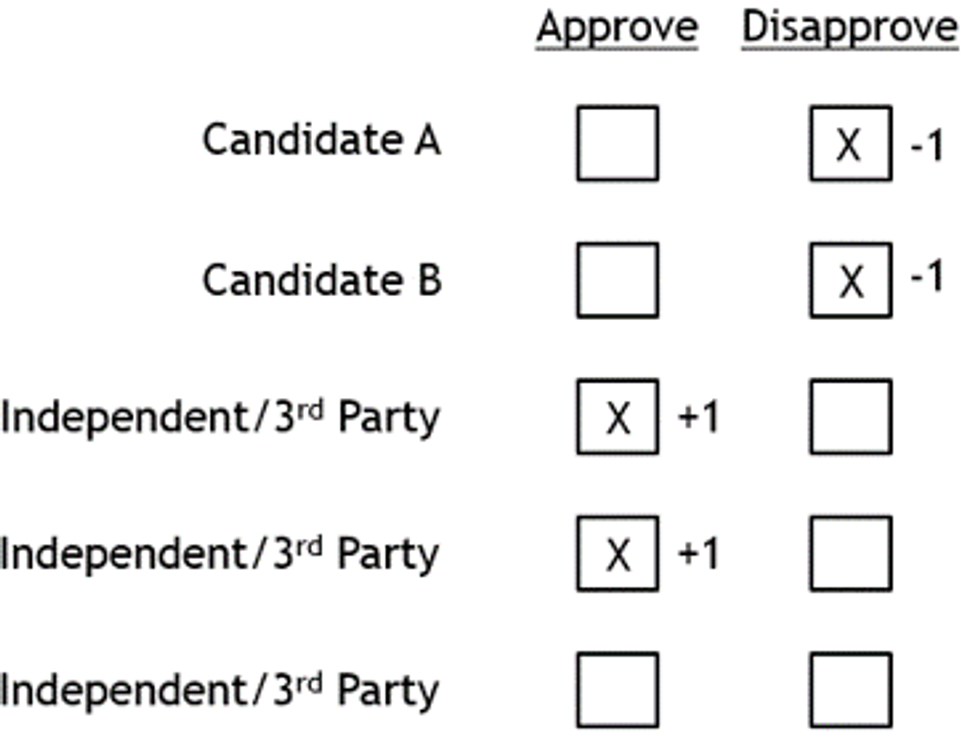
By introducing a negative vote, we turn approval voting into a condensed range vote. Simply check the approve box for all the candidates you like, and the disapprove box for those you don't.
There's a bonus: A balanced approval ballot reduces the influence of money in politics. Consider that being too well-known could be a disadvantage.
If these alternatives are dizzying, we can achieve similar results simply by furnishing each voter one thumbs-up vote and one thumbs-down vote.
As our group's global ambassador, Sam Chang, likes to say: Ranked-choice and approval voting are each worthless in an election with just one candidate. For example, candidates for 60 percent of elected offices in Illinois run unopposed. With a negative vote, voters could express their sentiments for unopposed candidates and we could establish minimum thresholds for claiming victory.
Yes, vote-splitting can be isolated or eliminated with ranked-choice or approval voting respectively. But neither will reverse our nation's current path to divorce. As proven by game-theory mathematician Arkadii Slinko, only the power of a negative vote can do that.
Ranked-choice and approval voting can each be made more effective, and simpler with a minor tweak.
Embraced, a negative vote option can also end infighting between reform factions regardless of which system they prefer.
Most importantly, balanced ballots can neutralize the tribalists that govern us with their unbalanced minds — intent on destroying one another at the expense of our union.




















