Plenty of congressional districts get mocked for looking like parts of a Rorschach test. But only now have some creative folks conjured up the letters A through Z.
It was hard not to see "a rabbit on a skateboard" in last decade's map for Illinois, or "Goofy kicking Donald Duck" in the Philadelphia suburbs until a few years ago, or — most famously — a salamander slithering across Massachusetts in the 19 th century map approved by Gov. Elbridge Gerry, which gave rise to the derisive term gerrymandering for such convoluted contouring.
But today's map of the House of Representatives, it turns out, contains an unsightly but still readily readable alphabet.
Redistricting reformers with a sense of humor, or at least looking for a fresh way to make their point, are welcome to go to UglyGerry.com and download the letters for free.
The letter Z
Ugly Gerry
Indiana's 8th is held by Republican Larry Bucshon. Ohio's 8th is held by Republican Warren Davidson.
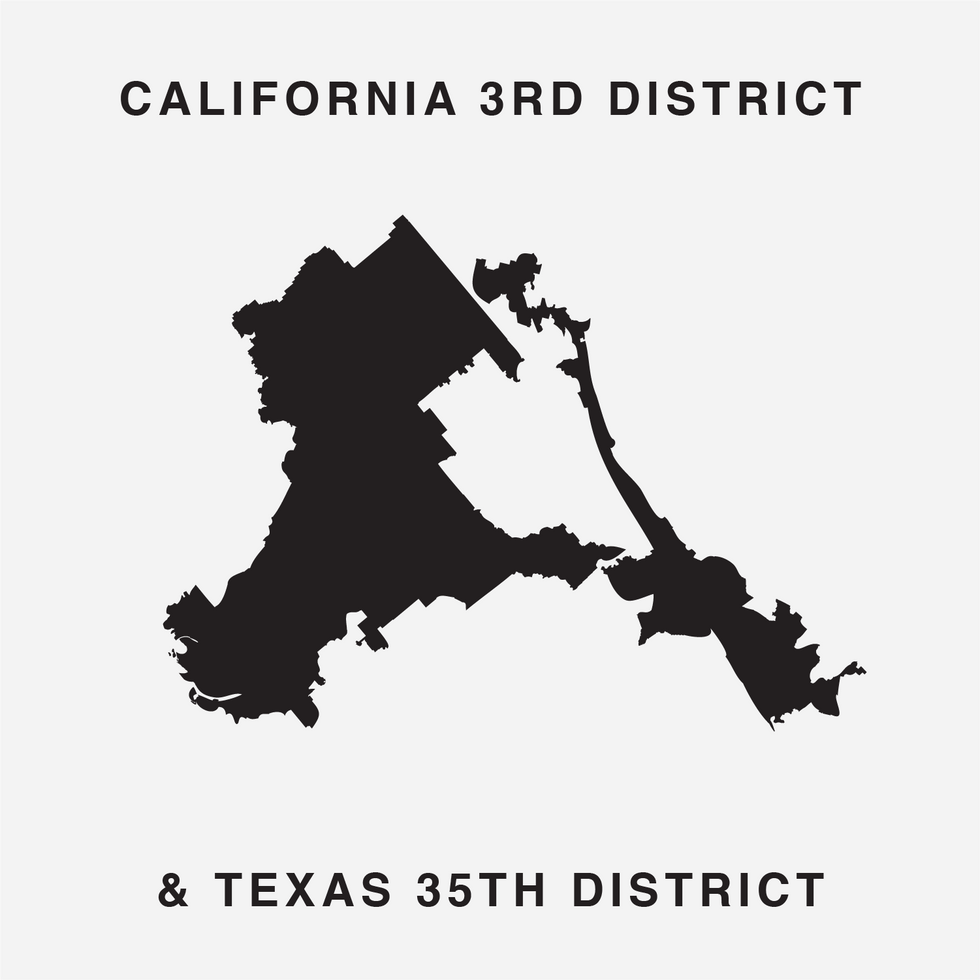

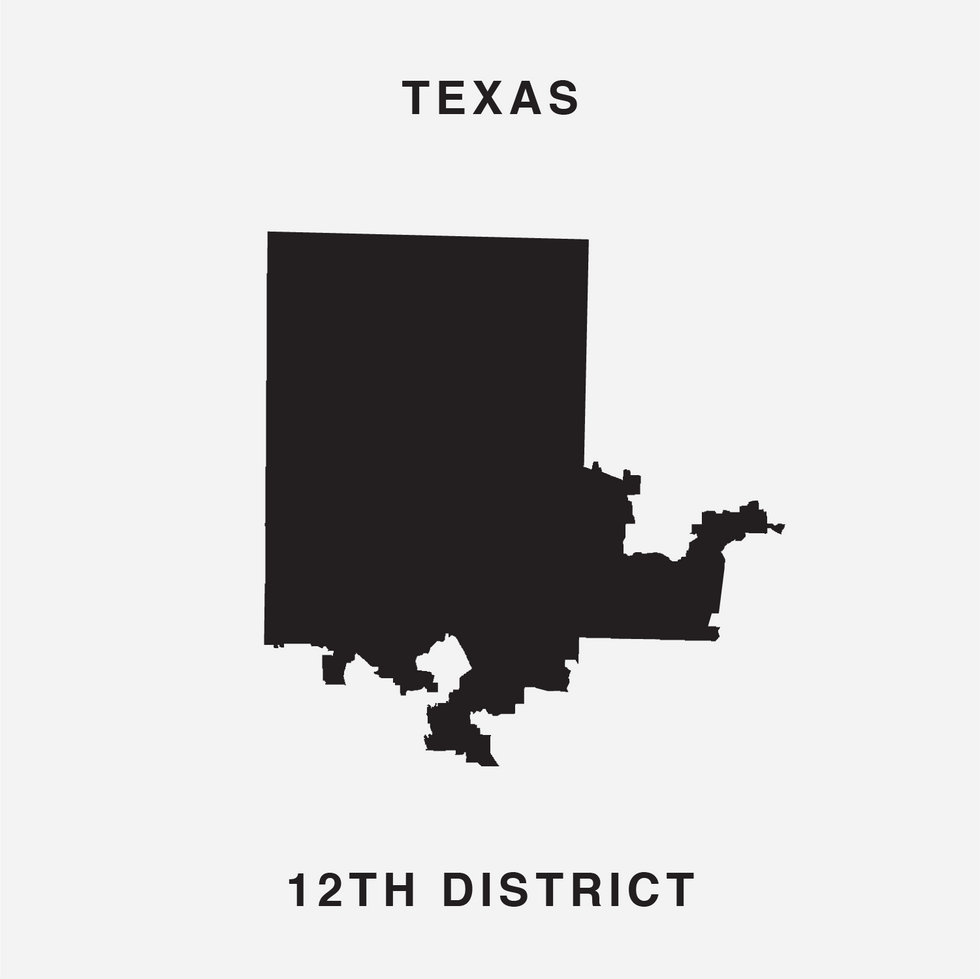
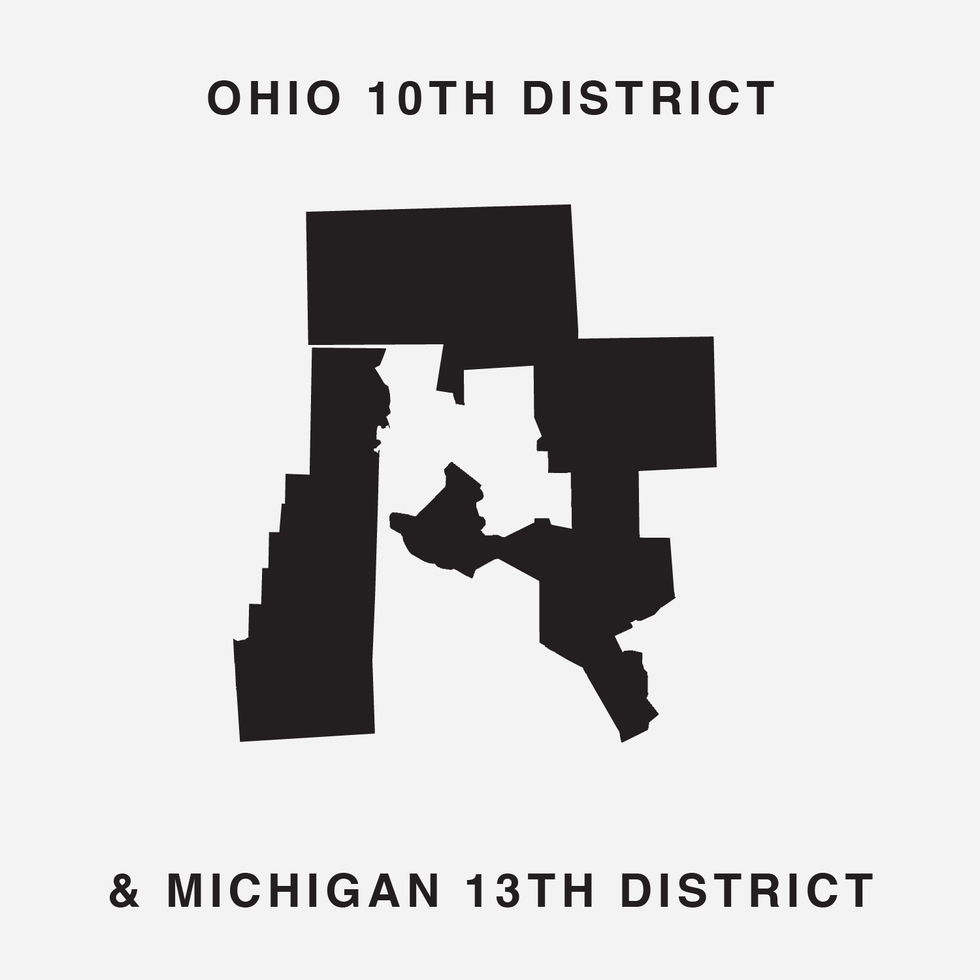
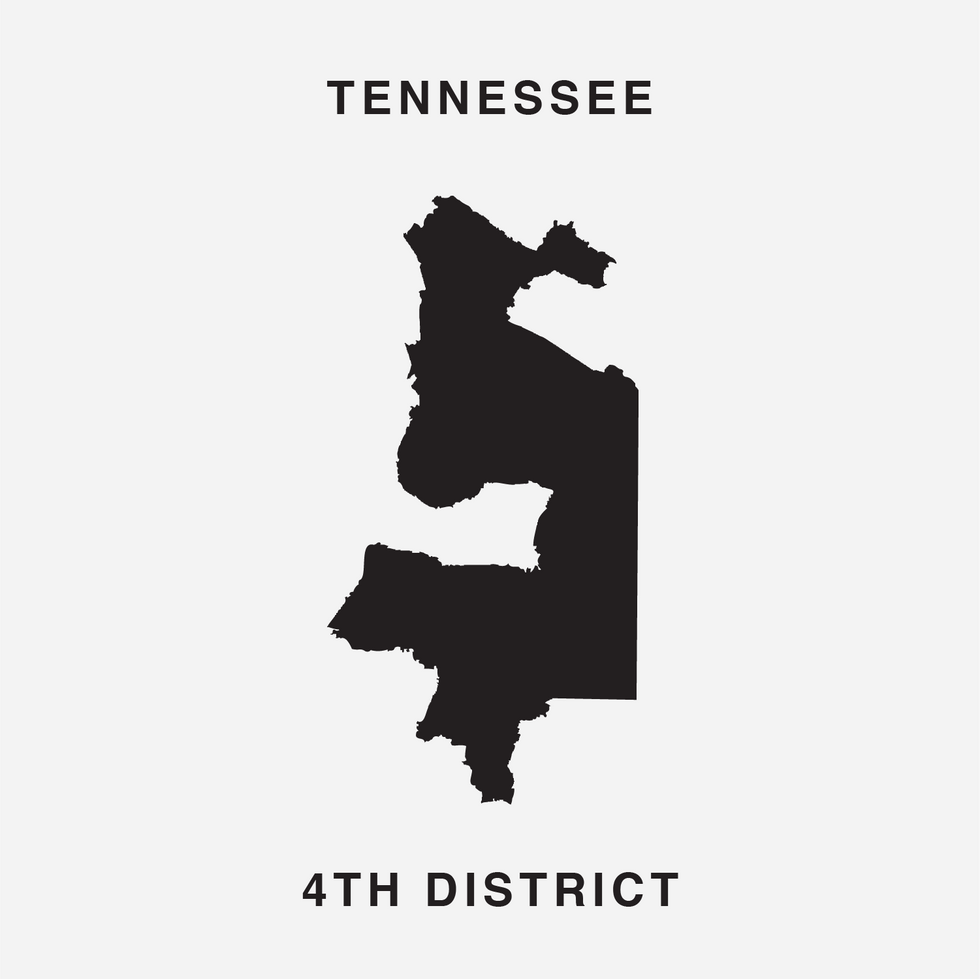
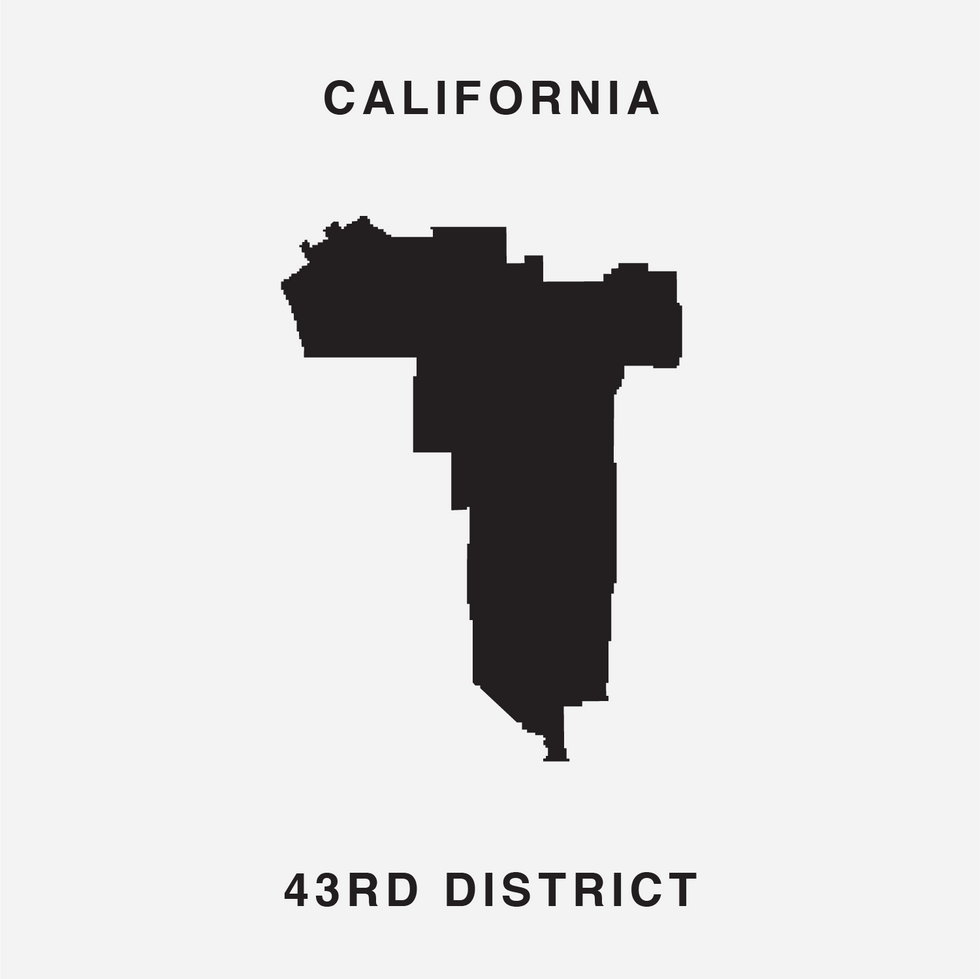
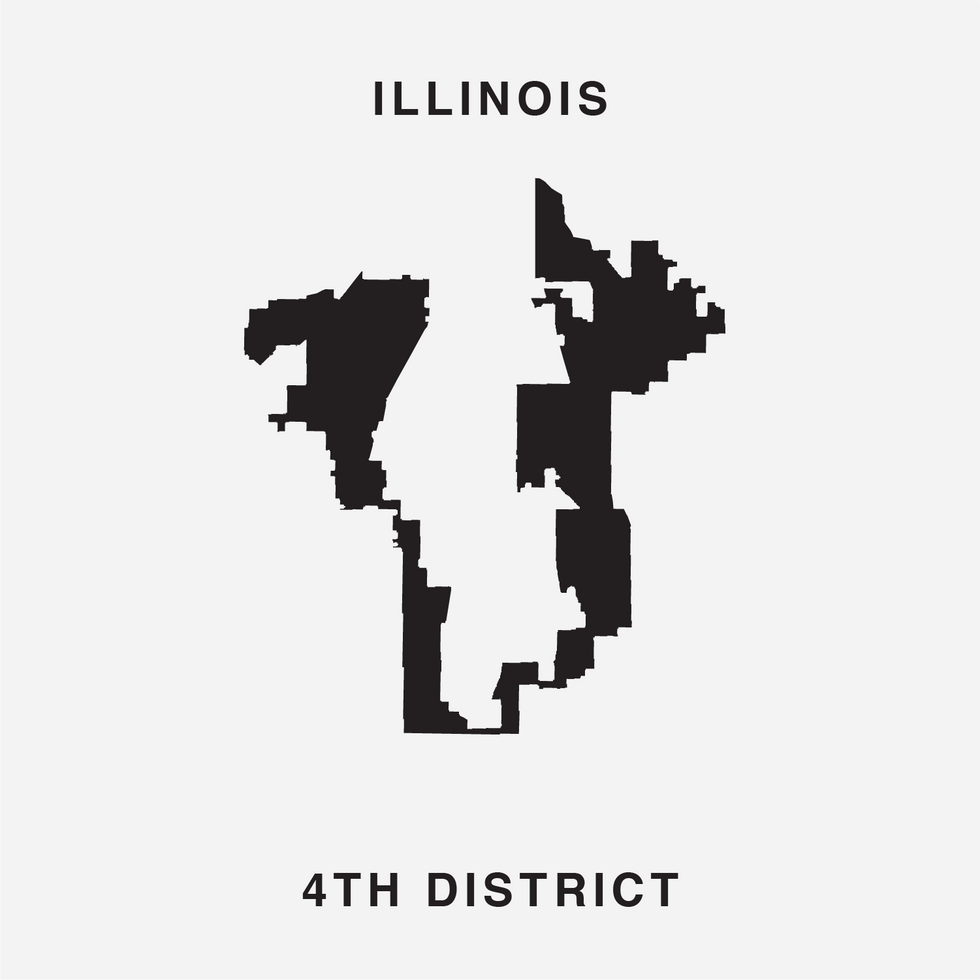




The font was unveiled at the end of July by Chicago digital creatives Ben Doessel, James Lee and Kevin McGlone. Their inspiration, they said, was realizing their home congressional district, the Illinois 4th, looked quite a bit like a letter U – albeit one lying on its side. (To the political world it's long been the legendary "earmuffs" district, with Latino neighborhoods north and south of the Loop stitched together to comply with a federal court command that Chicago have a Hispanic-majority seat.)
After that realization, the team noticed how rotating North Carolina's rural 6th district 90 degrees turned it into a pretty good letter H. Before too long, they had come up with the other two dozen letters as well.
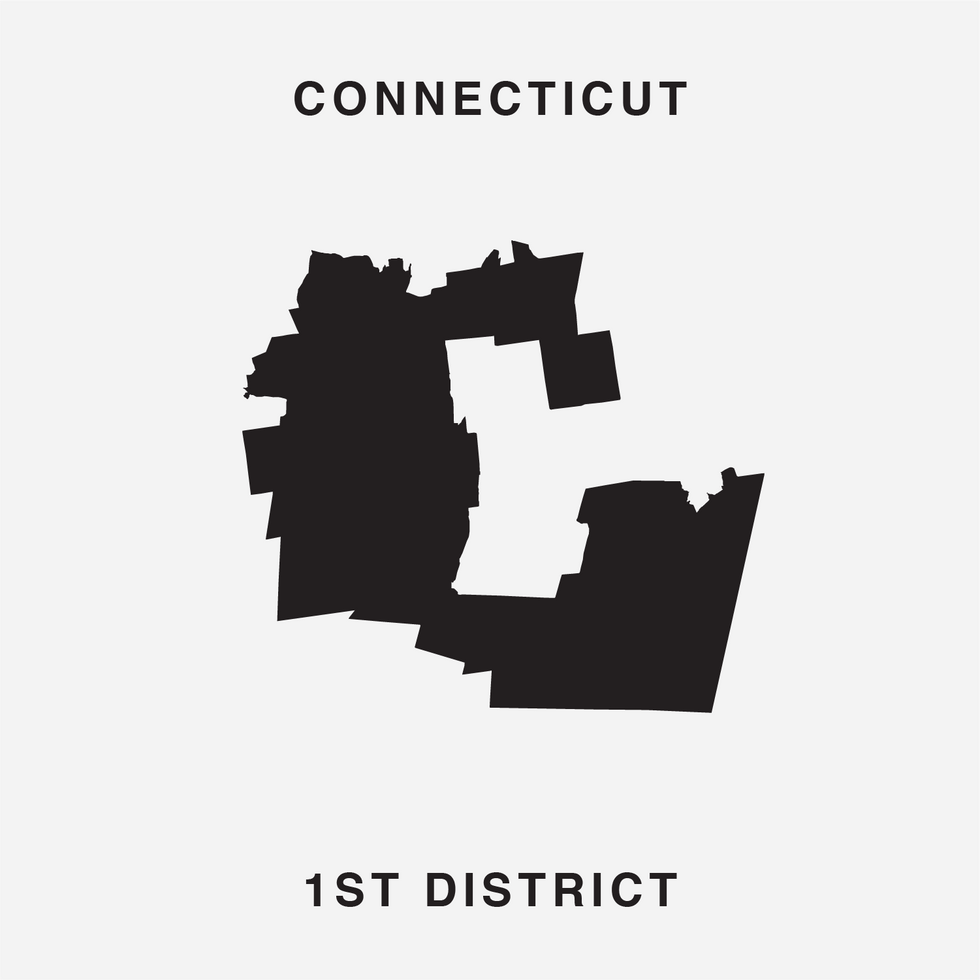
To finish the job, a pair of districts had to be mashed up to create five letters. But, intentionally or not, the 31 districts chosen underscore the central reality of gerrymandering: It is a bipartisan practice that's been used with remarkable effect to assure the vast majority of the 435 seats are not competitive between the parties.
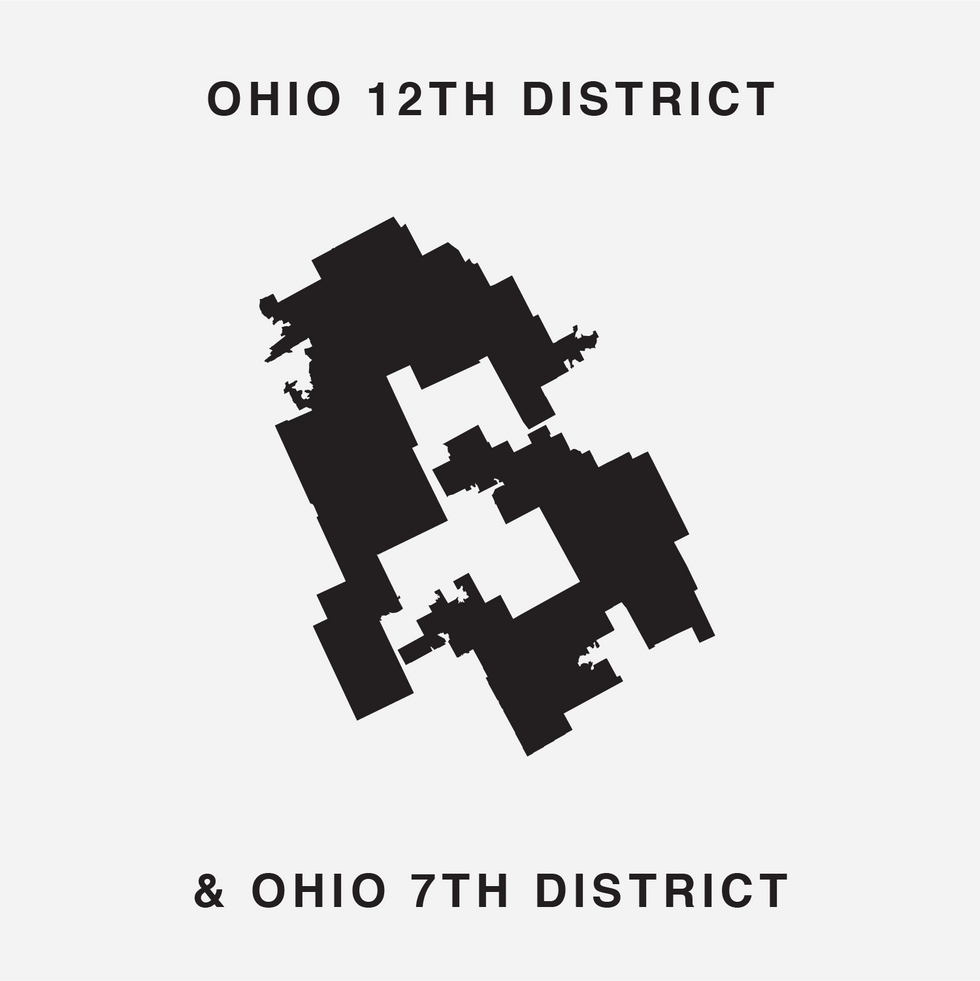
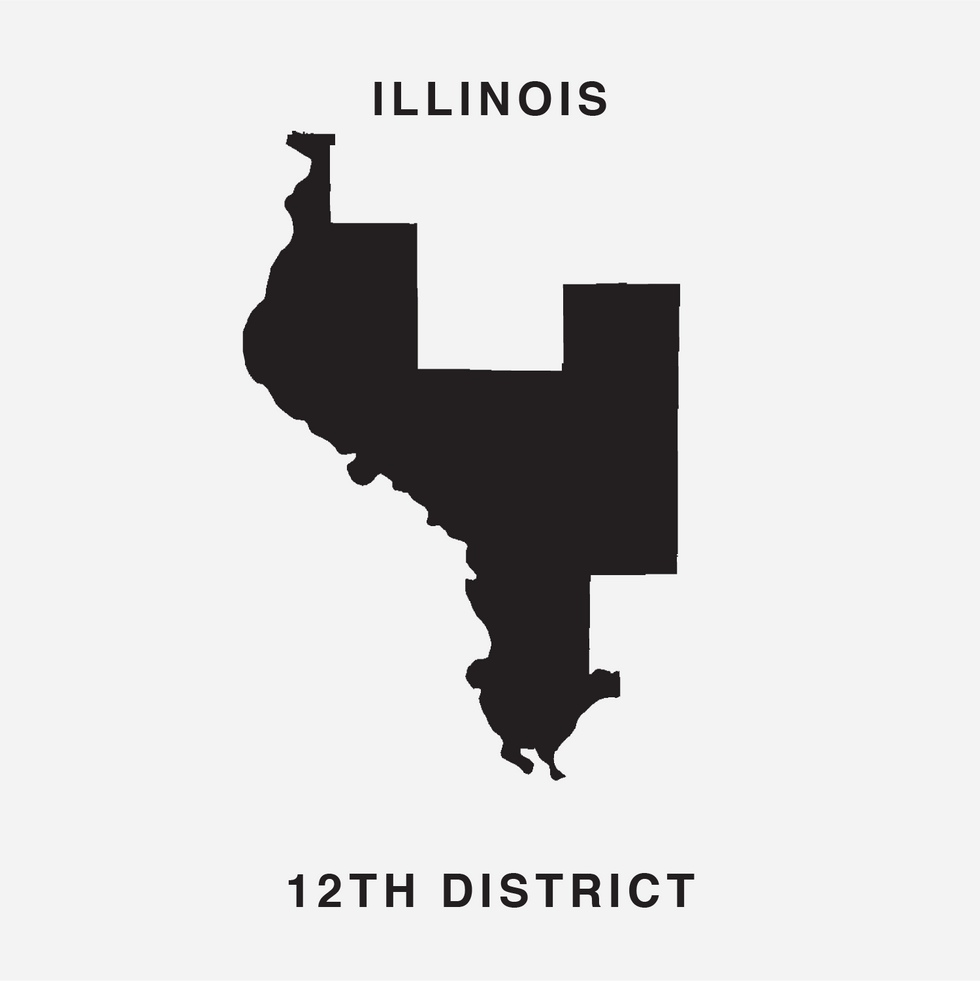
The new font uses 15 districts where Republicans now appear to be prohibitive favorites to win again in November 2020 and 15 others where the Democrats are similarly safe bets. Only Ohio's 12th (the spine of the letter B) looks to be competitive, Republican Troy Balderson having won twice quite narrowly in a suburban Columbus district that President Trump also carried.
The Gerry font — which looks like a cousin of the eclectic, early '90s font Wingdings — employs districts from 16 states. And, in another potential coincidence that could prove confounding to gerrymandering critics, the three states represented most draw their maps different ways. The map for Ohio (5 seats in the front) was drawn by Republicans and the Illinois map (4) by Democrats, but the California map (also 4) was the work of an independent commission.
Still, the creators have a strikingly simple message for anyone who views their handiwork. Other than the detailed maps, their website says only: "Tweet your rep. Do something about it."
Clicking on that message allows the user to compose a message, in Gerry, which can then be tweeted to the author's House member.
And, now that the Supreme Court has ruled the federal courts have no jurisdiction to decide when partisan power plays in mapmaking have gone too far, the burden falls squarely on state courts and legislators – either in state capitals or in Washington. Several state legislatures are mulling legislation, and several lawsuits challenging maps as violating state constitutions.
Congress could set a national rule, but that seems impossible in the currently divided Capitol. The House-passed political overhaul, HR 1, would require non-partisan panels to draw the congressional lines for every state, for example, but Majority Leader Mitch McConnell says the bill will never be taken up in the Senate because the Republican majority has no interest.
Font crafters Doessel and Lee work for the advertising firm Leo Burnett. McGlone, an alumnus of the agency, designed the site. The project is independent of the firm.
"To ensure the eroding of democracy isn't an issue that is lost in the news cycle," they said via email, they "concocted a creative way to keep our warped voting districts top-of-mind."
Ready to test your gerrymandering knowledge? Take our quiz.